Method for producing methane chloride through byproduct hydrogen chloride in production process of tetrachloroethylene
A production process, tetrachloroethylene technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, organic chemistry, halogenated hydrocarbon preparation, etc., can solve problems such as the impact of monochloromethane production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
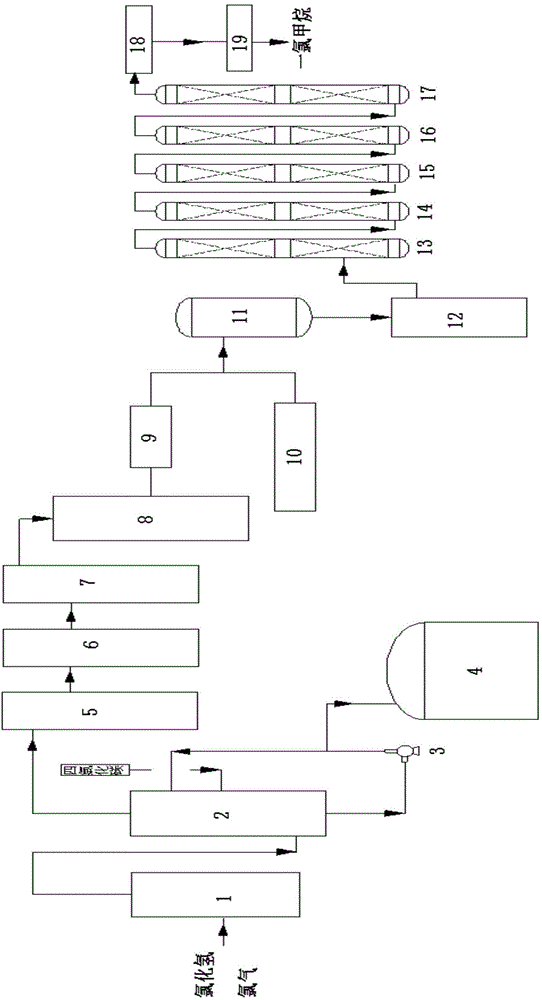
[0036] Such as figure 1Shown, a kind of method utilizing the hydrogen chloride of by-product in the tetrachlorethylene production process to produce monochloromethane, the steps are as follows:
[0037] (1) After the mixed gas of the by-product hydrogen chloride and chlorine in the tetrachlorethylene production process is condensed to-18.9 ℃ through raw material condenser 1, introduce chlorine gas absorption tower 2, carbon tetrachloride is housed in chlorine gas absorption tower 2, pass through Carbon tetrachloride absorbs chlorine, and discharges thick hydrogen chloride gas at chlorine absorption tower 2 tower top; The tower bottom temperature-9.2 ℃ of chlorine absorption tower 2, tower top pressure 42kPa, tower top temperature-6.3 ℃; Described mixed gas and tetrachloride The mass ratio of carbonized carbon is 0.3:1.0;
[0038] The crude hydrogen chloride gas enters the hydrogen chloride condenser 5, condenses again at -10.2°C, and then enters the hydrogen chloride demister...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Utilize the method for the hydrogen chloride production monochloromethane of by-product in the perchlorethylene production process as described in embodiment 1, difference is:
[0047] In step (1), the temperature at the bottom of the chlorine absorption tower 2 is -10.1°C, the pressure at the top of the tower is 45kPa, and the temperature at the top of the tower is -6.9°C; the mass ratio of the mixed gas to carbon tetrachloride is 1.0:1.0;
[0048] In step (2), the compressed hydrogen chloride gas is superheated through the heater 9 to a temperature of 220° C., and then enters the reactor 11 together with the superheated methanol 10 having a temperature of 221° C., at 242° C. and 0.19 MPa, under the action of an alumina catalyst Response 5s.
[0049] The purity of the dichloromethane obtained in this embodiment reaches 99.94%, the methanol conversion rate is 99.1%, and the selectivity of the dichloromethane is 98.7%.
Embodiment 3
[0051] Utilize the method for the hydrogen chloride production monochloromethane of by-product in the perchlorethylene production process as described in embodiment 1, difference is:
[0052] In the step (1), the temperature at the bottom of the chlorine absorption tower 2 is -7.6°C, the pressure at the top of the tower is 47kPa, and the temperature at the top of the tower is -5.2°C; the mass ratio of the mixed gas to carbon tetrachloride is 0.6:1.0;
[0053] In step (2), the compressed hydrogen chloride gas is superheated through the heater 9 to a temperature of 230° C., and then enters the reactor 11 together with the superheated methanol 10 having a temperature of 225° C., at 270° C. and 0.19 MPa, under the action of an alumina catalyst Response 3s.
[0054] The purity of the monochloromethane obtained in this embodiment reaches 99.89%, the conversion rate of methanol is 98.9%, and the selectivity of monochloromethane is 98.1%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com