A high-fiber feed biodegradation fermentation device
A fermentation device and biodegradation technology, applied in the direction of feed, food science, application, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control of fermentation conditions, difficulty in loading and unloading materials, poor fermentation effect, etc. The effect of too much material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1: Composition and function analysis of fermentation system
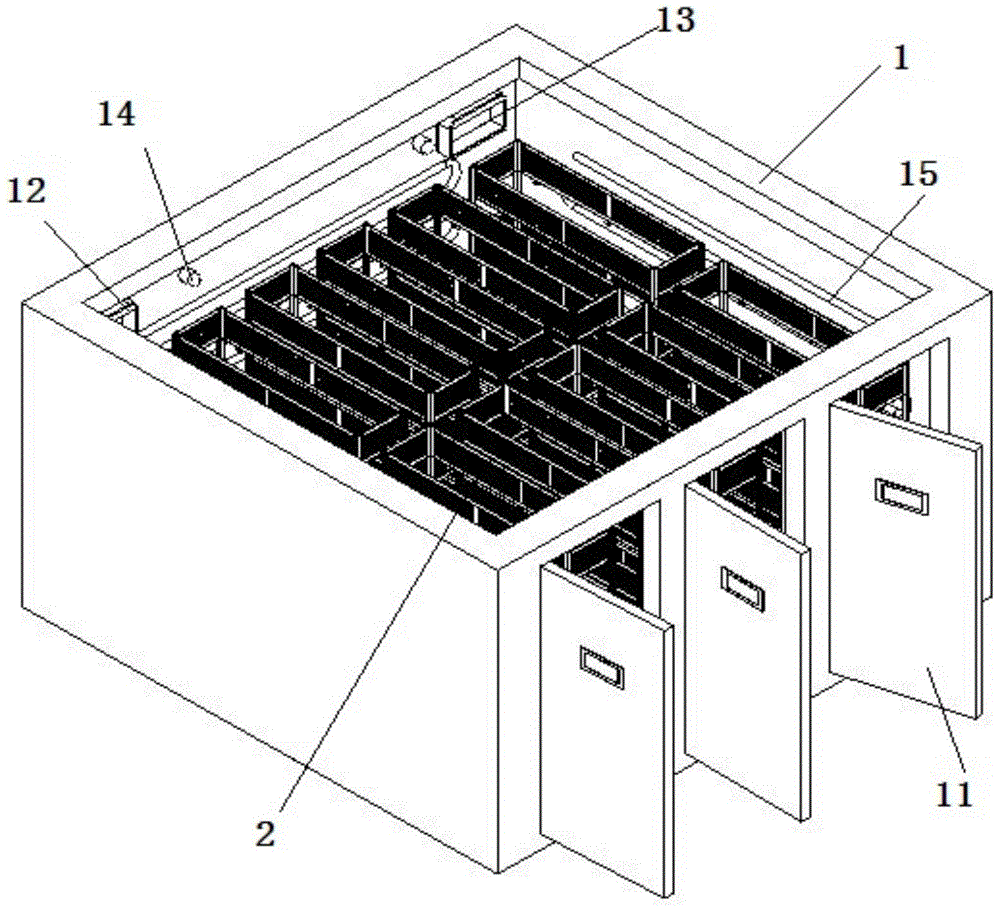
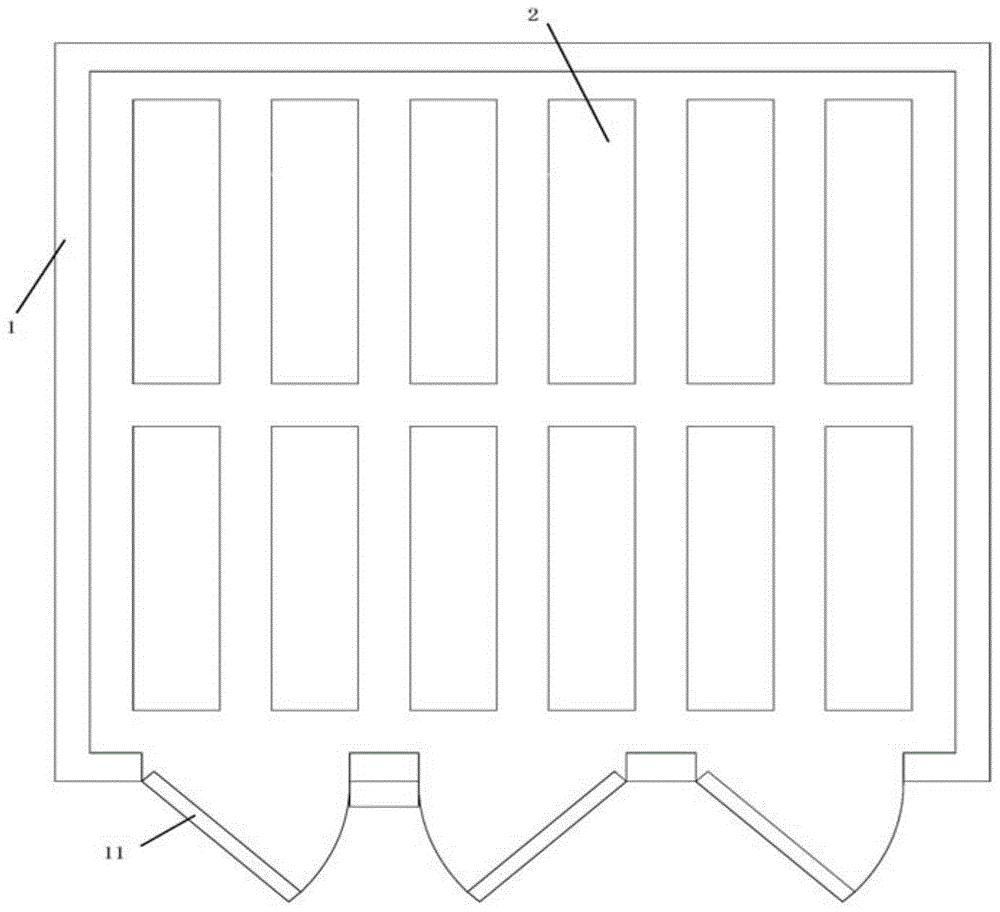
[0026] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, the fermentation system of the present invention includes a fermentation chamber 1 and a mobile fermentation car 2. A fermentation tray 3 is installed on the mobile fermentation cart 2, wherein the bottom of the fermentation tray 3 includes two base plates 31 that can rotate around the shaft. The two bottom plates 31 can be closed by the plug-in latch 32 .
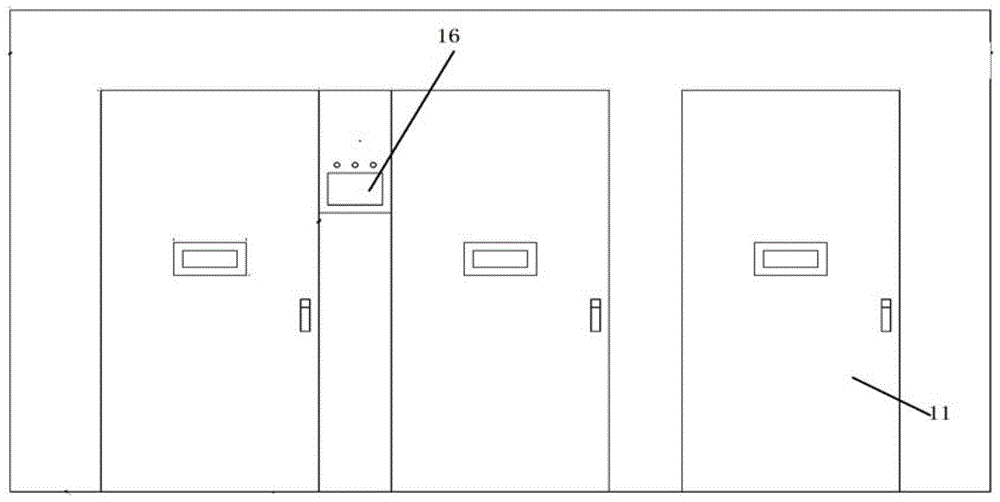
[0027] A door 11 for moving in and out of the fermenting vehicle 2 is installed on the fermenting chamber 1;
[0028] An ultraviolet disinfection lamp 12, a lighting lamp 13, a temperature and humidity sensing probe 14 are installed in the fermentation chamber 1;
[0029] And a steam pipe 15 is installed in the fermentation chamber 1 , and is regulated by a control panel 16 installed outside the fermentation chamber 1 .
[0030] The front two wheels of described mobile fermentation vehicle 2 are universal...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: Composite strain fermented soybean hull comparative test
[0039] Step 1: Composite bacterial liquid production. The bacterial strain is composed of Penicillium oxalicum, lactic acid bacteria, Bacillus natto, and Candida ruthenicum, which are mixed according to the volume fraction ratio of 2:1:2:1 (in the fermentation broth).
[0040] Step 2: Culture medium production: Mix the compound bacterial solution evenly into the soybean hull feed to be fermented according to the proportion, and add the inoculum according to the weight fraction of 10%; the soybean hull addition ratio in the soybean hull feed solid-state fermentation medium is 90%, and the The nitrogen source is urea, and the addition ratio is 1.5% by weight fraction; the inorganic salt is disodium hydrogen phosphate and calcium carbonate, and the addition ratio is 0.2% and 0.3% by weight fraction, and fully stirred.
[0041] Step 3: Loading: Put the processed soybean hull feed to be fermented into ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Embodiment 3: Composite strain fermented grape seed meal comparison test
[0049] Step 1: Composite bacterial liquid production. The bacterial strain is composed of Penicillium oxalicum, lactic acid bacteria, Bacillus subtilis, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which are mixed according to the volume fraction ratio of 3:1:2:1 (in the fermentation broth).
[0050] Step 2: Culture medium production: Mix the compound bacterial solution evenly into the grape seed meal feed to be fermented according to the proportion, and add the inoculation amount according to the weight fraction of 20%; the grape seed meal addition ratio in the solid fermentation medium of the grape seed meal feed is 80% , bran is 20%; the nitrogen source is ammonium nitrate, the addition ratio is 2.0% by weight fraction; the inorganic salt is disodium hydrogen phosphate and calcium carbonate, the addition ratio is 0.2% and 0.1% by weight fraction, and fully stirred.
[0051] Step 3: Loading: Put the processe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com