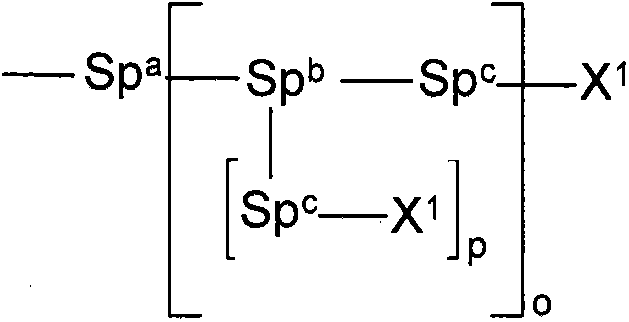Liquid crystalline media with homeotropic alignment
A medium and polymerized liquid crystal technology, applied in the direction of liquid crystal materials, organic compound preparation, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problem that VA display is not fully satisfactory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0379] 2-Methacrylic acid 2-[2′-ethyl-4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-4″-pentyl-[1,1′; 4′,1″]terphenyl-3-yl] Synthesis of ethyl ester 1
[0380]
[0381] 1) Synthesis of 4'-bromo-2'-ethylbiphenyl 4-alcohol A
[0382]
[0383] Add 223ml of water to 110.3g (1.04mol) Na 2 CO 3 , and 154 g (0.49 mol) 4-bromo-2-ethyl-1-iodobenzene, 75.1 g (0.54 mol) 4-hydroxyphenylboronic acid and 850 ml 1,4-dioxane were added and the mixture was degassed . 14.5 g (19.8 mmol) of bis(1,1-diphenylphosphinoferrocene)palladium(II) chloride were added, and the mixture was stirred at 80° C. for 18 hours. When the reaction was complete (checked by thin layer chromatography using heptane / ethyl acetate 1:1), the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with water and methyl tert-butyl ether and acidified to pH 1-2 using 2N HCl. The phases were separated, and the aqueous phase was extracted with methyl tert-butyl ether, and the combined organic phases were washed with Na 2 SO 4 Dry, filter a...
Embodiment 2
[0420] 2-Methacrylic acid 2′-ethyl-4″-(2-hydroxyethyl)-6″-(2-methyl-acryloyloxy)-4-pentyl-[1,1′;4′ , Synthesis of 1″]terphenyl-3″-yl ester 2
[0421]
[0422] 1) Synthesis of 4-bromo-2-ethyl-4'-pentyl biphenyl A2
[0423]
[0424] Dissolve 45.0g (234mmol) of 4-pentylphenylboronic acid, 70.0g (225mmol) of 4-bromo-2-ethyl-1-iodobenzene in 300ml of toluene, 200ml of ethanol and 200ml of Na 2 CO 3 The mixture of solutions (2 moles) was filled with nitrogen. Subsequently 8.00 g (6.92 mmol) of tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) were added, and the reaction mixture was refluxed for 18 hours. When the reaction was complete, the mixture was cooled to room temperature, and water was added, the phases were separated, and the organic phase was washed with water and washed with Na 2 SO 4 Dry, filter and evaporate in vacuo. The crude product (orange oil) was filtered through silica gel using heptane to give 56.2 g of product as a colorless oil.
[0425] 1 H NMR (500MHz, ...
Embodiment 3
[0459] 2-{5-[2-Ethyl-4-(4-pentylphenyl)phenyl]-2-[4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)butoxy]phenyl}ethyl 2- Synthesis of methylprop-2-enoate 4
[0460]
[0461] 1) Synthesis of 4'-bromo-2'-ethylbiphenyl-4-alcohol A
[0462]
[0463] 223ml of water was added to 110.3g (1.04mol) of Na 2 CO 3 , and 154 g (0.49 mol) of 4-bromo-2-ethyl-1-iodobenzene, 75.1 g (0.54 mol) of 4-hydroxyphenolboronic acid and 850 ml of 1,4-dioxane were added, and the mixture was degassed. 14.5 g (19.8 mmol) of bis(1,1-diphenylphosphinoferrocene)palladium(II) chloride were added, and the mixture was stirred at 80° C. for 18 hours. When the reaction was complete (checked by thin layer chromatography using heptane / ethyl acetate 1:1), the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with water and methyl tert-butyl ether and acidified to pH 1-2 using 2N HCl. The phases were separated, and the aqueous phase was extracted with methyl tert-butyl ether, and the combined organic phases were washed ov...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Layer thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com