Polyamide-imides, graphite films and preparation for the graphite film
A polyamide-imide and polymer technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of low degree of graphitization and inability to form artificial graphite films.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] According to another embodiment of the present invention, the present invention provides a method for preparing a graphite film, comprising: performing a heat treatment process on a polyamide-imide (PAI) polymer to prepare a graphite film.
[0024] The temperature of the heat treatment process is generally between 25-2,900°C.
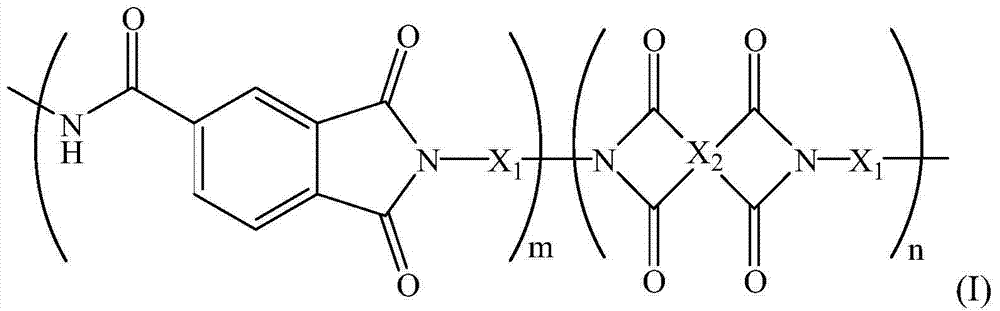
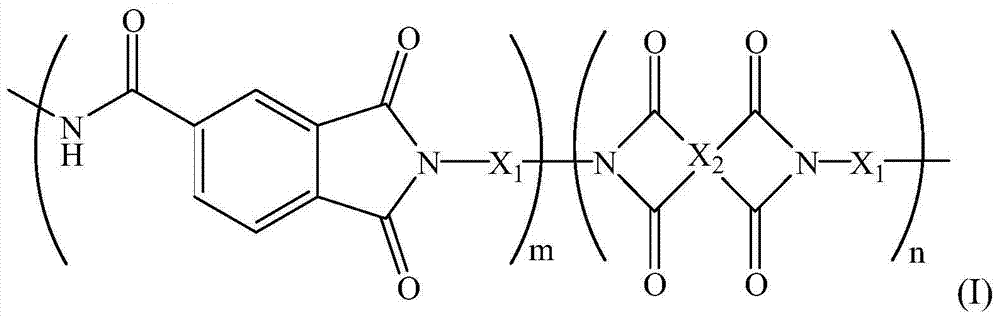
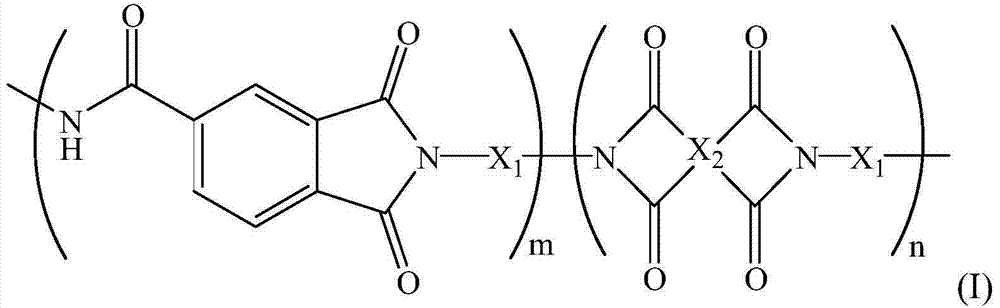
[0025] Above-mentioned polyamide-imide polymer has following chemical formula (I):
[0026]
[0027] In chemical formula (I), X 1 can include
[0028] x 2 can include
[0029] The ratio of m to n can be between 8:2˜6:4, or 7.5:2.5˜6.5:3.5. The weight average molecular weight of the polymer is 20,000-60,000, or 30,000-50,000.
[0030] The aforementioned heat treatment process may include a carbonization process and a graphitization process.
[0031] The temperature of the above-mentioned carbonization process is generally between 25-1,300°C, and the temperature of the above-mentioned graphitization process is generally between 1,8...
Embodiment 1
[0035] The preparation of graphite film PAI-1 of the present invention (polyamide-imide polymer (X 1 =MDI,X 2 =PMDA+BPDA))
[0036] At room temperature, put a stirrer and a heating mantle on a 2-liter four-port reactor, and mix 153.60 grams of trimellitic anhydride (TMA), 24.96 grams of pyromellitic dianhydride (PMDA), 67.20 grams of 3,3',4,4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride (3,3',4,4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride, BPDA) and 300.00 grams of diphenylmethane diisocyanate (methylene diphenylene Diisocyanate, MDI) was dissolved in 1637.00 g of NMP solvent and stirred evenly. The temperature was raised to 80°C for 1 hour, then the temperature was raised to 120°C for 2 hours, and finally the temperature was raised to 170°C for 2 hours. After the reaction is completed, wait for it to cool down to room temperature, put the solution into a PE bottle and seal it for storage. The composition molar ratio m of this polymer was 7, n was 3, and the weight average molecular w...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The preparation of graphite film PAI-2 of the present invention (polyamide-imide polymer (X 1 =MDI,X 2 =PMDA+BPDA+ODPA))
[0039]At room temperature, put a stirrer and a heating mantle on a 1-liter four-port reactor, and mix 67.74 grams of trimellitic anhydride (TMA), 12.81 grams of pyromellitic dianhydride (PMDA), 17.28 grams of 3,3',4,4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride (3,3',4,4'-biphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride, BPDA), 36.45 grams of 4,4'-oxodiphenylene Dissolve phthalic anhydride (4,4'-oxydiphthalic anhydride, ODPA) and 150.00 g of methylene diphenylene diisocyanate (MDI) into 852.00 g of NMP solvent, and stir evenly. The temperature was raised to 80°C for 1 hour, then the temperature was raised to 120°C for 2 hours, and finally the temperature was raised to 170°C for 2 hours. After the reaction is completed, wait for it to cool down to room temperature, put the solution into a PE bottle and seal it for storage. The composition molar ratio m of this pol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com