Novel brake pad and manufacturing method thereof
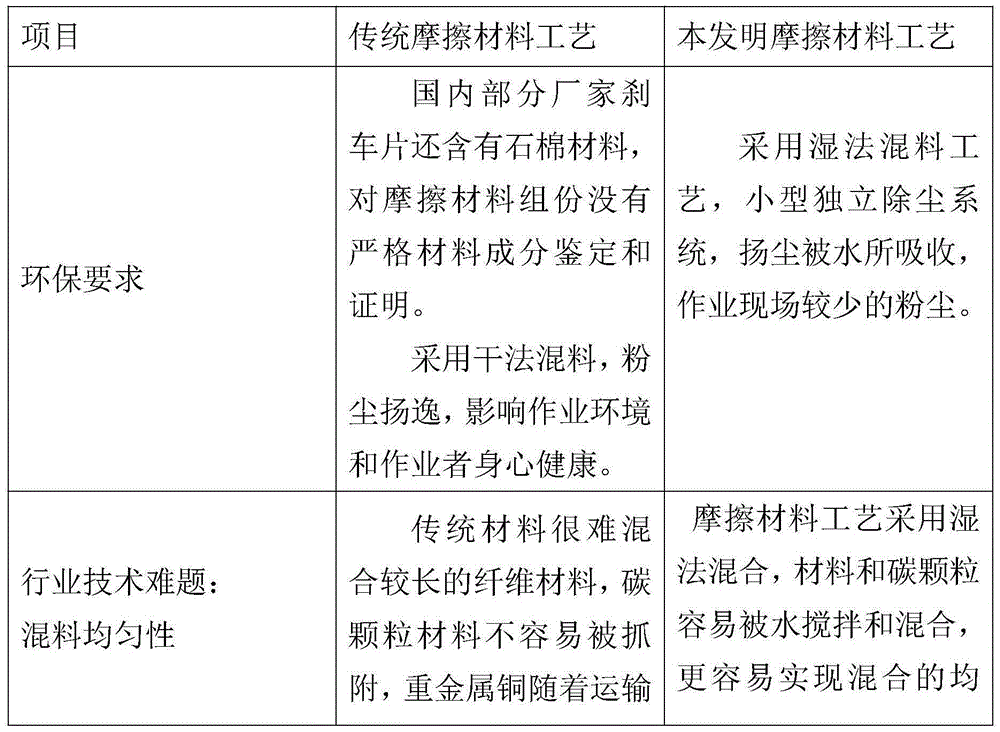
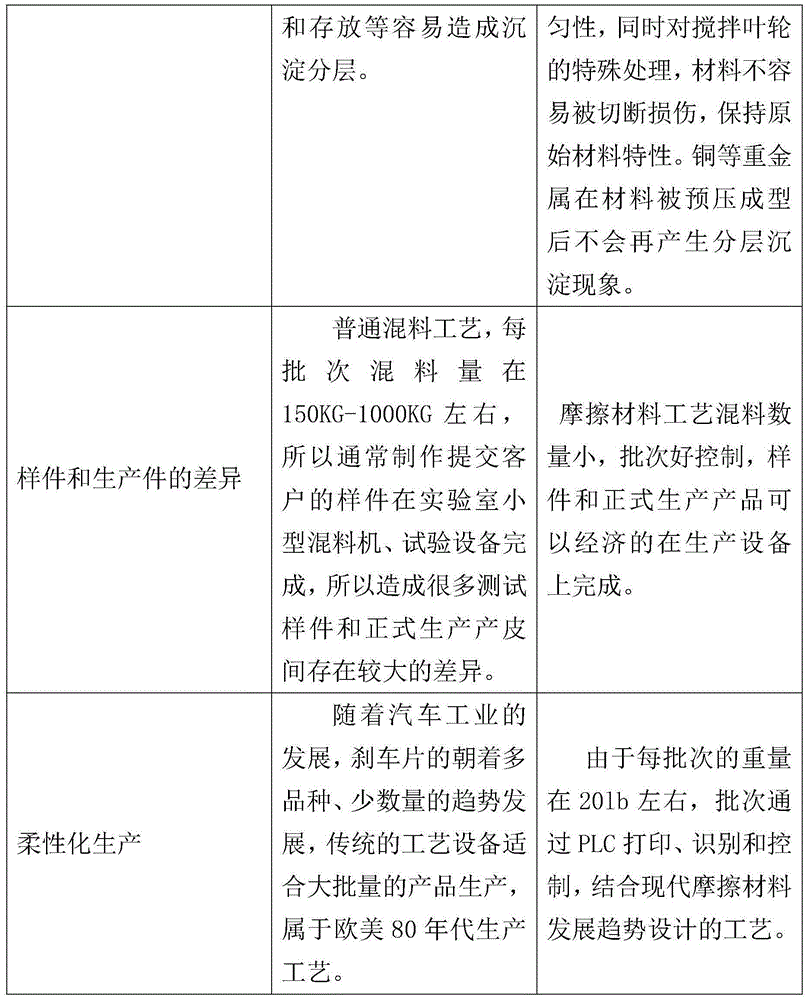
A manufacturing method and technology for brake pads, applied in chemical instruments and methods, friction linings, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of unstable performance of friction materials, uneven mixing, etc., to prevent fiber agglomeration and reduce dust. Contamination, wear-reducing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A new type of brake pad, including a friction material and a steel back. The friction material includes the following components by weight: 5 parts by weight of aramid pulp, 1 part by weight of aramid fiber, 5 parts by weight of zirconia, 2 parts by weight of graphite, petroleum 1 part by weight of coke, 0.5 parts by weight of rubber powder, 2 parts by weight of antimony sulfide, 5 parts by weight of barite, 1 part by weight of friction powder, 5 parts by weight of copper fiber, 2 parts by weight of mineral fiber, 2 parts by weight of mica, and 5 parts by weight of resin parts, 5 parts by weight of potassium titanate, and 1 part by weight of curing agent.
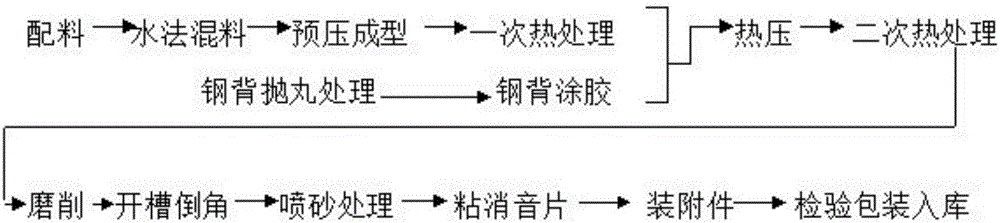
[0031] A method for manufacturing a novel brake pad, comprising the following steps
[0032] (1), batching, water mixing, pre-press forming and heat treatment to produce friction material blanks;
[0033] (2) The steel back is shot blasted, and then glued to the steel back;
[0034] (3) hot pressing the friction ma...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A new type of brake pad, including a friction material and a steel back. The friction material includes the following components by weight: 8 parts by weight of aramid pulp, 3 parts by weight of aramid fiber, 12 parts by weight of zirconia, 5 parts by weight of graphite, petroleum 3 parts by weight of coke, 2 parts by weight of rubber powder, 6 parts by weight of antimony sulfide, 10 parts by weight of barite, 3 parts by weight of friction powder, 10 parts by weight of copper fiber, 6 parts by weight of mineral fiber, 6 parts by weight of mica, and 7 parts by weight of resin parts, 8 parts by weight of potassium titanate, and 5 parts by weight of curing agent.
[0042] A manufacturing method of a novel brake pad, including steps consistent with the embodiments.
Embodiment 3
[0044] A new type of brake pad, including a friction material and a steel back. The friction material includes the following components by weight: 12 parts by weight of aramid pulp, 5 parts by weight of aramid fiber, 20 parts by weight of zirconia, 8 parts by weight of graphite, petroleum 5 parts by weight of coke, 4 parts by weight of rubber powder, 10 parts by weight of antimony sulfide, 15 parts by weight of barite, 5 parts by weight of friction powder, 15 parts by weight of copper fiber, 10 parts by weight of mineral fiber, 10 parts by weight of mica, and 10 parts by weight of resin parts, 10 parts by weight of potassium titanate, and 8 parts by weight of curing agent.
[0045] A manufacturing method of a novel brake pad, including steps consistent with the embodiments.
[0046] The equipment used in embodiment 1, 2 and 3 in the present invention is as shown in table 1 below,
[0047] Table 1
[0048]
name Remark 1 wet mixer
2 Preforming e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com