Meloidogyne javanica effect gene Mj-1-1, related protein and application of effect gene Mj-1-1
A Java root-knot nematode and effector gene technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve problems such as lack of nematode-resistant germplasm resources, chemical control of environmental pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Cloning of embodiment 1 root-knot nematode javanica MJ-1-1 protein and its coding gene
[0083] 1. Use the TRIZOL method to extract the RNA of the second instar larvae of Meloidogyne javanica, and reverse transcribe it into cDNA.
[0084] 2. Design the downstream primer DC6R2 (sequence shown in SEQIDNO.5), pair with the trans-splicing sequence SL1 (sequence shown in SEQIDNO.6), amplify with the cDNA obtained in step 1 as a template, and obtain Mj-1 -1 cDNA coding sequence.
[0085] PCR amplification system: cDNA 2 μL, two primers 3 μL each, 10×KODplusBuffer 5 μL, MgSO 4 2 μL, dNTP 5 μL, Kodplus NeoDNApolymerase 1 μL, ddH 2 O34 μL. PCR amplification program: 94°C for 3min, 30× (94°C for 30s, 55°C for 30s, 68°C for 2min), 68°C for 5min, and store at 20°C. Agarose electrophoresis detection amplification results are attached figure 1 shown.
[0086] 3. Using DNA as a template, use primers to amplify Mj1DNAF (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.7) and Mj1DNAR (sequence shown i...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2 Expression Analysis of Mj-1-1 Gene in Different Developmental Stages of Meloidogyne javanica
[0089] 1. Extract the RNA of M. javanica at different developmental stages and reverse transcribe it into cDNA.
[0090] 2. Using primers qMj1F (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.9) and qMj1R (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.10) to perform fluorescence quantitative PCR analysis on gene Mj-1-1. The root-knot nematode β-actin gene was used as an internal reference, and the primers were qActinF (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.11) and qActinR (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.12). Reaction conditions: 94°C for 30s, 40× (94°C for 30s, 55°C for 30s, 72°C for 30s).
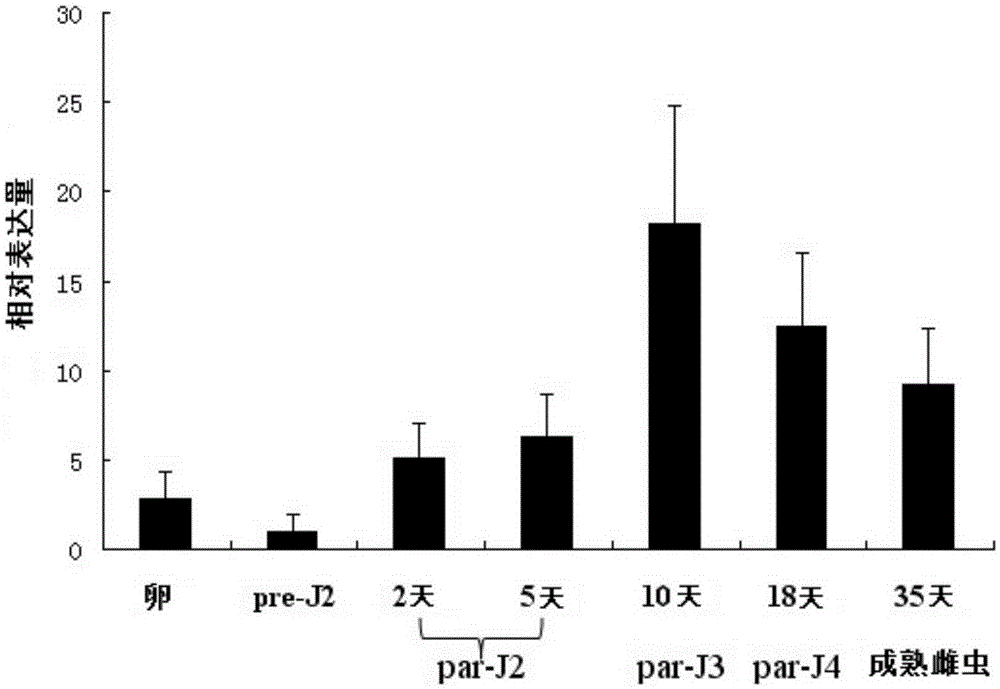
[0091] 3. The results are attached image 3 shown. The results showed that the Mj-1-1 gene was expressed in all developmental stages of M. javanica, the expression level was the lowest in the second instar larvae before infection, and the expression level increased significantly after infection, and the expression level in th...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Example 3 Exogenous dsRNA soaking method to silence the Mj-1-1 gene and analyze its function
[0093] 1. The exogenous dsRNA was obtained according to the method of Li et al. (2011).
[0094] (1) Synthesis of the sense and antisense strands of the Mj-1-1 gene: use primer pairs Mj1ST7 (sequence such as SEQ ID NO.15) and Mj1A (sequence such as SEQ ID NO.16), and Mj1S (sequence such as SEQ ID NO.17) and Mj1AT7 (sequence such as SEQ ID NO.18); PCR amplification annealing temperature 55° C., extension time 1 min.
[0095] (2) Synthetic positive control GFP gene sense and antisense strand: use primer pair GFPST7 (sequence such as SEQIDNO.19) and GFPA (sequence such as SEQIDNO.20), and GFPS (sequence such as SEQIDNO.21) and GFPAT7 (sequence such as SEQIDNO. 22); the PCR annealing temperature is 55° C., and the extension time is 1 min.
[0096] (3) Synthesis of dsMj-1-1 and dsGFP was performed referring to the instructions of ScriptMAXThermoT7TranscriptionKit.
[0097] 2. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com