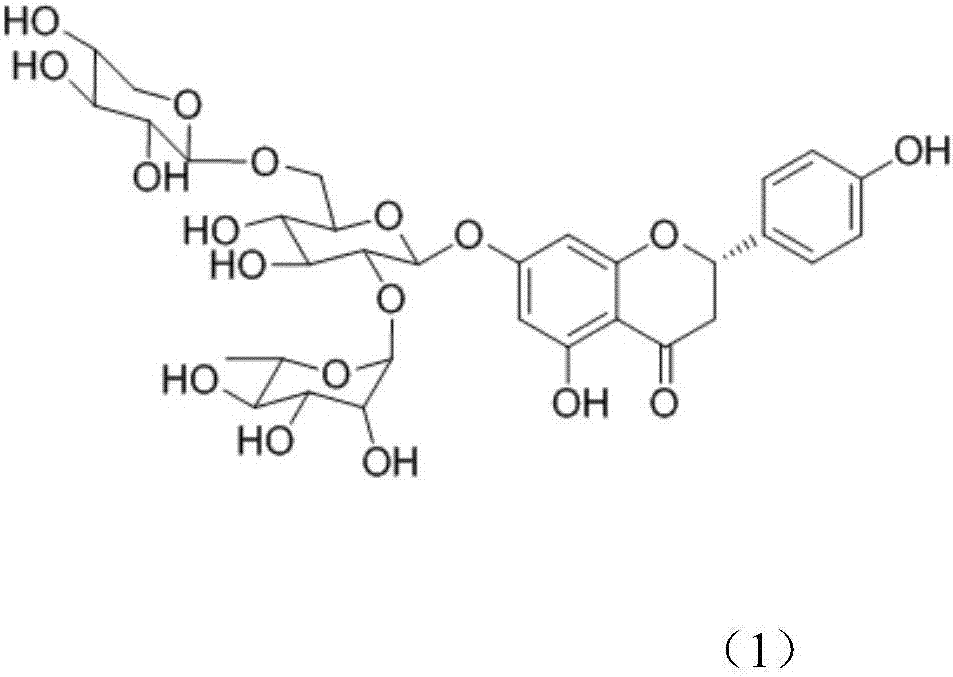
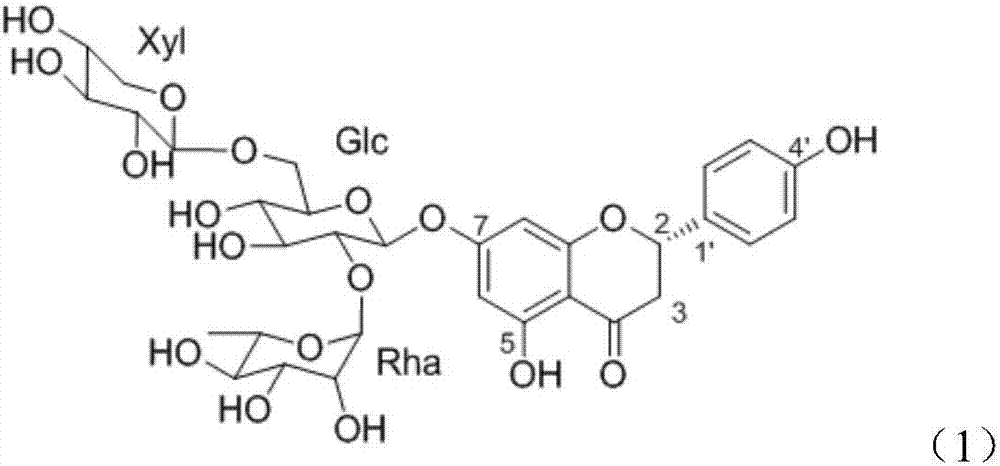
Application of flavonoid compound theaflavanoside II in the control of plant nematode diseases
A technology of flavonoids and plant nematodes, applied in the direction of application, nematicides, plant growth regulators, etc., to achieve the effect of easy degradation and good compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: the preparation of the flavonoid compound theaflavanoside II described in compound (1)
[0024] The residue (tea seed cake) of Camellia oleifera seed is pulverized with a plant pulverizer, passed through a 40-mesh sieve, soaked in 95% edible ethanol with 8 times the sample size (w / v), and placed in a cool place. Stir frequently. After 5-7 days, filter, add ethanol to the residue and soak, repeat twice, and combine the filtrate. The ethanol filtrate was decompressed on a rotary evaporator, concentrated below 45°C, and then extracted three times with petroleum ether to remove excess oil in the material. Add 3% hydrogen peroxide to the solution after extraction and degreasing, adjust the pH value to 10, put it in a water bath at 60° C., and decolorize it for 90 minutes. The decolorized solution was concentrated to a paste on a rotary evaporator, and dried in vacuo to obtain a crude extract. The crude extract is used as the material, and the components are ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: Determination of Egg Hatching Inhibitory Activity to Plant Nematodes
[0027] Bioassay of egg hatching inhibitory activity: use 24-well biological culture plate (draw a good line at the bottom), add 0.5mL of 1mg / mL medicinal solution (the final concentration of the solution after adding egg grains is 0.83%), and then add 0.1 Egg fluid with a mL concentration of 1000 grains / mL was repeated 4 times for each treatment, and sterile water was used as a control, placed in a 25°C incubator, and the hatched second-instar larvae were recorded under an inverted microscope on the 3rd, 5th, and 7th day respectively Number, and calculate the egg hatch inhibition rate:
[0028]
[0029] The results of bioassay showed that the hatching inhibition rates of M. incognita eggs were 71%-90% when the eggs were treated with 0.83 mg / ml concentration for 3, 5, 7, and 9 days. See Table 1 for details.
[0030] Table 1 Determination of the inhibitory activity of 0.83mg / mL theaflava...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: Determination of poisonous activity to plant nematodes
[0035] Weigh 0.05g of compound (1) flavonoid theaflavanoside II, and dissolve it in 10mL of sterilized pure water (the sample is first dissolved with a small amount of sterilized water at about 50°C, and then adjusted to 10mL), to obtain a concentration of 5mg / mL concentration, and then diluted with sterilized pure water to the required gradient concentration. Use a 24-well biological culture plate, add 0.5mL of each concentration gradient drug solution to each well (the final concentration of the drug solution is 0.83mg / ml), and then add 0.1mL of nematode suspension (about 100-200), each treatment Set 4 repetitions, use sterile water as a control, put in a 25°C incubator, observe and count at 24h, 36h, 48h, 72h, and 96h (clean water resuscitation 24h), record the nematode life and death data under an inverted microscope, and calculate Adjusted mortality rate:
[0036]
[0037]
[0038] The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com