Green-light LED (Light Emitting Diode) epitaxial layer structure and growing method
A growth method and epitaxial layer technology, applied in electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of weakening LED luminous intensity, increasing electron leakage, reducing electron injection efficiency, etc., to reduce polarization electric field intensity, improve Luminous efficiency, the effect of reducing the QCSE effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
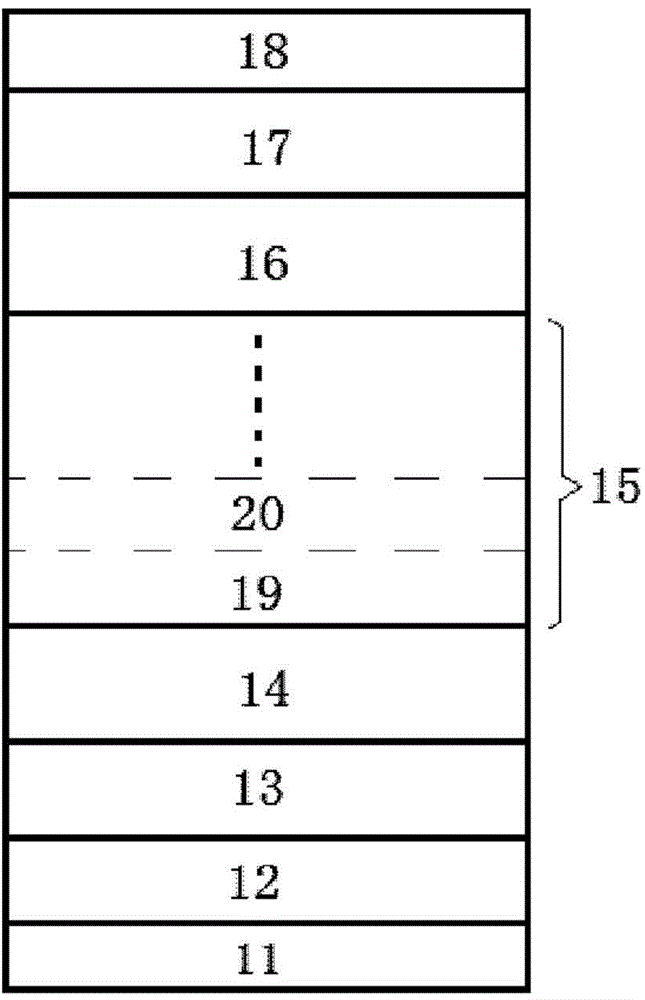
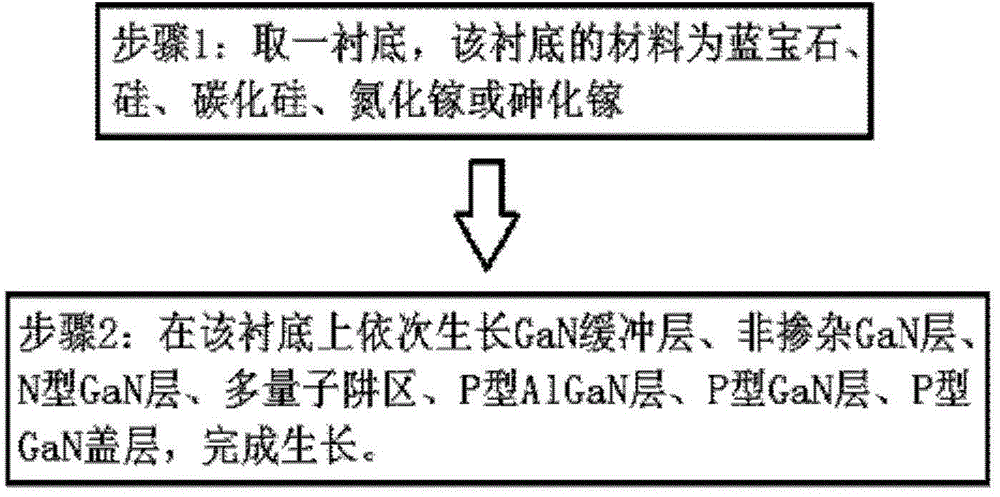
[0027] For a green LED epitaxial layer structure provided by the present invention, please refer to figure 1 shown, including:
[0028] A substrate 11, the material of the substrate 11 is sapphire, silicon, silicon carbide, gallium nitride or gallium arsenide;
[0029] a GaN buffer layer 12 grown on the substrate 11;
[0030] a non-doped GaN layer 13 grown on the GaN buffer layer 12;
[0031] An N-type GaN layer 14 grown on the non-doped GaN layer 13 . The thickness of the N-type GaN layer 14 is 1-3 μm, wherein the doping concentration of Si is greater than 10 18 / cm 3 ;
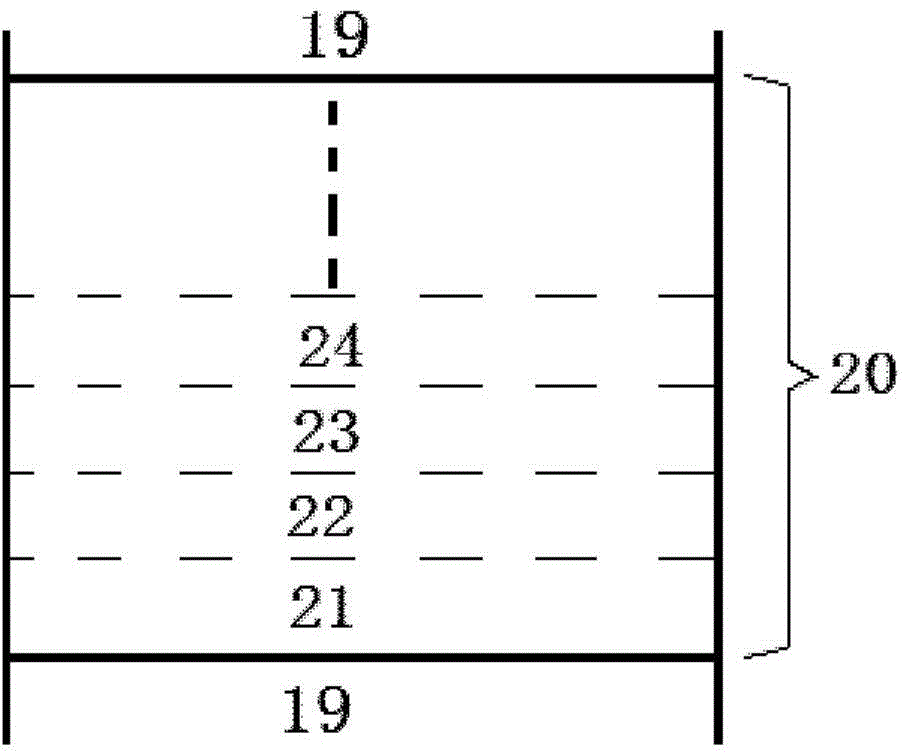
[0032] A multi-quantum well region 15 is grown on the N-type GaN layer 14 .
[0033] A P-type AlGaN layer 16 is grown on the multiple quantum well region 15 . The thickness of the layer is 30-50nm, the Al content is 5%-10%, and the P-type Mg doping concentration is greater than 10 18 / cm 3 ;
[0034] A P-type GaN layer 17, which is grown on the P-type AlGaN layer 16, the thickness of this layer is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com