Method for depositing film through high ionization rate high power pulse magnetron sputtering
A high-power pulse and magnetron sputtering technology, which is applied in sputtering plating, ion implantation plating, metal material coating technology, etc., can solve problems such as uneven bonding force, non-dense and poor film, and achieve Uniform binding force, improved ionization rate, high binding force effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] This embodiment is a method for depositing a thin film by high ionization rate and high power pulse magnetron sputtering, which is specifically carried out according to the following steps:
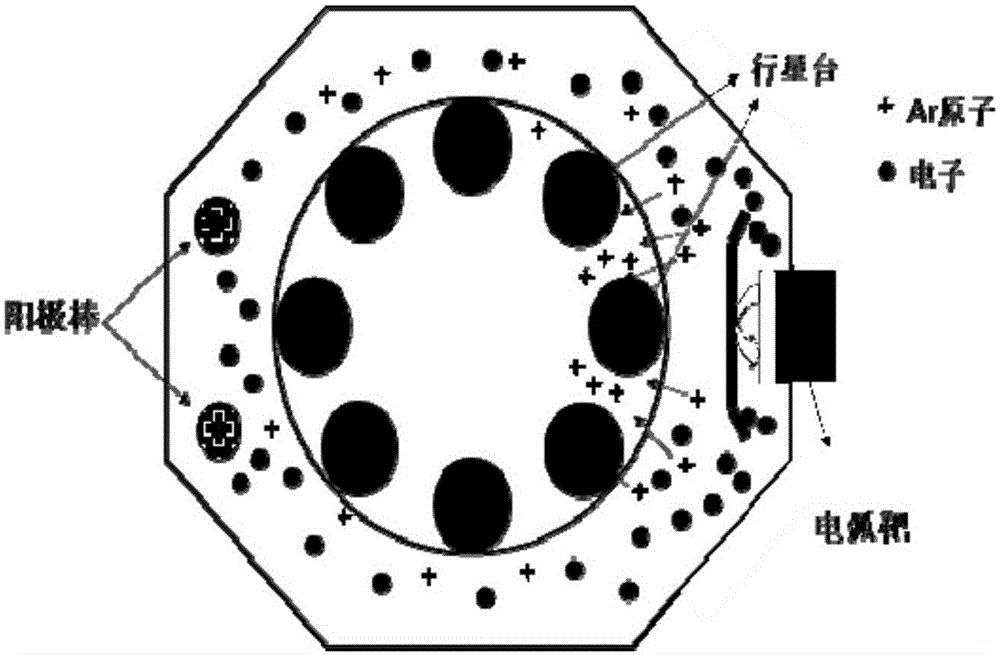
[0041] 1) Ti metal is selected as the target material, and the M2 high-speed steel sample cleaned by acetone alcohol ultrasonic cleaning is dried, fixed on a three-dimensionally rotatable planetary table, and placed in a cleaned vacuum chamber. The target base distance is 10cm;
[0042] 2) Seal the vacuum chamber, and use high-purity Ar gas to pump the chamber to a background vacuum of 4×10 through a mechanical pump and a molecular turbo pump. -5 mbar, and then set the infrared electric heating tube to heat at 600°C to remove moisture on the surface of the sample and adsorb air impurities;
[0043] 3) The vacuum is stable at 4×10 -5 After mbar, the infrared electric heating tube is set to 500°C, the sample is applied with a negative bias voltage of 300V, the pulse frequency is 20...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the commercially available ground YT14 is selected as the test material, the roughness is 144nm, and the Vickers hardness is 1725HV 0.2 , others are identical with embodiment 1.
[0057] Brief results of this example:
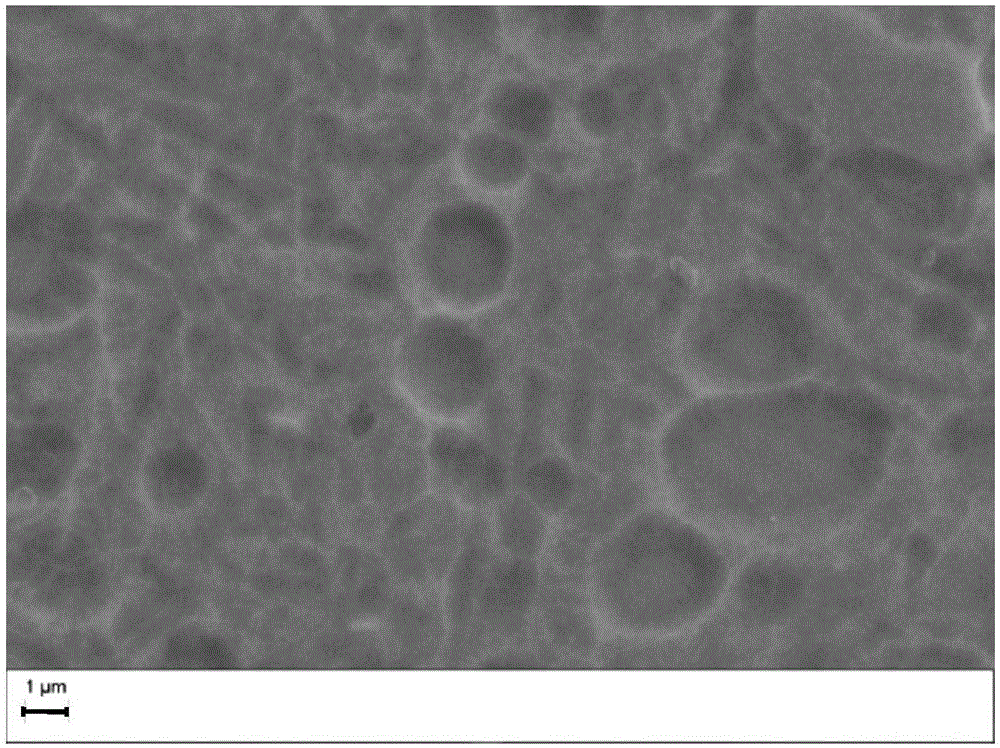
[0058] The surface morphology of the ground YT14 cemented carbide after coating by the above-mentioned high-ionization rate high-power pulse magnetron sputtering method is shown in Fig. Figure 7 , its surface hardness is 1725HV 0.2 , the thickness is about 300nm~500nm, and the film-base bonding interface is dense, see Figure 8 .
[0059] The ground YT14 cemented carbide has an original roughness of 144nm. During the coating process, due to the bombardment of Ar+ and the deposition of the film layer, the roughness becomes 240nm. The rating results of the indentation method are shown in Figure 9 .
Embodiment 3
[0061] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that the commercially available polished nano-hard alloy is selected as the test material, and its composition mass fraction is C0.84%, W84.64%, Cr1.34%, Co13.18%, Roughness is 240nm, Vickers hardness is 1787HV 0.2 , probably because the indenter is pressed too deeply, showing a composite Vickers hardness. Others are the same as in Example 1.
[0062] Brief results of this implementation:
[0063] The surface morphology of the polished nano-hard alloy after coating by the above-mentioned high-ionization rate high-power pulse magnetron sputtering method is shown in Fig. Figure 10 , its surface hardness is 1787HV 0.2 Increase to 2056HV 0.2 , the thickness is about 700nm~1000nm,.
[0064] The polished nano-hard alloy has an original roughness of 240nm. During the coating process, due to the bombardment of Ar+ and the deposition of the film, the roughness becomes 62nm. It can be seen that the film particles are v...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com