A method for non-destructive extraction of mineral elements from Lycium barbarum leaves by flash shearing
A non-destructive, mineral element technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, measurement of color/spectral properties, etc., can solve problems such as large environmental pollution, adverse health, low temperature element loss, etc., and achieve short extraction time and low solvent consumption. , the effect of convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
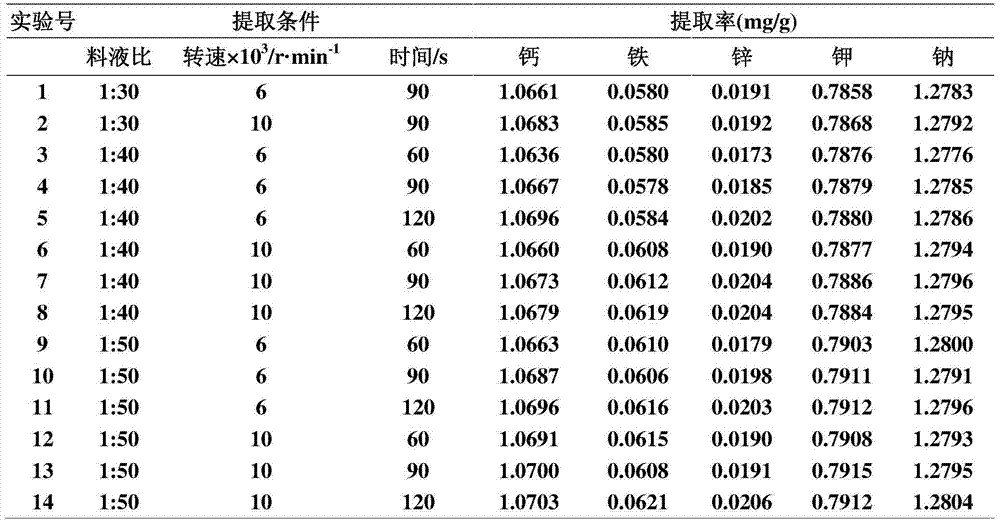
[0038] 1. Wash the wolfberry leaves (Foliis medlar), dry (dry at 60°C for 6 hours), grind and pass through a 60-mesh sieve.
[0039] 2. Accurately weigh 50g of the sieved powder into a beaker, add acetone to make the acetone liquid level 2cm below the wolfberry leaf powder, shake for 20min, filter and dry to obtain the fat-removed wolfberry leaf powder.
[0040] 3. Move the filter cake into a beaker and add 1.5L of deionized water to dissolve it, add cellulase to make the concentration reach 150U / mL, let stand for 2h, then add 100mL of glacial acetic acid solution (the volume of glacial acetic acid and water in the glacial acetic acid solution) The ratio is 1:1).
[0041] 4. Use a flash extractor (motor speed: 6000r / min) to extract for 90s, homogenize and filter with suction, and then extract the residue twice with a flash extractor after suction.
[0042] 5. Combine the extracts obtained three times, concentrate and dry by freeze-drying (110kPa, -50°C, drying for 12h). The content of...
Embodiment 2
[0044] 1. Wash the wolfberry leaves (Foliis medlar), dry (dry at 60°C for 6 hours), grind and pass through a 60-mesh sieve.
[0045] 2. Accurately weigh 50g of the sieved powder into a beaker, add acetone to make the acetone liquid level 2cm below the wolfberry leaf powder, shake for 20min, filter and dry to obtain the fat-removed wolfberry leaf powder.
[0046] 3. Move the filter cake into a beaker and add 1.5L of deionized water to dissolve it, add cellulase to make the concentration reach 150U / mL, let stand for 2h, then add 100mL of glacial acetic acid solution (the volume of glacial acetic acid and water in the glacial acetic acid solution) The ratio is 1:1).
[0047] 4. Use a flash extractor (motor speed: 10000r / min) to extract for 90 seconds, homogenize and filter with suction, and then extract the residue twice with a flash extractor after suction.
[0048] 5. Combine the three extracts, concentrate and dry them by freeze-drying (110kPa, -50°C, drying for 12 hours). The content...
Embodiment 3
[0050] 1. Wash the wolfberry leaves (Foliis medlar), dry (dry at 60°C for 6 hours), grind and pass through a 60-mesh sieve.
[0051] 2. Accurately weigh 50g of the sieved powder into a beaker, add acetone to make the acetone liquid level 2cm below the wolfberry leaf powder, shake for 20min, filter and dry to obtain the fat-removed wolfberry leaf powder.
[0052] 3. Move the filter cake into a beaker and add 2L of deionized water to dissolve it, add cellulase to make the concentration reach 150U / mL, let stand for 2h, then add 100mL of glacial acetic acid solution (volume ratio of glacial acetic acid to water in glacial acetic acid solution 1:1).
[0053] 4. Use a flash extractor (motor speed: 6000r / min) to extract for 60 seconds, homogenize and filter with suction, and then extract the residue twice with a flash extractor after suction.
[0054] 5. Combine the extracts obtained three times, concentrate and dry by freeze-drying (110kPa, -50°C, drying for 12h). The content of calcium is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com