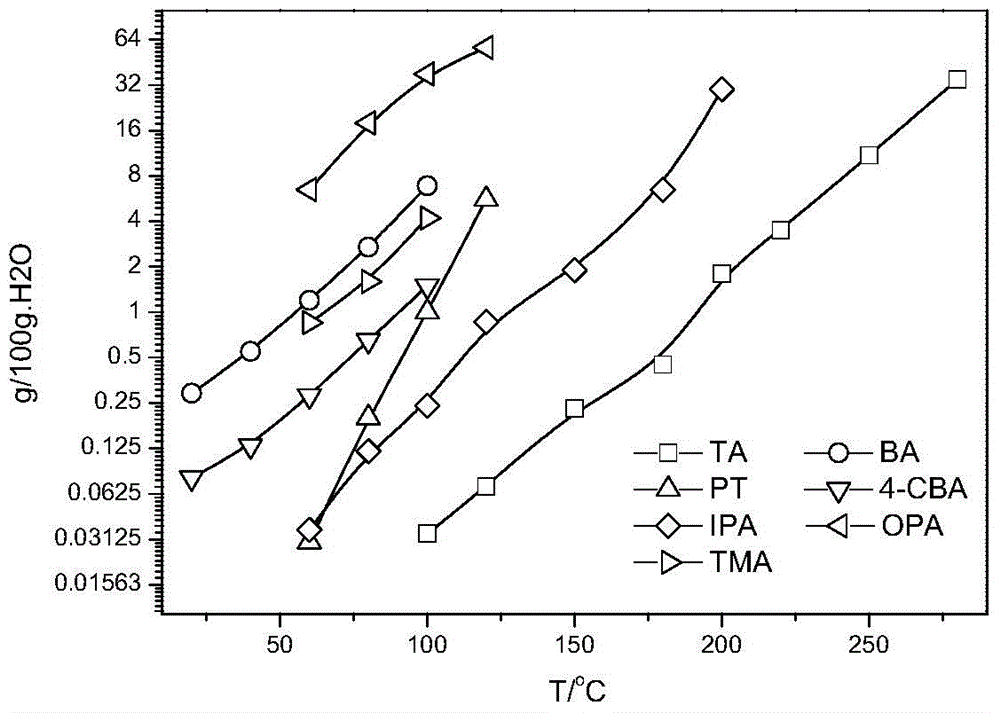
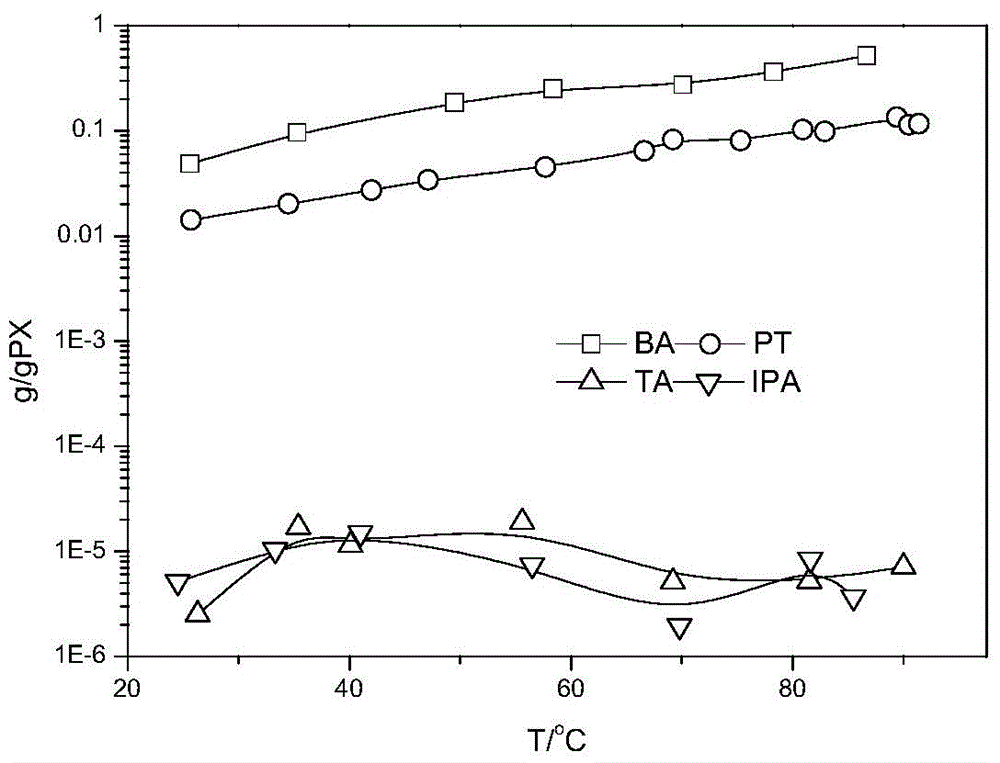
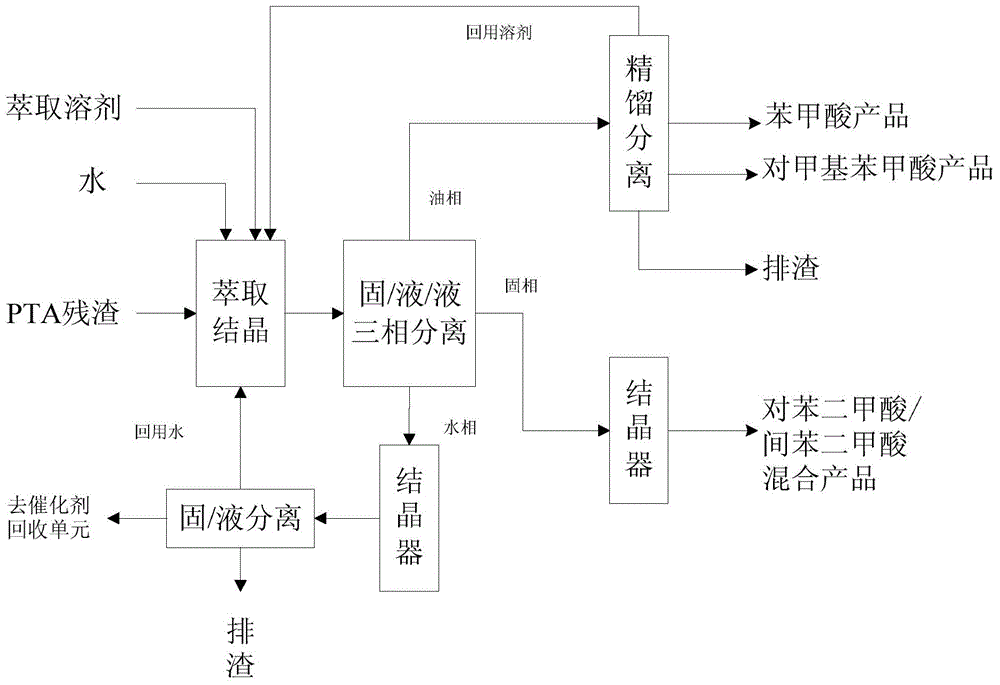
Method for recycling PTA oxidation residue
A residue and oil phase technology, applied in the field of recycling of PTA oxidation residues, can solve the problems of low recovery efficiency, difficulty and low industrial feasibility, and achieve the effect of reducing the discharge of waste residue and protecting the environment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036]The PTA oxidation residue A treated in this example comes from the crude terephthalic acid (CTA) mother liquor removal system of the PTA plant, and its main composition (dry basis) is shown in Table 1.
[0037] Table 1. Main composition of PTA oxidation residue
[0038]
[0039]
[0040] Get 99.5 grams of residue A and 101.3 grams of water into a 1000ml three-necked flask with stirring and reflux, and add 196.4 grams of p-xylene extractant simultaneously (the mass ratio of residue, water and extractant in the batching is maintained at about 1:1: 2), then place it in a water bath at 81°C for heating, seal it, turn on the stirring and cooling water. After the slurry temperature of the residue, water, and p-xylene mixture is raised to 80±1.0° C., stir at constant temperature for 1 hour. The obtained liquid / solid / liquid three-phase slurry was filtered at a room temperature of 25° C., and the filter cake was washed with water and p-xylene at a room temperature of 25° C...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The PTA oxidation residue treated in this example is residue B, and its main composition (dry basis) is shown in Table 1. The PTA oxidation residue was extracted in a similar manner to Example 1, and the ingredients were composed of: 100.4 grams of residue B, 101.1 grams of water, and 203 grams of p-xylene (the mass ratio of ingredients was also maintained at about 1:1:2). The difference from Example 1 is that the heating method used in this example is oil bath heating, the temperature of the oil bath is controlled at 105° C., and the extraction temperature is controlled at greater than 100° C. and stirred for 1 hour. The solid samples, oil phase filtrate samples and water phase filtrate samples were taken, and the components were quantitatively analyzed respectively, and the obtained results are listed in Table 2 and Table 3.
Embodiment 3
[0045] The PTA oxidation residue treated in this example is residue B, and the extraction treatment of the PTA oxidation residue is carried out in a manner similar to that of Example 1, and the extraction temperature is also controlled at 80±1.0°C. Different from Example 1, this example uses toluene as the extractant. The composition of ingredients is: 80.6 grams of residue B, 79.8 grams of water and 241.0 grams of toluene, and the quality of ingredients is maintained at 1:1:3. The solid samples, oil phase filtrate samples and water phase filtrate samples were taken, and the components were quantitatively analyzed respectively, and the obtained results are listed in Table 2 and Table 3.
[0046] Table 2. Aromatic carboxylic acid composition comparison of each sample in different embodiments
[0047]
[0048] Table 3. The recovery rate (wt%) of each main component in each phase
[0049]
[0050] From the results of Examples 1 to 3, it can be seen that the efficient sepa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com