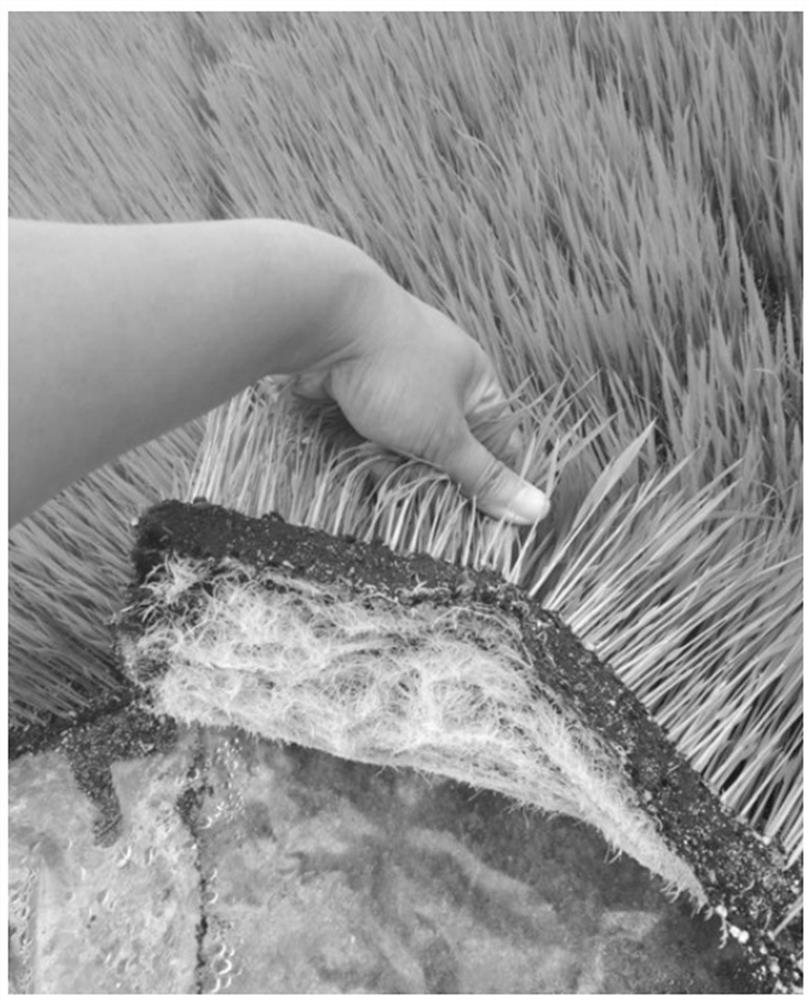
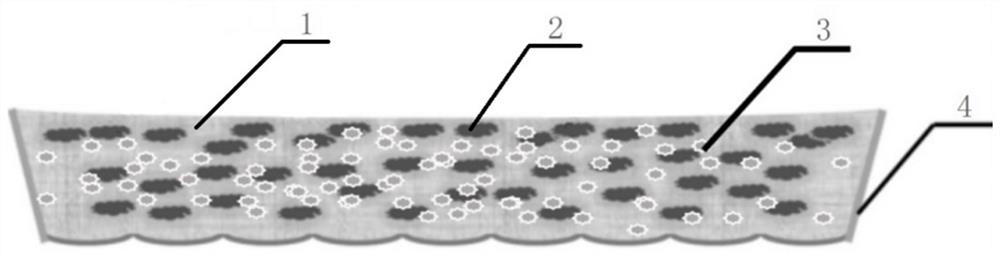
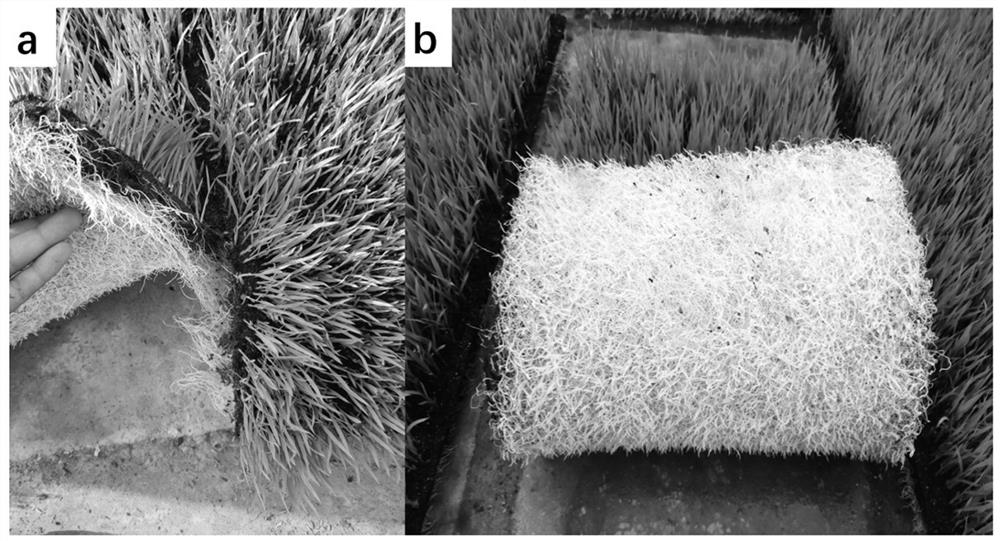
Preparation method and application of a kind of total nutrient degradable straw seedling raising matrix block
A technology of raising seedling substrate and full nutrition, which is applied in the field of seedling raising substrate and rice seedling raising, which can solve problems such as unstable raw materials, sticking of substrate blocks, and unbalanced nutrients, so as to improve the quality of seedlings, increase the temperature of biological fermentation, and reduce the cost of seedling raising Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1 Biorefining plastic silky straw fiber
[0053] 120kg urea is dissolved in 6 tons of water, is sprayed to contain 25kg active microbial bacterial agent (in the present embodiment Streptomyces Louchei, Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis, Aspergillus oryzae quality are respectively: 10kg, 6.25kg, 6.25kg and 2kg) on the straw fiber segment with a mass of 2.5 tons, throw it to the mixed straw material with a moisture content of 60±5%, adjust the carbon-nitrogen ratio to 25, and then stack it in a box-type fermenter for biological pretreatment 12 Days later, the first static aerobic fermentation was carried out for 4 days, and the continuous ventilation was 0.42m 3 / min, the material is turned and thrown; the second static anaerobic fermentation is carried out for 4 days, after being evenly turned and thrown; the third static aerobic fermentation is carried out for 4 days, the fermentation temperature is 69 ° C ± 2 ° C, the material is discharged, and air-d...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2 Nutrient-controllable slow-release conditioner carrier
[0056] 1. Roast the rice husk in a tube furnace at 120°C for 60 minutes, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain carbonized rice husk.
[0057] 2. Mix 10 parts of compound fertilizer and 3 parts of urea-formaldehyde slow-release fertilizer (conventional slow-release fertilizer, refer to literature for preparation method: Qu Ping, Chang Zhizhou, Zhao Yongfu, Huang Hongying. Structure of protein hydrolyzate modified urea-formaldehyde slow-release fertilizer and nitrogen release characteristics [J], Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2016 (21): 240-245.), 1.5 parts of potassium fulvic acid, 3 parts of polyglutamic acid and 1.5 parts of diammonium phosphate are mixed evenly, and the concentration is 5 % of slow-release nutritional conditioners.
[0058] The "urea-formaldehyde slow-release fertilizer" can use conventional slow-release fertilizers in the field. The preparation method of the slow...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Synthesis of Example 3 Functional Polymer Degradable Polymer
[0062] Put hydrolyzed protein with a concentration of 25%, water and paraformaldehyde in the reaction kettle according to the volume ratio of 1:1:2, stir evenly, heat up to 45°C, add urea (the molar ratio of urea to paraformaldehyde is 1.4: 1), adjust the pH to 8.5 with potassium hydroxide, raise the temperature to 90°C and keep it for 60-90min, add polyvinyl alcohol with 5% of the total amount of urea, react for 30min, adjust the pH to 5.5 with 85% phosphoric acid, and react at 85°C After 45-70 minutes, add diatomaceous earth, a nano-scale functional material with 2% of the total amount of urea, adjust the pH to 6.5, continue stirring for 15 minutes, cool down to 40°C, and discharge to obtain a functional polymer degradable polymer.
[0063] One or more of nanoscale diatomite, attapulgite or tourmaline can be selected as the nanoscale functional material during implementation.
[0064] The above-mentioned ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com