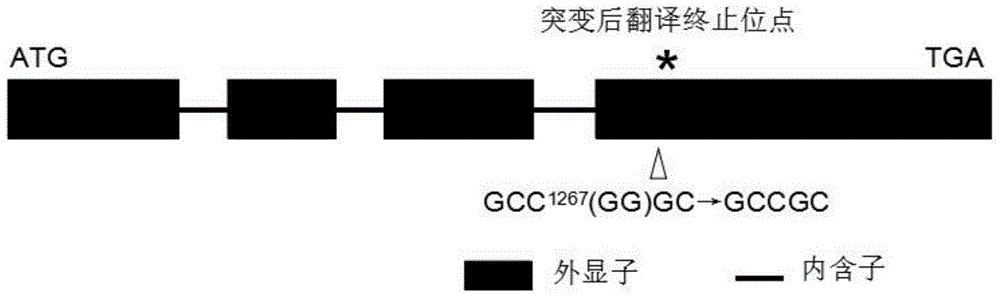
Rice CYP704B2 gene mutant, as well as molecule identification method and applications thereof
A CYP704B2, rice technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as poor quality, adverse effects of utilization, variation of non-target traits, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1: Cobalt 60 radiation mutagenesis mutant library
[0039] Indica rice backbone parent variety 93-11 was selected as the material for radiation treatment. The whole genome sequence of this variety has been completed, which is very beneficial for molecular breeding of rice.
[0040] In the summer of 2013, in Changsha Cobalt 60 ( 60 Co) Radiation 93-11 Seed (M 0 generation) 10 kg, planted in Hainan Lingao field in July, and harvested by individual plants. 1 A total of about 6,500 seeds were harvested.
[0041] choose M 1 There are 3200 strains of generation seeds, and 50 individual plants are planted for each strain. In the spring of 2014, it was planted in Lingao Field, Hainan. After transplanting, carefully observe the field traits at the tillering stage, booting stage, heading stage, flowering stage, and filling stage, and screen various types of mutants such as plant type, panicle type, fertility, and yield. A single plant is harvested and stored as a...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2: M 2 Substitute Planting and Character Observation
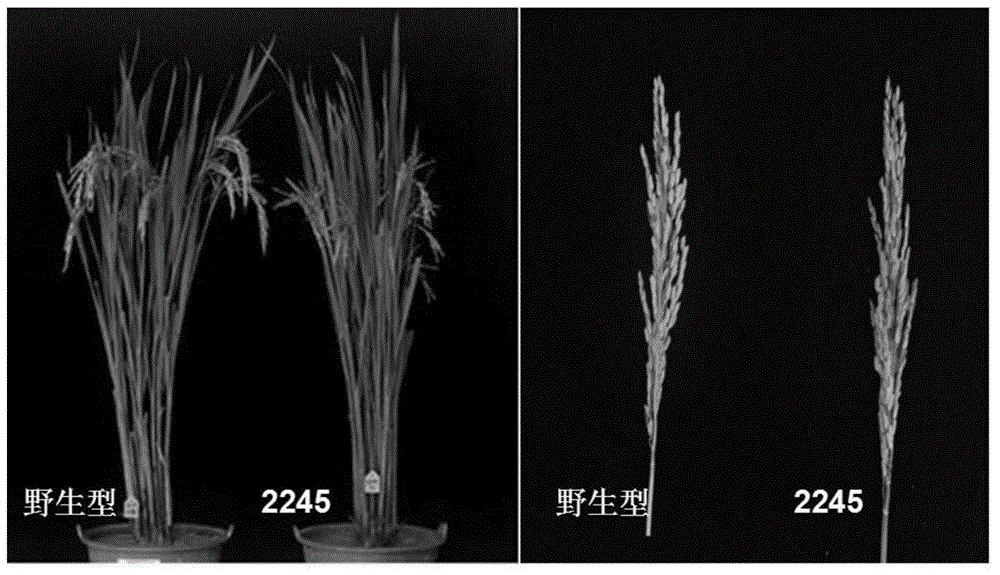
[0043] in M 2 During the period of heading and flowering, the morphology of anthers was observed in the field, and anthers with abnormalities such as light white color, small shape, and small pollen amount were selected for further microscopic examination under a microscope. A plant with abnormal fertility was found in the family numbered 2245, and the mutant had no obvious difference from the wild type in terms of vegetative growth, heading stage, and panicle type. figure 1 is the plant type of the mutant plant and the wild-type plant ( figure 1 left) and panicle ( figure 1 Right) Comparison photos, but the anthers are smaller than the wild type, the color is light yellow, and the seed setting rate is very low, so it is selected as a candidate mutant material for further research.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: Microscopic examination of pollen, selfing, outcrossing
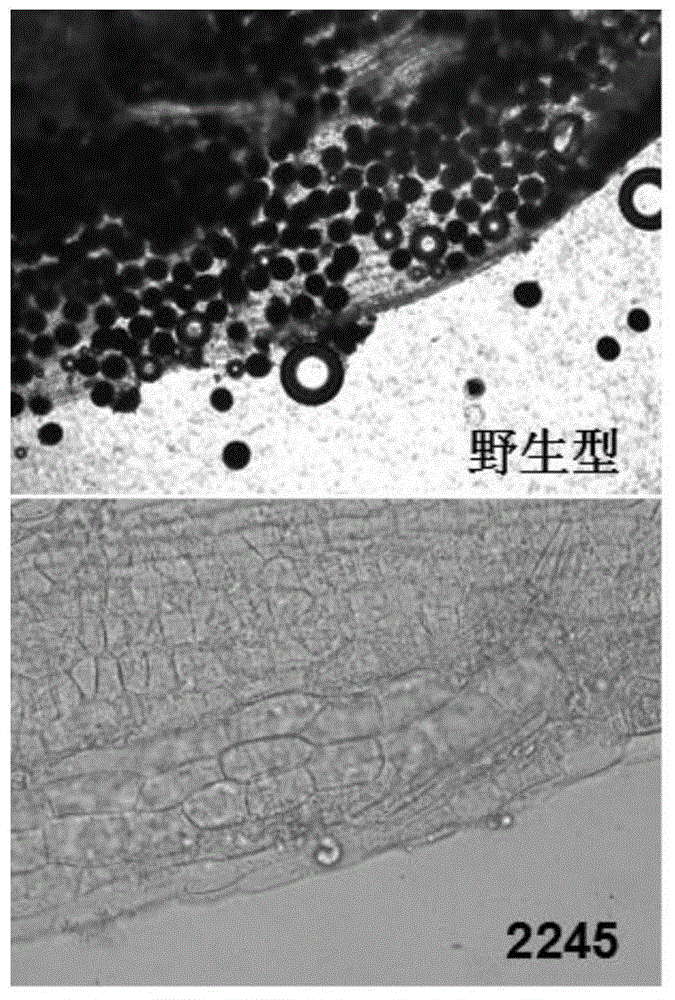
[0045] The pollen fertility was counted by counting the ratio of iodine-stained pollen to non-colored pollen. The floret morphology of the 2245 mutant was observed under a stereomicroscope, and it was found that the pistil was not significantly different from the wild type, and the anthers were smaller and lighter in color than the wild type. Collect florets at the flowering stage in the field, take out the anthers with tweezers, and put them in iodine-potassium iodide solution (0.6% KI, 0.3% I 2 , w / w), gently squeeze the anthers, drop on the glass slide, cover with a cover glass, observe the pollen iodine staining under the microscope and take pictures ( figure 2 ). The wild type has more pollen and is stained blue-black, while the mutant has no pollen grains.
[0046] The wild-type plants of the same family set fruit normally after bagging selfing, but the 2245 mutant did not set fruit. When...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com