Internal electrolysis-electric flocculation method for processing phosphor-containing wastewater
A technology of electrocoagulation and internal electrolysis, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete settlement, discharge or reuse of phosphorus-containing wastewater, and achieve Meet the treatment requirements, reduce operating costs, simple process effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The phosphating wastewater used in this study was obtained from an automobile industry company in Suzhou, China. The initial pH value of the raw wastewater was 6.41 and the content of total phosphorus was 88.279mg / L. At room temperature (25°C), the phosphating tank water is treated without adjusting the pH value and enters the internal electrolysis device under continuous aeration conditions. The filler in the internal electrolysis device is iron filings and a small amount of copper filings. After the phosphating tank water is treated by internal electrolysis, the pH value of the solution changes to 8.87. After the wastewater has been treated to meet the discharge standard, it is left to stand for a period of time in the device, and the yellow supernatant after static sedimentation is taken to enter the next step of the electrocoagulation treatment process. The electrocoagulation is performed directly without adjusting the pH value, and the output current density is con...
Embodiment 2
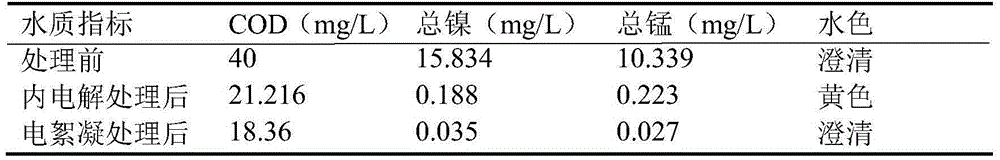
[0027] The phosphating wastewater used in this study was obtained from an automobile industry company in Suzhou, China. The pH value of the raw wastewater was 6.41, and the contents of COD, nickel and manganese were 40mg / L, 15.834mg / L and 10.339mg / L, respectively. At room temperature (25°C), the phosphating tank water is treated without adjusting the pH value and enters the internal electrolysis device under continuous aeration conditions. The filler in the internal electrolysis device is iron filings and a small amount of copper filings. The pH value of the phosphating tank water was changed to 8.75 after internal electrolysis treatment. After the wastewater has been treated to meet the subsequent treatment requirements, it is left to stand for a period of time in the device, and the yellow supernatant after static sedimentation is taken into the next step of electrocoagulation treatment process. The electrocoagulation is directly performed without adjusting the pH value of t...
Embodiment 3
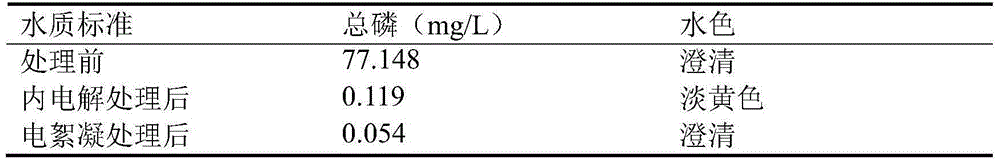
[0031]The phosphating wastewater used in this study was obtained from an automobile industry company in Suzhou, China. The pH value of the wastewater is 4.01, and the total phosphorus content is 77.148mg / L. At room temperature (25° C.) without adjusting the pH value, enter the internal electrolysis device for continuous aeration, and the filler in the internal electrolysis device is iron filings and a small amount of copper filings. The pH value of the phosphating tank water changed to 7.57 after internal electrolysis treatment. After the wastewater has been treated to meet the subsequent treatment requirements, it is left to stand for a period of time in the device, and the yellow supernatant after static sedimentation is taken into the next step of electrocoagulation treatment process, and the pH value of the wastewater is not adjusted directly for electrocoagulation, and the output is controlled by a DC power supply The current density is 3mA / cm 2 , the working voltage is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com