Method for preparing Al/Ni reaction laminated foil by EBPVD (electron beam physical vapor deposition)
A technology of reactive lamination and lamination, applied in coating, metal material coating process, ion implantation plating, etc., can solve the problems of easy introduction of impurities at the interface of Al/Ni layer, unfavorable self-propagation rate, low production efficiency, etc. , to achieve the effect of no pollution on the interface, low cost and high production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: This embodiment is a method for preparing Al / Ni reaction laminated foil by EBPVD according to the following steps:
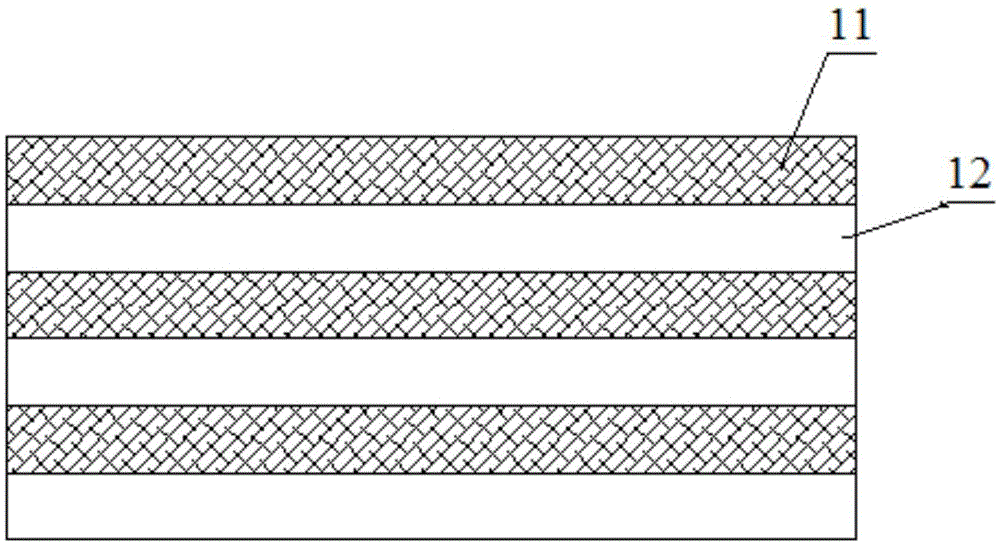
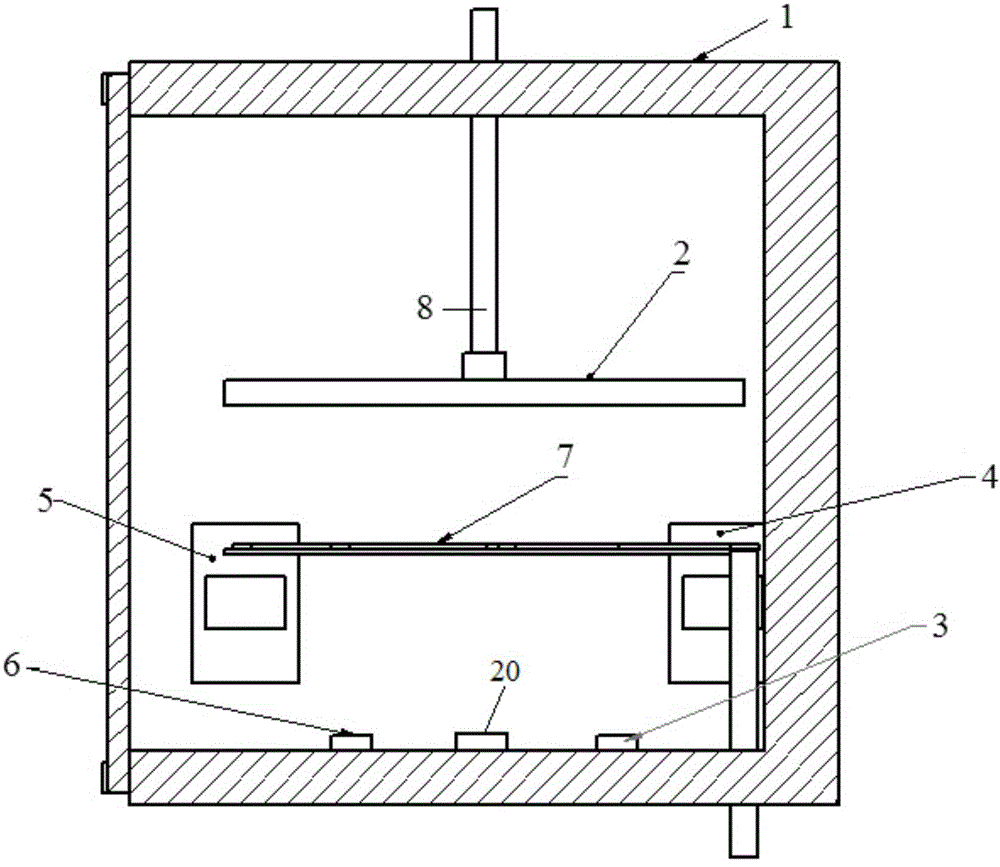
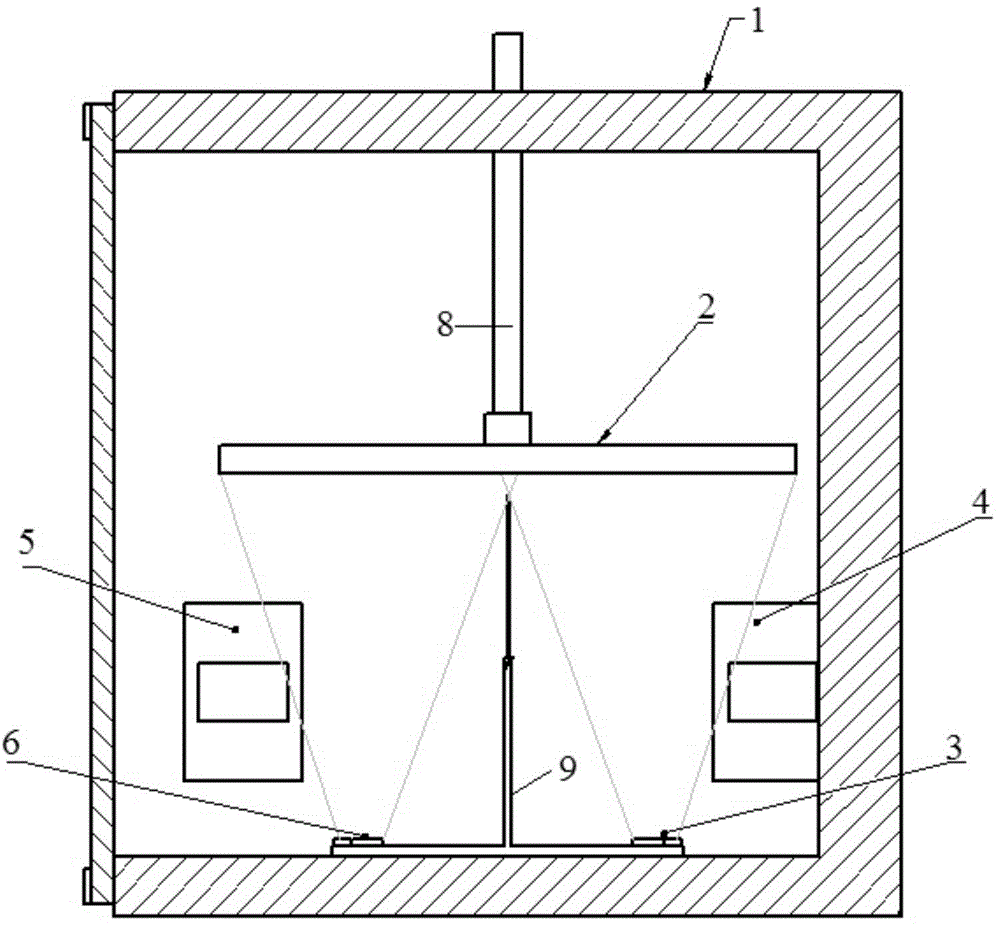
[0030] 1. Preliminary preparations for EBPVD: clean the ingots I and II, clean the vacuum chamber of the EBPVD equipment, and install the substrate. There are two electron guns in the vacuum chamber of the EBPVD equipment, which are electron guns I and II. The ingot I is placed under the electron gun I, the cleaned ingot II is placed under the electron gun II, the separation layer material is placed between the ingot I and the ingot II, the substrate is wiped, and the baffle is closed; Ingot I is pure Al, and the ingot II is pure Ni;
[0031] 2. Preheating the ingot: close the vacuum chamber and evacuate until the vacuum degree is 6×10 -3At Pa, turn on the electron gun Ⅰ and electron gun Ⅱ, set the current of the electron gun Ⅰ to 0.02A~0.1A, and the current of the electron gun Ⅱ to 0.02A~0.1A, use the electron gun Ⅰ to scan the ingot Ⅰ for...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the material of the separation layer in step 1 is sodium chloride or calcium chloride. Other steps are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the substrate described in Step 1 is a large heat sink integral substrate, a circulating water-cooled substrate, a static water-cooled substrate, a segmented substrate, The base plate of the radiation tube or the base plate of the water cooling box, and the thickness of the base plate is greater than 40mm. Other steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com