Method for treating lignite upgrading wastewater by virtue of micro-aerobic co-metabolism
A treatment method and co-metabolism technology, which is applied in the field of lignite upgrading wastewater treatment, can solve the problems that organic pollution components cannot be completely mineralized, bacteria are difficult to adapt to wastewater, and microbial proliferation is difficult, so as to improve biological treatment effect and strengthen biological Effects of processing power and shortened start-up time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
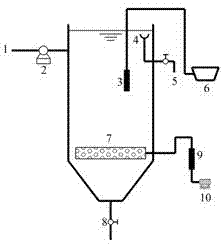
[0009] Specific implementation mode one: this implementation mode is a micro-aerobic co-metabolism method for degrading lignite upgrading wastewater, which is specifically completed according to the following steps:
[0010] ① Select lignite upgrading wastewater, which is collected by the lignite upgrading process, cooled and precipitated in the intermediate sedimentation tank, and then undergoes demulsification, coagulation, and sedimentation treatment. The water quality is as follows: COD concentration 1250~1500mg / L, BOD 5 The concentration is 300~350mg / L, the total phenol concentration is 70~80mg / L, the ammonia nitrogen concentration is 70~90mg / L, and the total phosphorus concentration is 3~4mg / L.
[0011] ② Use the return sludge from the secondary settling tank of the urban sewage treatment plant as the seed sludge to start the microaerobic activated sludge reactor. The dosage of inoculum sludge is 4~6g / L.
[0012] ③Using trehalose as the first co-metabolism s...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0018] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the lignite upgrading wastewater in step 1 is collected from the lignite upgrading process and treated by cooling and sedimentation in the intermediate sedimentation tank. The water quality is as follows: COD concentration 2800~ 3300mg / L, BOD 5 The concentration is 500~600mg / L, the total phenol concentration is 90~110mg / L, the ammonia nitrogen concentration is 70~90mg / L, the total phosphorus concentration is 9~13mg / L, and the cyanide concentration is 0.75~1.25mg / L. same.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0019] Specific embodiment three: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in step ②, the initial inoculated sludge dosage in the micro-aerobic activated sludge reactor is 5.5g / L, and other specific implementations Way 1 or 2 are the same.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com