Electro-optic mode converter with Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure and implementing method thereof
A technology of a mode converter and an implementation method, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problems of slow conversion speed, complex structure, insufficient stability, etc., and achieve the effect of wide operating wavelength range and fast conversion speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
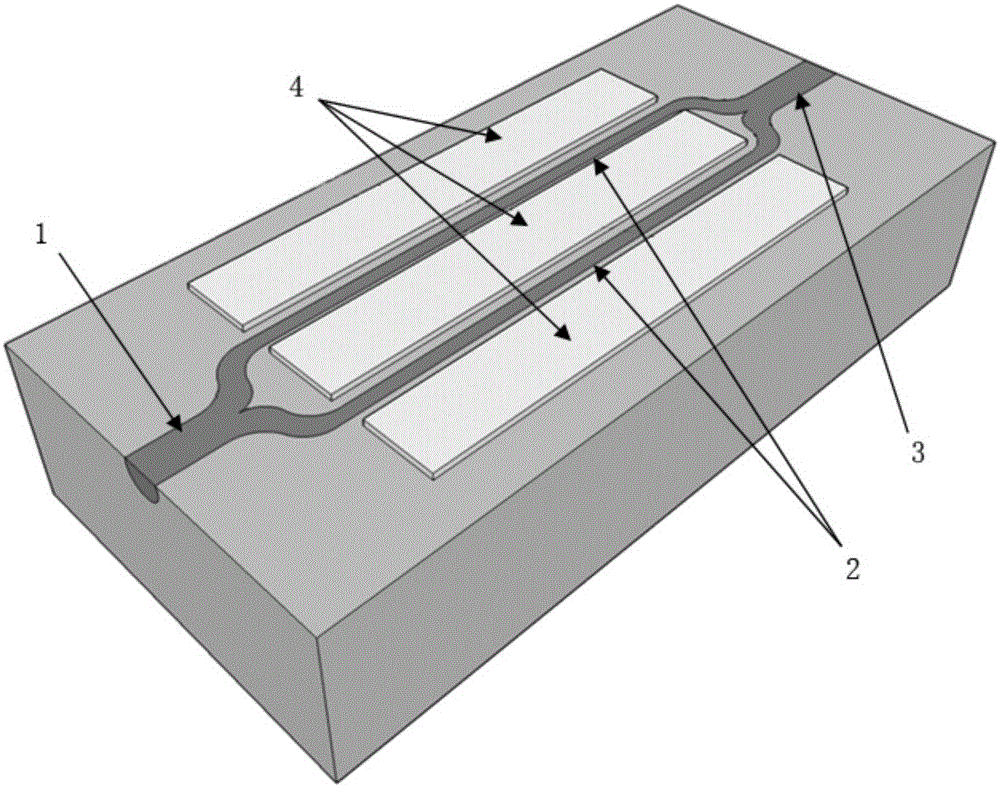
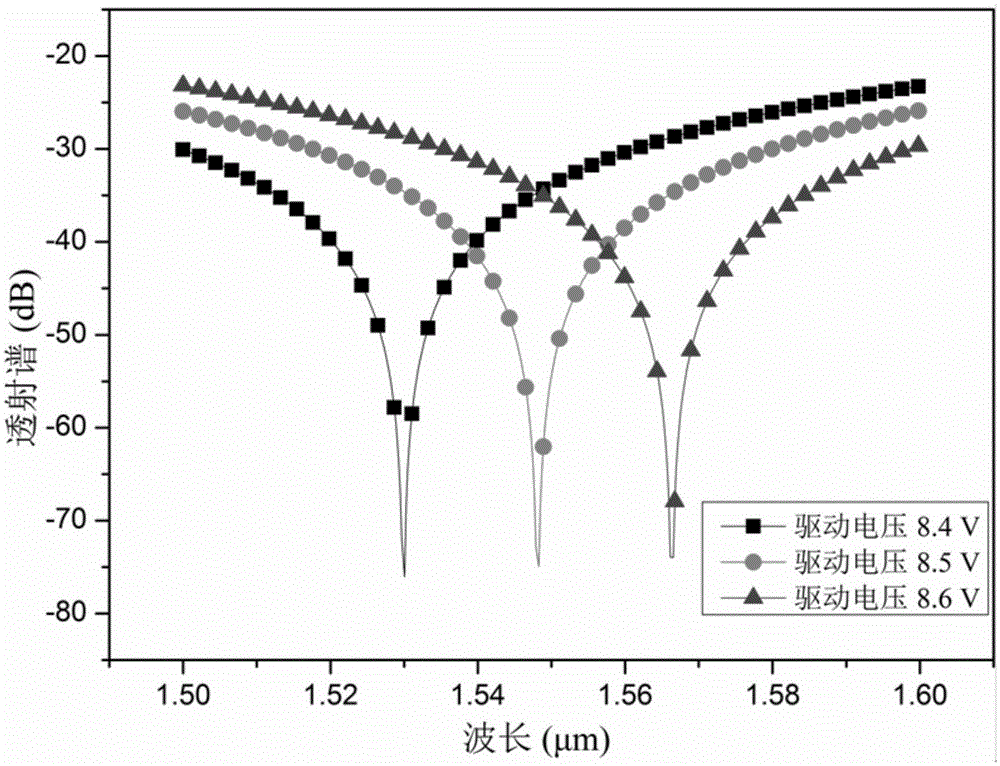
[0027] figure 1 The basic structure diagram of a new electro-optical mode converter based on the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure realized by X-cut lithium niobate material. It mainly includes an input waveguide 1, two interference arms 2, an output waveguide 3 and an electro-optical phase modulation electrode 4.
[0028] Both input waveguide 1 and output waveguide 3 are dual-mode waveguides; input waveguide 1 and output waveguide 3 support two modes, and the LP in the fiber 01 The light wave of the mode is mainly excited in the input waveguide 1 to produce the fundamental mode, LP 11The light wave of the mode is mainly excited in the input waveguide 1 to generate the first-order mode. The two interference arms 2 are single-mode waveguides; the two interference arms 2 are symmetrical structures, one end of the input waveguide 1 and the two interference arms 2 is connected through the first Y branch waveguide, and the other end of the output waveguide 3 and the two inter...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Figure 4 The basic structure diagram of a new electro-optical mode converter based on the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure realized by Z-cut lithium niobate material. It mainly includes an input waveguide 1, two interference arms 2, an output waveguide 3 and an electro-optical phase modulation electrode 4.
[0035] Both input waveguide 1 and output waveguide 3 are dual-mode waveguides; input waveguide 1 and output waveguide 3 support two modes, and the LP in the fiber 01 The light wave of the mode is mainly excited in the input waveguide 1 to produce the fundamental mode, LP 11 The light wave of the mode is mainly excited in the input waveguide 1 to generate the first-order mode. The two interference arms 2 are single-mode waveguides; the two interference arms 2 are symmetrical structures, one end of the input waveguide 1 and the two interference arms 2 is connected through the first Y branch waveguide, and the other end of the output waveguide 3 and the two int...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Figure 5 The basic structure diagram of the new electro-optic mode converter based on the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure realized by the electro-optic polymer material. The core layer of the electro-optic polymer is amorphouspolycarbonateEOmaterial, and the cladding is su8; the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure mainly includes an input waveguide 1, two interference arms 2, an output waveguide 3 and an electro-optic phase modulation electrode 4.
[0040] Both input waveguide 1 and output waveguide 3 are dual-mode waveguides; input waveguide 1 and output waveguide 3 support two modes, and the LP in the fiber 01 The light wave of the mode is mainly excited in the input waveguide 1 to produce the fundamental mode, LP 11 The light wave of the mode is mainly excited in the input waveguide 1 to generate the first-order mode. The two interference arms 2 are single-mode waveguides; the two interference arms 2 are symmetrical structures, one end of the input wavegui...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com