Nucleic acid membrane strip and kit for detecting gene of hereditary hearing loss
A hereditary deafness and gene detection technology, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of uncertainty, time-consuming and labor-intensive, expensive equipment, etc., and achieve multiple detection sites, convenient operation, The effect of short detection times
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0015] 1. Technical basis
[0016] The genes and their specific loci to be detected were determined according to the epidemiological results of non-syndromic hereditary deafness. Design PCR primers according to the determined regions to amplify the target DNA fragments on GJB2, GJB3, SLC26A4 and 12SrRNA; design specific hybridization probes according to the characteristics of the gene sequences to be detected; The color and result interpretation are used for the diagnosis of deafness genes.
[0018] According to the detection target of the DNA chip, specific gene sequences are selected from the relevant gene database as probes; the probe sequence and its layout are designed according to the selected nucleic acid sequence, and special marking or design is carried out according to the sequence specificity of individual probes. The designed probe combination has strong hybridization specificity for the gene to be tested, good correlation between pr...
Embodiment 2
[0094] This embodiment provides a kind of reagent kit (PCR-reverse dot hybridization method) of hereditary deafness gene detection
[0095] 1. Purpose
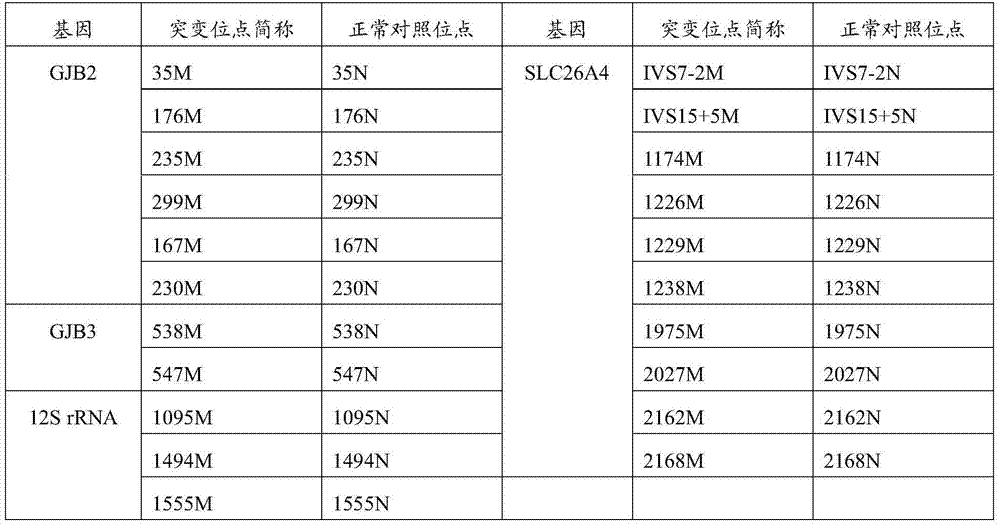
[0096] for testing Chinese Whole blood genomic DNA in clinical deafness patients, premarital or newborn samples can be qualitatively detected Chinese 21 site mutations in four genes of common non-syndromic hereditary deafness, including 6 mutations in GJB2 (35del G, 167delT, A176-191del 16, 230G>A, 235del C, 299-300del AT), 2 mutants on GJB3 (538C>T, 547G>A), 10 mutants on SLC26A4 (IVS7-2A>G, 2168A>G, 1174A>T, 1226G>A, 1229C>T, 1238A>G, IVS15 +5G>A, 1975G>C, 2027T>A, 2162C>T), and 3 mutant types on 12S rRNA (1095T>C, 1494C>T, 1555A>G).
[0097] 2. Principle
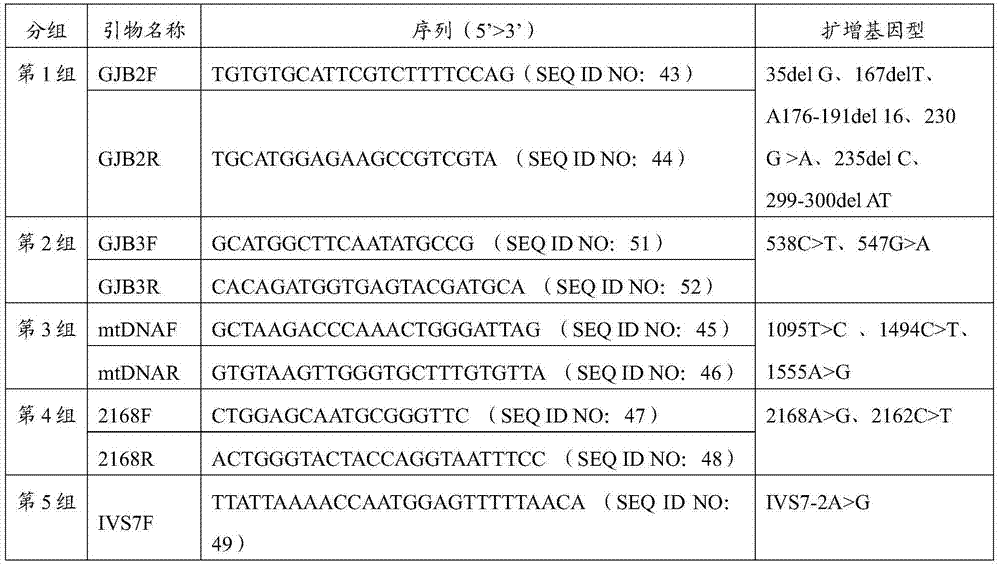
[0098] PCR and DNA reverse dot hybridization: design specific PCR primers and label their 5′ ends with biotin, and amplify to obtain a certain length of DNA fragments, which contain each site to be detected. According to the base difference of the detection site, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com