Semiconductor LED chip and manufacturing method thereof
A light-emitting diode and semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the conductivity of n-type semiconductors, uneven current distribution, and reducing the luminous efficiency of chips, so as to improve light extraction efficiency and reduce epitaxy. The effect of growth cost and high transmittance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
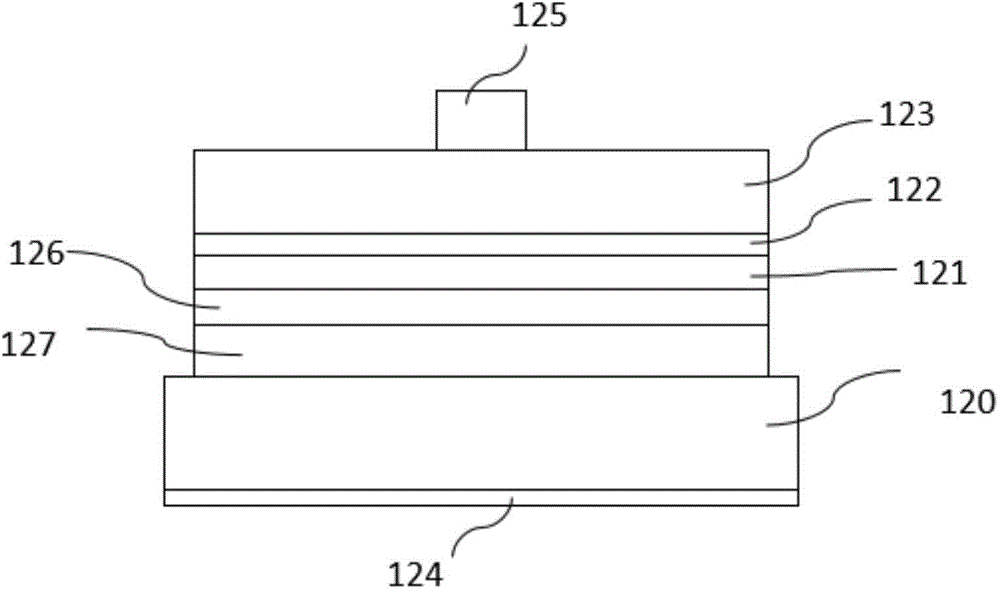
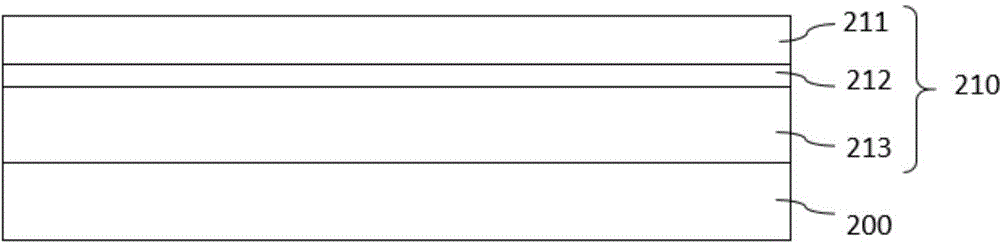
[0053] A semiconductor light-emitting diode chip, its structure from top to bottom is a transparent conductive layer 600, an n-type semiconductor layer 213, an active layer 212, a p-type semiconductor layer 211, a p-type contact layer 300, a dielectric insulating layer 400, and a plurality of The n-type contact layer 500 of the through hole is bonded to the metal layer 510 , the conductive substrate 520 , and the n-electrode 530 . The n-type contact layer 500 runs through the entire epitaxial layer 210 and is in contact with the transparent conductive layer 600 . The surface of the chip has a window 230 , the p-electrode 310 is located in the window area, and the p-electrode 310 is in contact with the p-type contact layer 300 . The n-type semiconductor layer and the p-type semiconductor layer used are gallium nitride (GaN), and the active layer is made of indium gallium nitride (InGaN) material.
[0054] The production method comprises the following steps, such as figure 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] As described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the depth of the through hole 220 only reaches the middle of the n-type semiconductor layer, as Figure 4 shown. The n-type contact layer 500 is in contact with the n-type semiconductor layer 213 without penetrating through the entire epitaxial layer. The material of the transparent conductive layer is zinc oxide (ZnO), and the thickness is
Embodiment 3
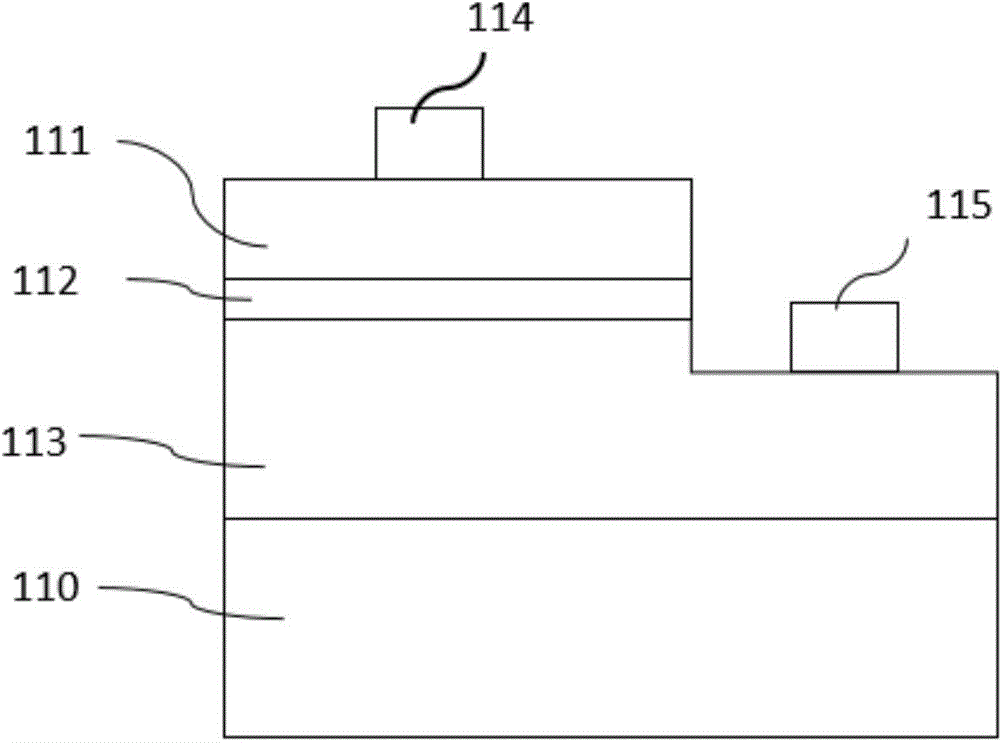
[0072] As described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the conductive substrate 520 is replaced by an insulating substrate 521, the insulating substrate is sapphire, and there are two windows on the chip surface, one of which is a p-electrode window, and the p-electrode and The p-type contact layer is in contact to realize the electrical connection between the p-electrode and the p-type semiconductor layer; the other window 240 is an n-electrode window, and an n-electrode is formed on the n-type contact layer to realize the electrical connection between the n-electrode and the n-type semiconductor layer. The p and n electrodes are located on the same side of the chip. structured as Figure 5 shown.
[0073] Preparation:
[0074] The first step to the fifth step are identical with embodiment 1;
[0075] In the sixth step, the epitaxial wafer is bonded to the insulating substrate 521, and the substrate 200 is removed by a combination of mechanical grinding and dry etchin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com