A l-aspartase recombinant Escherichia coli without malic acid by-product and its construction method and application
A technology for recombining Escherichia coli and aspartase, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of separation and purification of downstream products, reducing the conversion rate of target products, etc., so as to reduce the production of by-products, reduce production costs, and improve The effect of conversion yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This example illustrates the process of knocking out the fumarase fumB gene in the parental ammonium-resistant Escherichia coli BEW308 by using homologous recombination technology to obtain an apramycin-resistant strain.
[0033] (1) Using LB medium, cultivate Escherichia coli BEW308 to OD at 37°C under aerobic conditions 600 =0.4~0.6, prepared as electrotransfer competent;
[0034] (2) Electrotransform the recombinant plasmid into competent Escherichia coli BEW308. The electric shock conditions are: 200Ω, 25μF, electric shock voltage 2.3kv, electric shock time 4-5ms. Immediately after the electric shock, the bacteria were added to pre-cooled 1mL SOC medium, cultured at 150r / min, 30°C for 1h, and then spread on the LB medium plate with ampicillin (amp) to screen out the positive transformant BEW308 (pKD46);
[0035] (3) Adding 10 mM L-arabinose to LB medium, inducing plasmid pKD46 to express λ recombinase at 30°C to make electroporation competent;
[0036] (4) Using ...
Embodiment 2
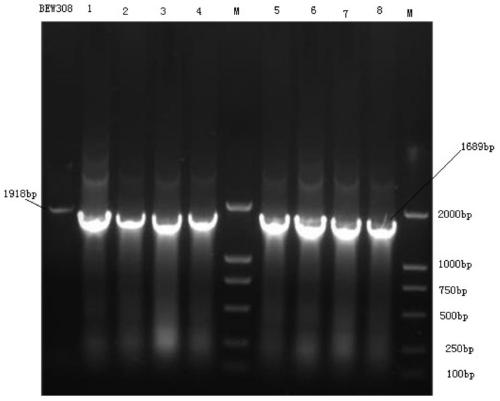
[0047] This example illustrates the use of homologous recombination technology to further knock out the fumarase fumAC gene in Escherichia coli BEW308 (ΔfumB), and introduce a mutant highly active aspartase gene.
[0048] The whole experimental operation process is consistent with Example 1, only the homologous sequence is different.
[0049] (1) In this example, the L-aspartase gene (aspC) of Escherichia coli K12 is used as the starting sequence, and the 236 and 249 amino acids are mutated, that is, Lys236Asn, Gly249Thr, and at the same time, the upstream of the initiation codon ATP is increased A signal peptide sequence atgttgaatccgaaggttgcctacatggtctggatgacgtgcctgggtttaacgttgcccagccaggca (shown in SEQ ID NO: 2), and finally adding fumAC homology arms and apramycin resistance gene sequences at both ends, the entire gene is artificially synthesized, the specific nucleotide sequence See shown in SEQ ID NO:5.
[0050] (2) The artificially synthesized linear DNA fragment was el...
Embodiment 3
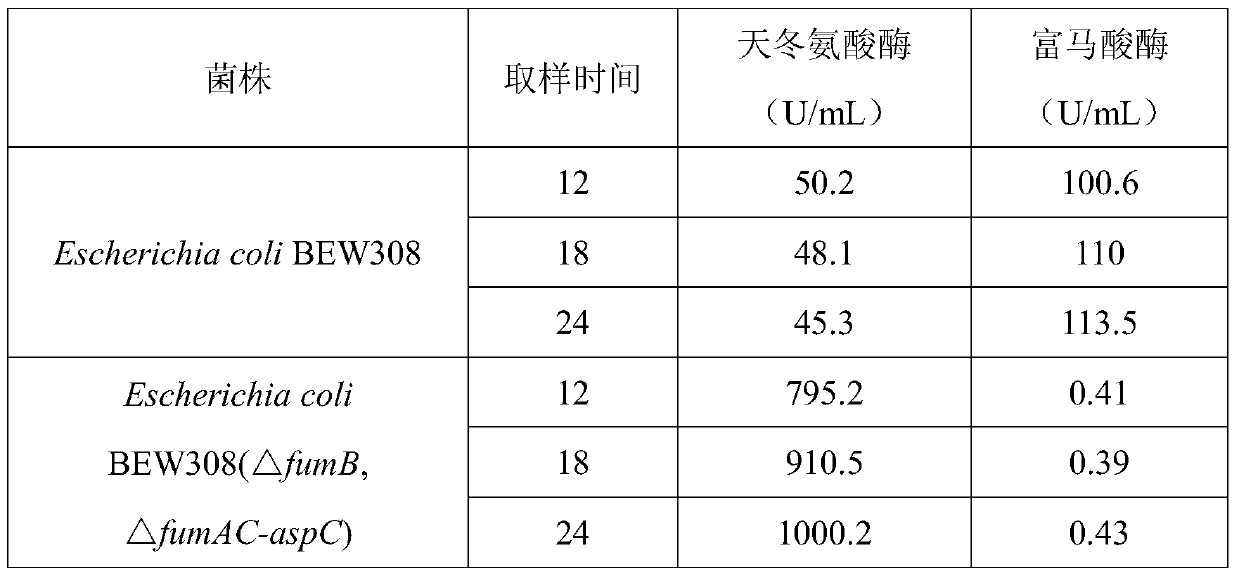
[0052] This example compares and investigates the change of fumarase and aspartase activities of the starting strain Escherichia coli BEW308 and the recombinant strain Escherichiacoli BEW308 (△fumB, △fumAC-aspC) in the FM fermentation medium and their use in natural Comparative data at aspartic acid conversion.
[0053] Specific steps are as follows:
[0054] (1) Use LB medium, transfer the inoculum amount from the cryopreservation tube to the Erlenmeyer flask according to 1-2% (v / v) inoculum amount, culture aerobically for 10-12 hours, and further increase the inoculum amount according to 1-2% (v / v) Inoculate into shake flasks or seed fermenters (the culture medium is also LB). The temperature of the seed cultivation process is controlled at 35-37°C. There is no need to adjust the pH during the cultivation, and the dissolved oxygen is controlled at 5-40%. After 4-6 hours of cultivation, the bacteria Body OD 600 Between 2.5 and 4, the fermentation medium FM is inoculated at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com