Method for producing gradient nanometer structure on martensitic steel surface
A martensitic steel and nanostructure technology, which is applied in the field of producing gradient nanostructures on the surface of martensitic steel, can solve the problems of peeling, complicated treatment process, scratched surface, etc., and achieves the effect of low cost and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
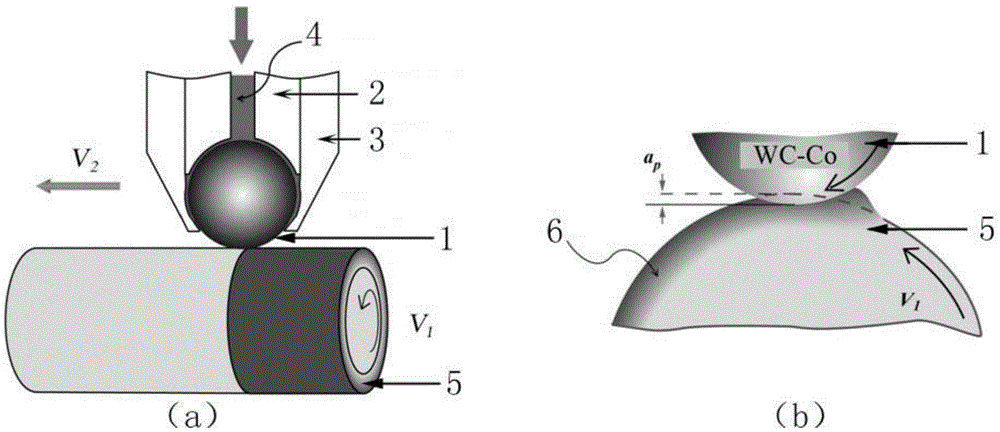
[0047] M3200 martensitic stainless steel cylindrical test bar with a diameter of 80mm, its chemical composition is (wt.%): C0.07%, Si1%, Mn0.75%, S0.025%, P0.03%, Cr16%, Ni5.5%, Mo0.95%, Co0.2%, Fe balance; the initial supply state is quenched + tempered state. The SMGT surface nanometerization method of the present invention is used for processing, and the diameter of the WC-Co cemented carbide ball of the SMGT processing tool is 8mm, and an oily coolant is used for lubrication and cooling during the processing. The main technical parameters are as follows:
[0048] The linear velocity v of the outer circle of the martensitic stainless steel test rod 1 =1.1×10 4 mm / min;
[0049] Feed speed v of SMGT machining tool 2 =6×10 -2 mm / r;
[0050] Processing pass n=6 times;
[0051] The indentation depth of cemented carbide balls on the surface of martensitic stainless steel for each processing pass is: a p(1) = 20 μm, a p(2) = 40 μm, a p(3) = 60 μm, a p(4) = 80 μm, a p(5...
Embodiment 2
[0054] 1Cr13 martensitic stainless steel shaft with a diameter of 100mm, its chemical composition is (wt.%): C0.10~0.15%, Si1%, Mn1%, S0.025%, P0.03%, Cr11.5~13.5% , Ni0.6%, Cu0.3%, Fe balance; the initial supply state is quenched + tempered state. The SMGT surface nanometerization method of the present invention is used for processing, and the diameter of the WC-Co cemented carbide ball (or GCr15 ball) of the SMGT processing tool is 8mm, and an oily coolant is used for lubrication and cooling during the processing. The main technical parameters are as follows:
[0055] The linear velocity v of the outer circle of the martensitic stainless steel shaft 1 =1.4×10 4 mm / min;
[0056] Feed speed v of SMGT machining tool 2 =3×10 -2 mm / r;
[0057] Processing pass n=1 time;
[0058] Indentation depth a of cemented carbide balls on the surface of martensitic stainless steel p = 50 μm.
[0059] The test results show that after SMGT surface nano-processing, the surface of 1Cr13 ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] 40CrNiMo7 martensitic steel shaft with a diameter of 120mm, its chemical composition is (wt.%): C0.37%, Si0.17%, Mn0.8%, S0.025%, P0.025%, Cr0.9% , Ni1.9%, Cu0.025%, Mo0.25%, Fe balance; initial supply state is quenched + tempered state. The SMGT surface nanometerization method of the present invention is used for processing, and the diameter of the WC-Co cemented carbide ball (or GCr15 ball) of the SMGT processing tool is 8mm, and an oily coolant is used for lubrication and cooling during the processing. The main technical parameters are as follows:
[0062] The linear velocity v of the outer circle of the martensitic steel shaft 1 =1.1×10 4 mm / min;
[0063] Feed speed v of SMGT machining tool 2 =3×10 -2 mm / r;
[0064] Processing pass n=2 times;
[0065] The indentation depth of cemented carbide balls on the surface of martensitic steel for each processing pass is: a p(1) = 25 μm, a p(2) = 50 μm.
[0066] The test results show that the surface roughness Ra va...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com