Preparation and application of anti-Coxsackie virus A16 monoclonal antibody
A coxsackie virus, A16 technology, applied in the field of biotechnology and immunology, can solve the problem of no monoclonal antibody
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0099] For the preparation of CA16 / SZ05 inactivated virus, see Cai Y et al., Vaccine2013Apr26; 31(18):2215-21. After mixing 4ug of inactivated virus (50ul volume) with an equal volume of aluminum adjuvant and 25ug CpG adjuvant, female Balb / c mice were immunized intraperitoneally for 6 weeks, and immunized once at 0 weeks, 2 weeks, 4 weeks, and 6 weeks. At week 7, mouse serum was taken to detect the neutralization titer. One mouse with the highest neutralizing titer was boosted with 10ug of inactivated CA16 virus through the tail vein at the 8th week. After 3 days, the mouse spleen was taken for the preparation of hybridoma cells.
[0100] Preparation and screening of hybridoma cell lines
[0101] Three days after the tail vein booster immunization of the mice, the spleen cells of the mice were fused with myeloma cells SP2 / 0 through PEG1500 to prepare hybridoma cells. After 9 days, neutralizing antibodies specifically secreted against CA16 were screened by ELISA and microneu...
Embodiment 1
[0128] Embodiment 1, establishment of hybridoma cell line 9B5
[0129] Hybridoma cells were obtained by fusion of splenocytes from mice immunized with inactivated CA16 and myeloma cell SP2 / 0. The supernatant of hybridoma cells was analyzed by ELISA and microneutralization titration experiments, and a hybridoma cell line was screened out. The antibody secreted by it could bind CA16 virus and had neutralizing effect in vitro. The hybridoma cell line was named 9B5.
Embodiment 2
[0130] Embodiment 2, characteristic analysis of monoclonal antibody 9B5
[0131] The characteristics of monoclonal antibody secreted by hybridoma cell line 9B5 were analyzed. Subtype identification showed that the light chain of monoclonal antibody 9B5 belonged to kappa chain, and the heavy chain belonged to IgG2B.
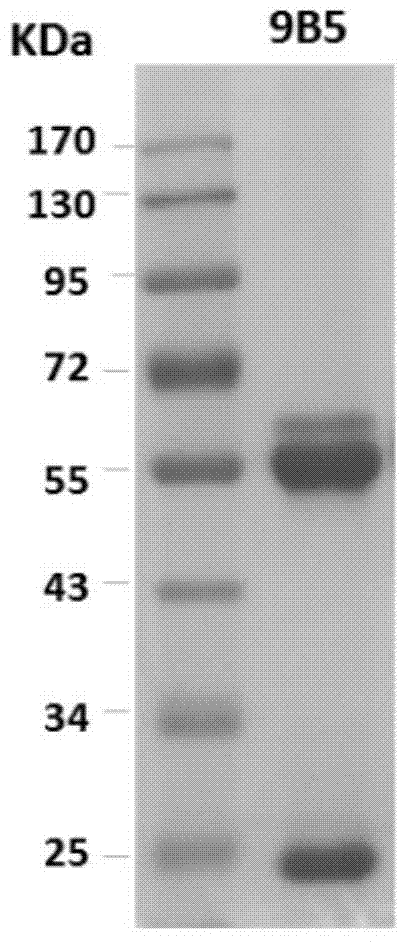
[0132] SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the heavy chain and light chain of mAb 9B5 were about 50KD and 25KD respectively, as shown in figure 1 .
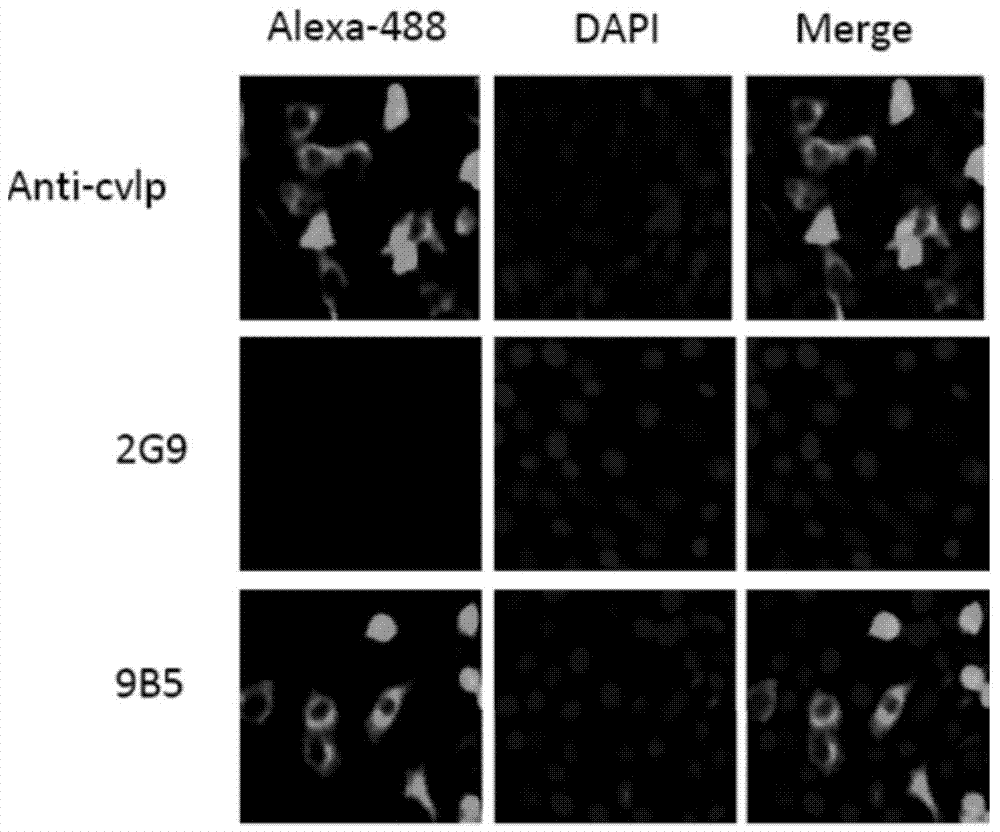
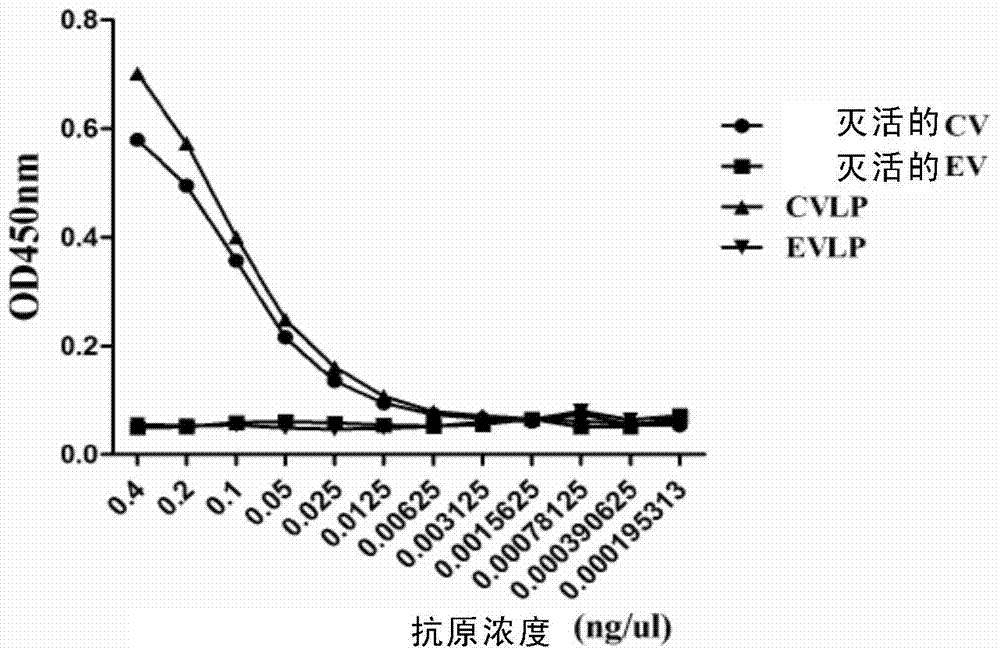
[0133] The reactivity of monoclonal antibody 9B5 with different antigens was detected by ELISA, and the results showed that 9B5 reacted with inactivated CA16 virus, but not with inactivated EV71 virus, indicating that the antibody specifically recognized CA16. In addition, none of the monoclonal antibodies reacted with the CA16 capsid protein VPO, VP1, or VP3 recombinantly expressed in E. coli, suggesting that the monoclonal antibody recognized a conformational epitope.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com