Method for producing mycoprotein feed by utilizing sweet sorghum straws and/or related waste residues
A sweet sorghum straw, protein feed technology, applied in animal feed, animal feed, application and other directions, can solve the problems of low utilization efficiency of pentose, poor feed palatability, complex process, etc., to improve feed protein conversion rate and palatability. , the effect of shortening the production cycle and improving the degradation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
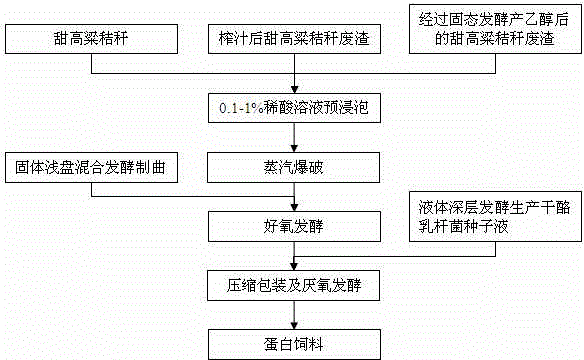
[0029] A method for producing bacterial protein feed by utilizing sweet sorghum stalks and / or related waste residues, the process flow is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0030] 1) Pretreatment: Cut fresh sweet sorghum stalks into short pieces of about 0.1 cm with a hay cutter, add dilute sulfuric acid (concentration 0.1%), pre-soak for 8 hours, and the water content reaches 60%, and blast with a steam explosion device. The blasting conditions are: temperature 210°C, pressure 2kPa, pressure maintenance time 90s;
[0031] 2) Koji production by solid fermentation: Inoculate Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma reesei preserved on the slant into Erlenmeyer shaker flasks containing potato dextrose agar medium, culture at 28°C and 150 rpm for two days, and the number of Aspergillus niger spores reaches : 3.8×10 9 Individuals / g, the number of Trichoderma reesei spores: 2.2×10 8 per g; the activated two kinds of bacterial liquids were inserted into the...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A method for producing bacterial protein feed by utilizing sweet sorghum stalks and / or related waste residues, the process flow is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0039] 1) Pretreatment: Use a hay cutter to cut the sweet sorghum stalks after dust removal and natural air-dry storage for 3 months into short pieces of about 0.1 cm, add dilute sulfuric acid (concentration 0.3%), pre-soak for 10 hours, and the water content reaches 65% , using a steam explosion device for blasting, the blasting conditions are: temperature 200°C, pressure 2.5kPa, pressure maintenance time 100s;
[0040] 2) Solid fermentation koji production: during activation culture, the number of spores of Aspergillus niger reaches: 2.7×10 9 Individual / g, the number of Trichoderma reesei spores: 2.6×10 8 Individual / g; Others are the same as in Example 1.
[0041] 3) Seed production by liquid fermentation: during activation culture, the number of viable Candida utilis ba...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A method for producing bacterial protein feed by utilizing sweet sorghum stalks and / or related waste residues, the process flow is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0048] 1) Pretreatment: add dilute sulfuric acid (concentration: 0.7%) to sweet sorghum stalk residue after squeezing the juice, pre-soak for 12 hours, and the water content reaches 70%, and use a steam explosion device to blast. The blasting conditions are: temperature 210 ° C, pressure 3 kPa, Maintain pressure for 110s;
[0049] 2) Solid fermentation koji production: during activation culture, the number of spores of Aspergillus niger reaches: 6.9×10 9 per g, the number of Trichoderma reesei spores: 4.2×10 8 Individual / g; Others are the same as in Example 1.
[0050] 3) Seed production by liquid fermentation: During activation culture, the number of viable Candida utilis: 2.5×10 8 Individual / g, the number of viable Lactobacillus casei reached: 1.8×10 8 Individual / g; Ot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com