A preparation method of cartilage inductive matrix for microfracture surgery
A technique of microfracture and surgery, applied in medical science, prostheses, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve problems such as irreparable damage, easy loss of bone marrow cells, and impact on the quality of life of patients, achieving long-term maintenance of joint function and simple and convenient operation , the effect of reducing cell density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
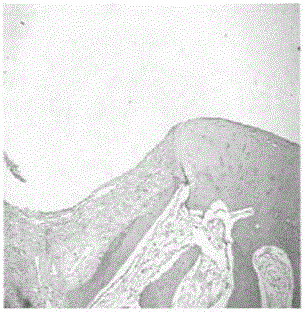
[0022] This embodiment provides a cartilage-inducing matrix for microfracture surgery, which can fix bone marrow cells in microfracture surgery, cover the defect area, and induce bone marrow cells to develop in the direction of hyaline cartilage, so as to meet the clinical application of many patients. Its joint function is maintained for a long time.
[0023] A cartilage-inducing matrix for microfracture surgery, including gel and additives, the gel is fibrin 100mg / ml; collagen 25mg / ml; hyaluronic acid 5%; thrombin 50U / ml; Cover the cartilage defect and solidify within 5 minutes to provide a fixed scaffold for bone marrow cells; the ingredients of the additives in the medium are based on the final concentration, including: vitamin C: 233μM-287μM; linoleic acid: 3.7μM-8.9μM; cholesterol : 9μM~17μM; Dexamethasone: 6nM~15nM; Acetylcysteine: 43μM~58μM; Transferrin: 18μg / mL~32μg / mL; Sodium Selenite: 22nM~52nM; Sodium Pantothenate: 13μM~24μM ; Biotin: 28μM~43μM; Insulin-like growt...
Embodiment 2
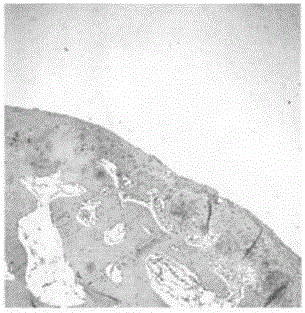
[0027] This embodiment provides a cartilage-inducing matrix for microfracture surgery, which can fix bone marrow cells in microfracture surgery, cover the defect area, and induce bone marrow cells to develop in the direction of hyaline cartilage, so as to meet the clinical application of many patients. Its joint function is maintained for a long time.
[0028]A cartilage-inducing matrix for microfracture surgery, including gel and additives, the gel is fibrin 100mg / ml; collagen 25mg / ml; hyaluronic acid 5%; thrombin 50U / ml; Cover the cartilage defect and solidify within 5 minutes to provide a fixed scaffold for bone marrow cells; the ingredients of the additives in the medium are based on the final concentration, including: vitamin C: 250 μM; linoleic acid: 4.5 μM; cholesterol: 13 μM; Methasone: 10nM; Acetylcysteine: 50μM; Transferrin: 25μg / mL; Sodium Selenite: 30nM; Sodium Pantothenate: 17μM; Biotin: 33μM; Insulin-like Growth Factor: 10μg / mL; Epidermal Growth Factor: 5ng / mL; ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] A method for preparing a cartilage-inducing matrix for microfracture surgery, comprising the steps of:
[0033] Step 1: Add vitamin C, linoleic acid, cholesterol, dexamethasone, acetylcysteine, transferrin, sodium selenite, sodium pantothenate, biotin, insulin-like growth factor, epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth Factor, platelet-derived growth factor, transforming growth factor, insulin transferrin were added to the basal medium so that the final concentration of the additive in the basal medium was:
[0034] Vitamin C: 233μM~287μM; Linoleic acid: 3.7μM~8.9μM; Cholesterol: 9μM~17μM; Dexamethasone: 6nM~15nM; Acetylcysteine: 43μM~58μM; Transferrin: 18μg / mL~32μg Sodium selenite: 22nM~52nM; Sodium pantothenate: 13μM~24μM; Biotin: 28μM~43μM; Insulin-like growth factor: 7μg / mL~18μg / mL; Epidermal growth factor: 2ng / mL~9ng / mL ; Fibroblast growth factor: 2ng / mL~9ng / mL; Platelet-derived growth factor: 2ng / mL~9ng / mL; Transforming growth factor: 30ng / ml~70ng / ml;
[0035...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com