Random access memory with redundant structure
A technology of random access and redundant structure, which is applied in the direction of static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve the problems of high process cost, difficult integration, low speed, etc., and achieve good process compatibility, small unit area, and design simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
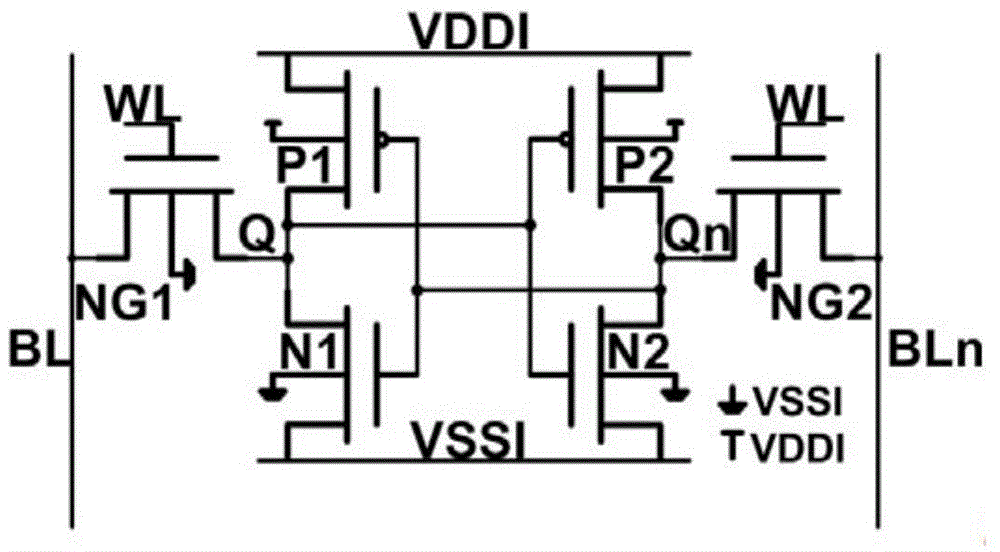
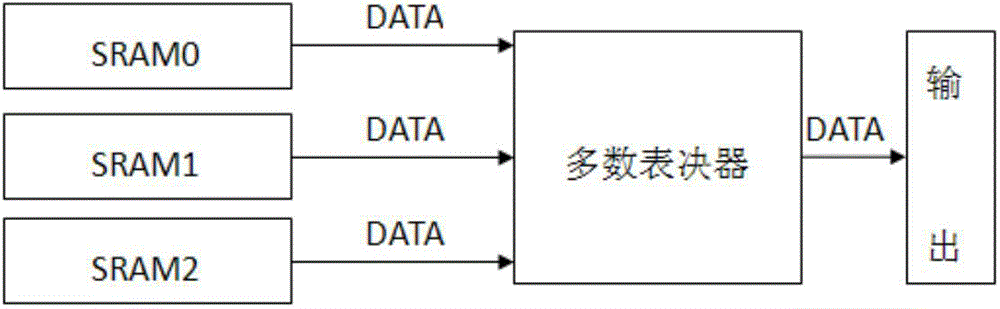
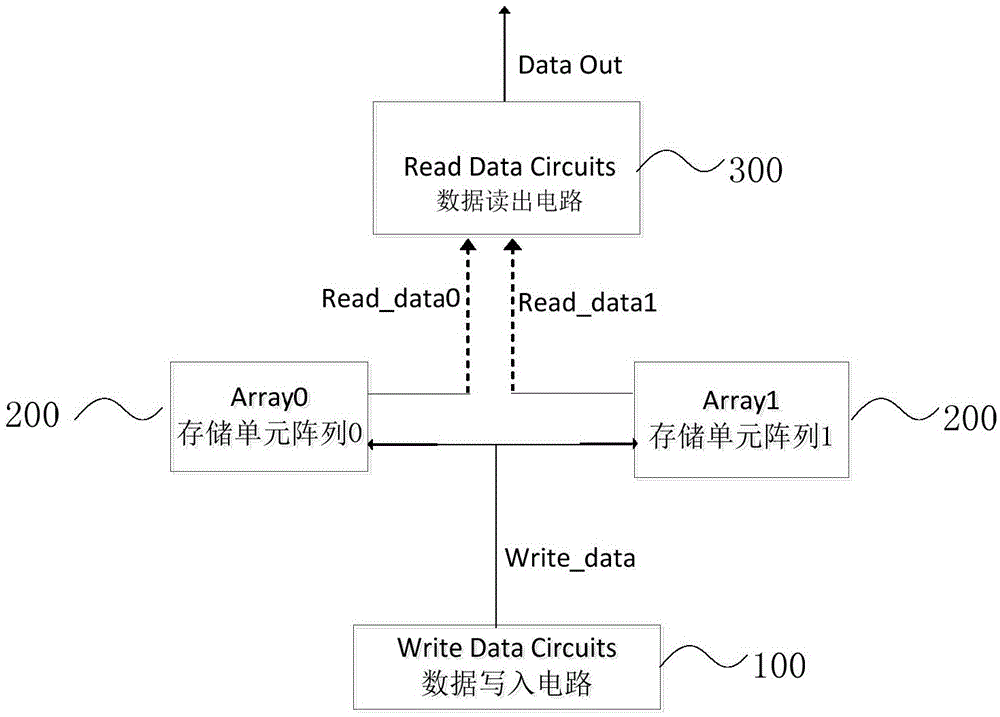
[0021] In order to make those skilled in the art understand better, the applicant makes a brief introduction to the prior art and its shortcomings. At this stage, the more commonly used reinforcement technology is the three-mode redundancy reinforcement technology, which belongs to the circuit design reinforcement technology. But strictly speaking, Triple Modular Redundancy (TMR) is an architecture-level reinforcement. The mechanism of its anti-SEU is as follows figure 2 shown. Its design idea is: add two redundant memory units, then send the output of the three memories to the majority voting circuit, and the result after voting is the final output result. The working truth table of the majority voting circuit is shown in the table. It can be seen from Table 1 that if the data in one of the three memories is flipped, the wrong data can be masked out after voting through the voting circuit.
[0022] Table 1 TMR hardened voting circuit truth table
[0023] SRAM0 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com