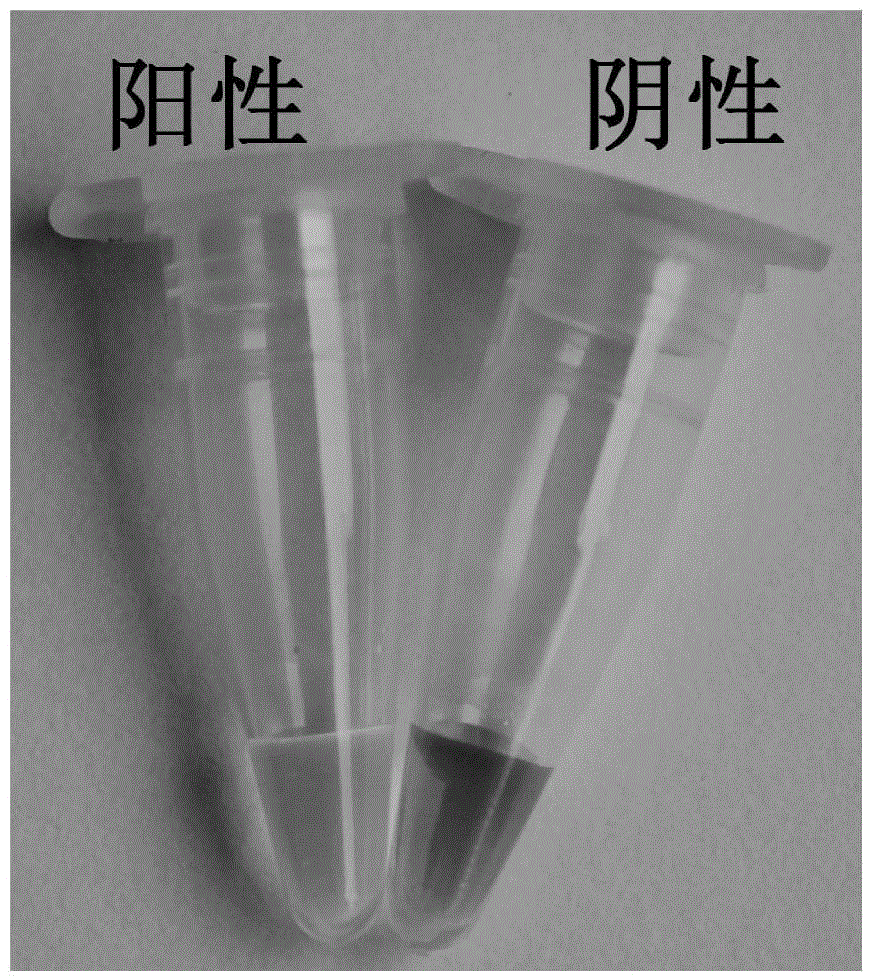
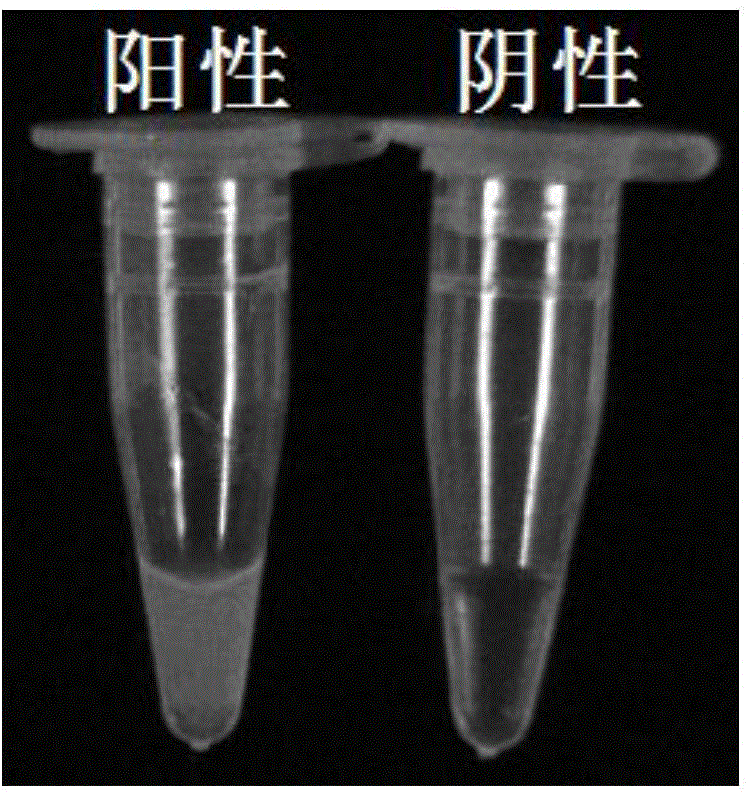
RT-LAMP method for identifying Japanese encephalitis virus gene types I and III
A RT-LAMP, Japanese encephalitis virus technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of long time, complicated operation, high cost, and achieve easy identification, visualization of results, and timeliness. The effect of sexual dominance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] 1. Primer Design
[0076] Sequence comparison: The Japanese Japanese encephalitis virus genome sequence was retrieved from GenBank, and according to the method established by Chen et al. (1990), the sequence was analyzed for phylogenetic evolution using Mega 5.0 to determine the virus genotype, and the genotype I was selected according to the analysis results Genome sequences of type III strains were compared and analyzed using the software DNAman 6.0 and DNAstar 7.1, and the SNPs loci were determined and analyzed.
[0077] Primer design: According to the results of sequence comparison analysis, LAMP primers were designed through the online software http: / / primerexplorer.jp / e / (Primer Explorer V4), and Primer premier 5.0 was used to edit and modify the primers, and two sets of specificity were designed respectively The primers were used to specifically amplify gene type Ⅰ (GI) and type Ⅲ (GⅢ) JEV, and each set of primers included 1 outer primer F3 / B3 and 1 inner primer ...
Embodiment 2
[0120] 1. Effect of reaction temperature on RT-LAMP reaction
[0121] In the present invention, different temperatures are set for the two sets of primers. Under the condition that other conditions are the same, the two sets of primers are respectively subjected to RT- For LAMP reaction, observe the results of each reaction and determine the optimal temperature of the reaction through 1.5-2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The results showed that the reaction could occur between 59-65°C, and finally determined that the optimal temperature for JEV G Ⅰ and GⅢ specific RT-LAMP reactions was 62°C ( Figure 5 , Figure 6 ).
[0122] 2. Effect of reaction time on RT-LAMP reaction
[0123] In the case of other conditions being the same, according to the optimized temperature, adjust the reaction time to 15, 30, 45, 60 and 75 minutes respectively, and explore the minimum reaction time of this method. The results showed that after 30 minutes of reaction, the electrophoresis of JEV G Ⅰ...
Embodiment 3
[0125] 1. Specificity test of RT-LAMP
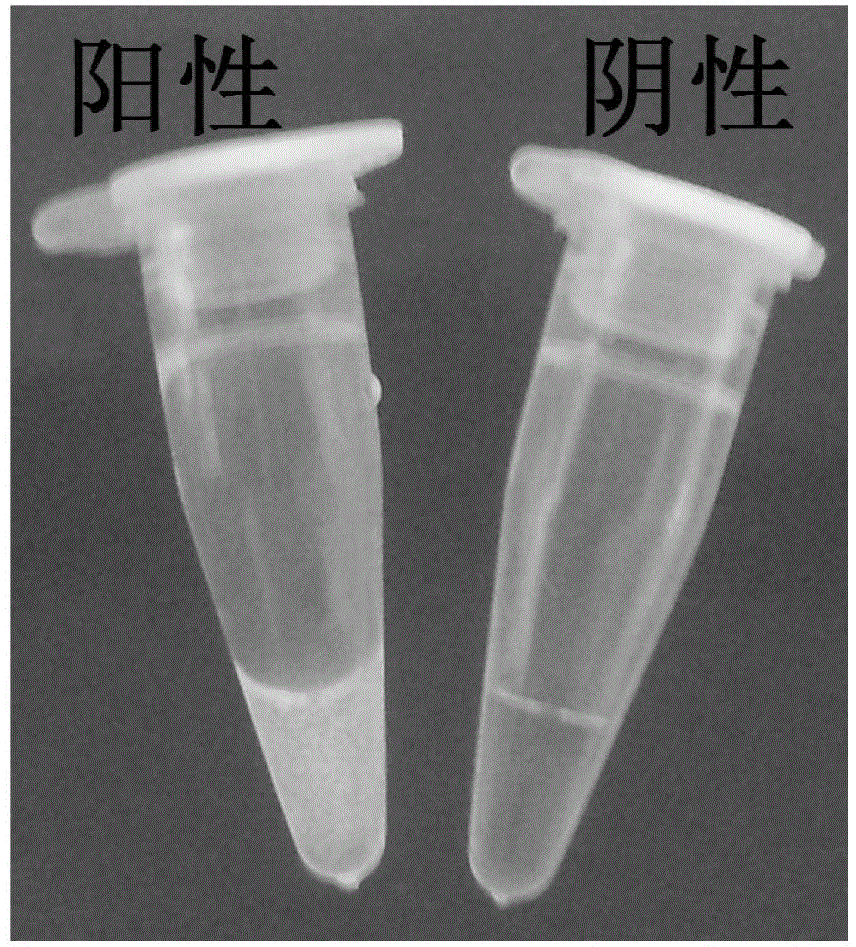
[0126] The present invention uses the JEV G Ⅰ specific primer set to detect JEV SCYA201201 (type Ⅰ), JEV SA14-14-2 (type Ⅲ), CSFV, PRRSV, PRV, PPV and PCV2 respectively. As a result, only JEV SCYA201201 is positive, and the others are all positive. Negative. At the same time, the present invention uses the JEV GⅢ specific primer set to detect JEV SCYA201201 (type I), JEV SA14-14-2 (type III), CSFV, PRRSV, PRV, PPV and PCV2, and only JEV SA14-14-2 is positive , all others are negative. Both detection methods showed good specificity, that is, JEV G Ⅰ and JEV G Ⅲ specific RT-LAMP detection methods could only detect the corresponding genotypes of JEV ( Figure 9 , Figure 10 ).
[0127] 2. Sensitivity test of RT-LAMP
[0128] Quantitative results of cRNA: G Ⅰ-cRNA A260=0.96, A280=0.52, A260 / A280=1.85, RNA concentration=768ng / μL, copy number: about 1.2×10 12 copies / μL; GⅢ-cRNAA260=0.73, A280=0.38, A260 / A280=1.92, RNA concentration=584ng...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com