A kind of preparation method of iron-based nano-catalyst for synthesis gas to light olefins
A nanocatalyst, low carbon olefin technology, applied in nanotechnology for materials and surface science, chemical instruments and methods, catalysts for physical/chemical processes, etc. problems of uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0037] In one embodiment of the present invention, the preparation method for the iron-based nano-catalyst of syngas system low-carbon olefins comprises steps:
[0038] In the first step, carbon carrier is mixed with potassium permanganate solution, and then oxidized to obtain carbon material 1;
[0039] In the second step, the iron precursor solution is impregnated onto the carbon material 1, aged and dried, and then calcined and reduced at high temperature to obtain an iron-based nano-catalyst.
[0040] The iron precursor involved in the above method includes iron nitrate, iron acetate, iron ammonium citrate and the like.
[0041] The calcination temperature has a great influence on the performance of the obtained iron-based nano-catalyst. Through experiments, the inventors found that calcination should be carried out at 150-500°C under an inert atmosphere. The preferred calcination temperature is 200-300°C; the calcination time is 2-10 hours, preferably 3-4 hours. Of cour...
Embodiment 1
[0055] Preparation of Fe loaded on manganese and potassium modified carbon materials (taking carbon nanotubes as an example) catalyst
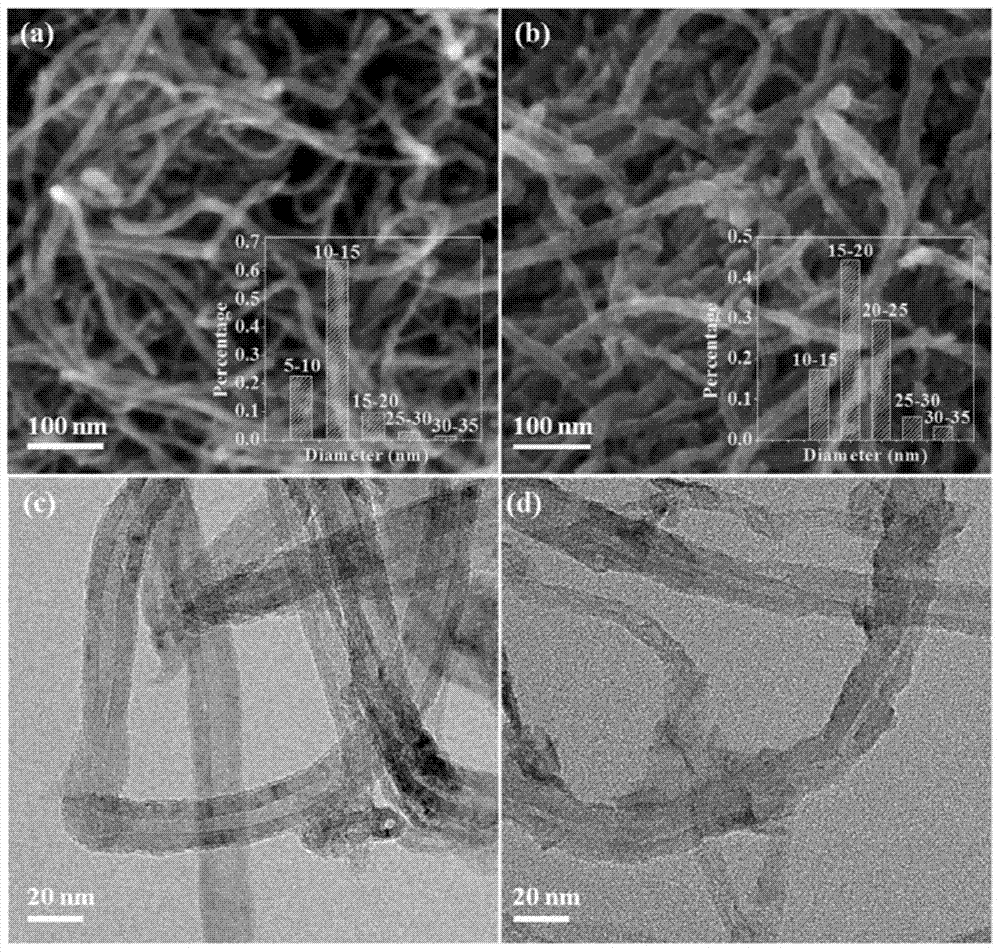
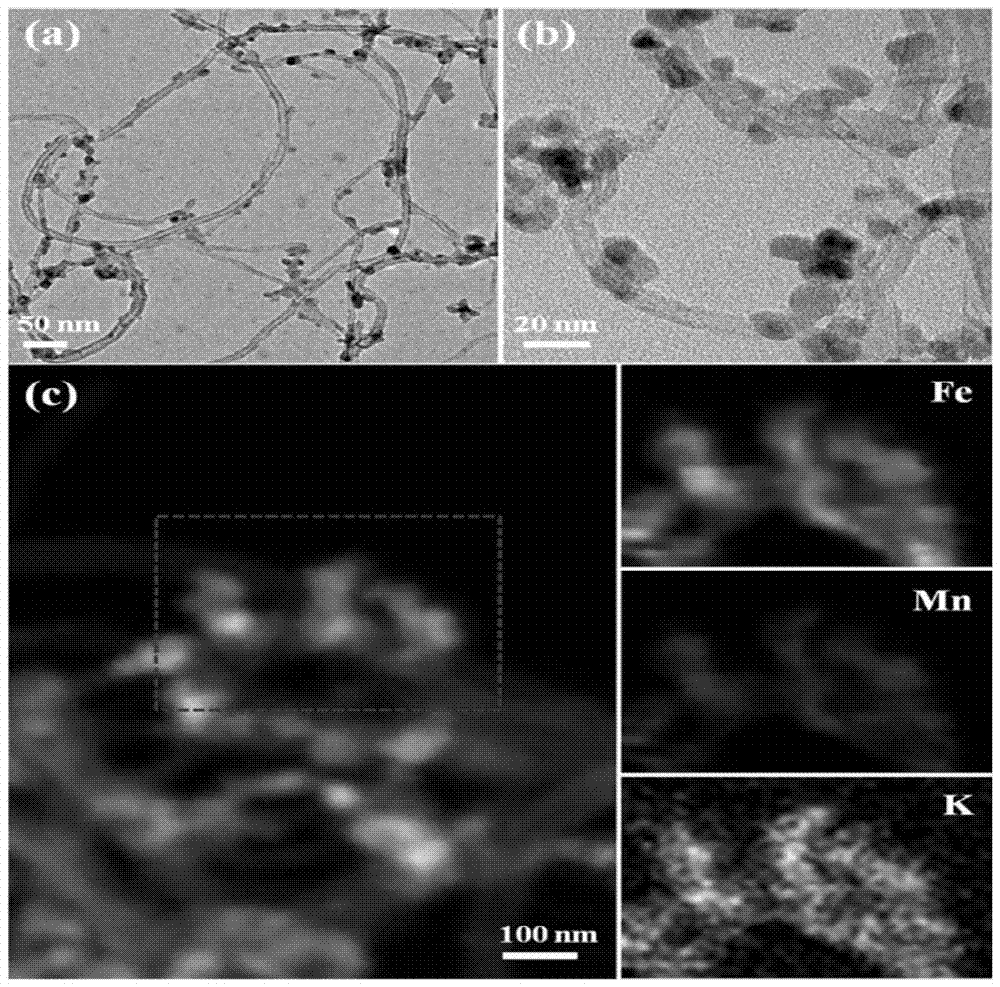
[0056] Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were oxidized with 0.1M potassium permanganate solution in a 70°C water bath and magnetically stirred for about 30 minutes, filtered, washed with 5L deionized water, and dried at 120°C to obtain Manganese, potassium-modified carbon nanotubes 1 (referred to as MnK-CNTs), in which the surface of the carbon nanotubes is coated with a thin layer of potassium-doped manganese dioxide, and the average diameter increases (see figure 1 ). The mass fractions of manganese and potassium in carbon nanotube 1 determined by ICP-AES are 16.3% and 2.0%, respectively. The water absorption of carbon nanotube 1 was measured. 1 g of manganese and potassium modified carbon nanotubes 1 was weighed and mixed with an appropriate amount of ferric nitrate solution, aged at room temperature for 24 hours, and then dried at 120° C. for 10 h...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Preparation of Fe-loaded carbon materials (taking carbon nanotubes as an example) catalysts modified by manganese and potassium calcined at different temperatures
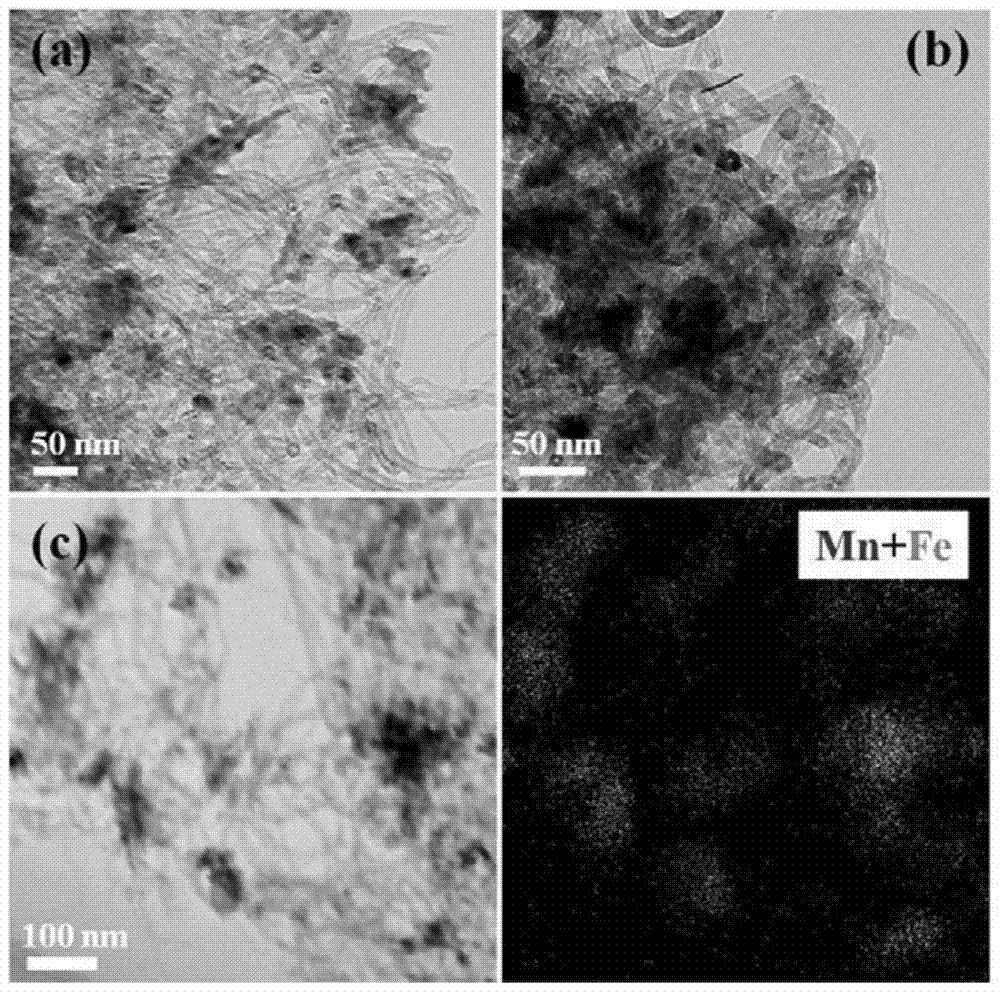
[0059] In the above-mentioned implementation cases, different calcination temperatures were selected to treat the manganese- and potassium-modified carbon materials loaded with iron nitrate. Use potassium permanganate solution with a concentration of 0.1M to oxidize carbon nanotubes for about 30 minutes under the condition of 70°C water bath and magnetic stirring, filter, wash residual ions with 5L deionized water, and dry at 120°C to obtain manganese and potassium modified carbon nanotube1. The mass fractions of manganese and potassium in carbon nanotube 1 determined by ICP-AES are 16.3% and 2.0%, respectively. The water absorption of carbon nanotube 1 was measured. 1 g of manganese and potassium modified carbon nanotubes 1 was weighed and mixed with an appropriate amount of ferric nitrate solution, aged ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com