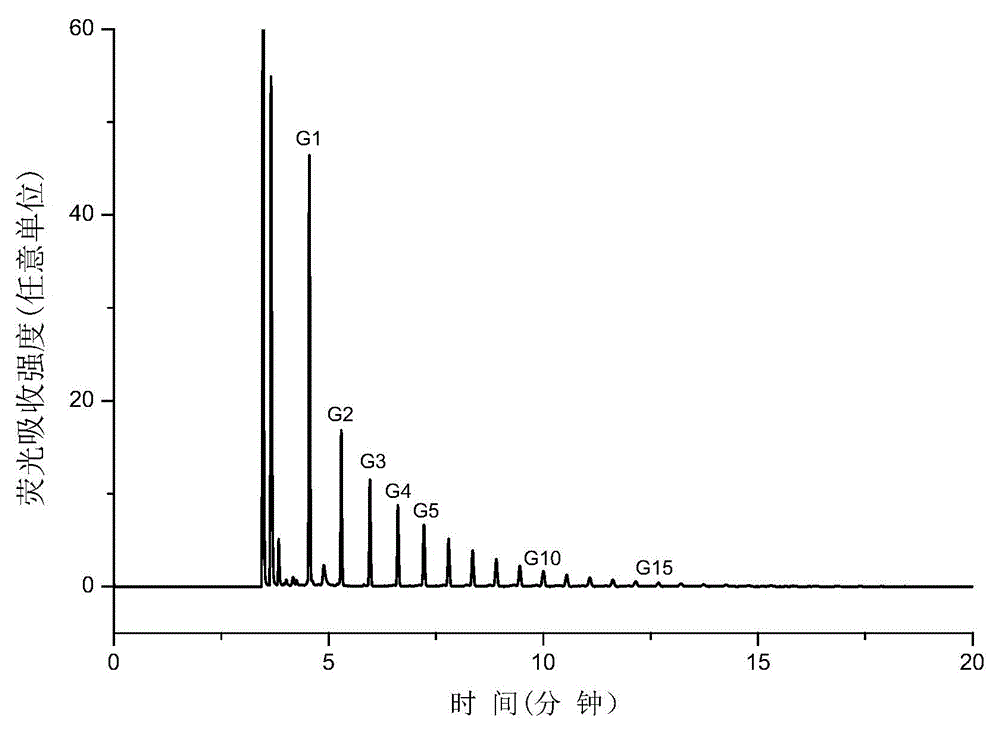
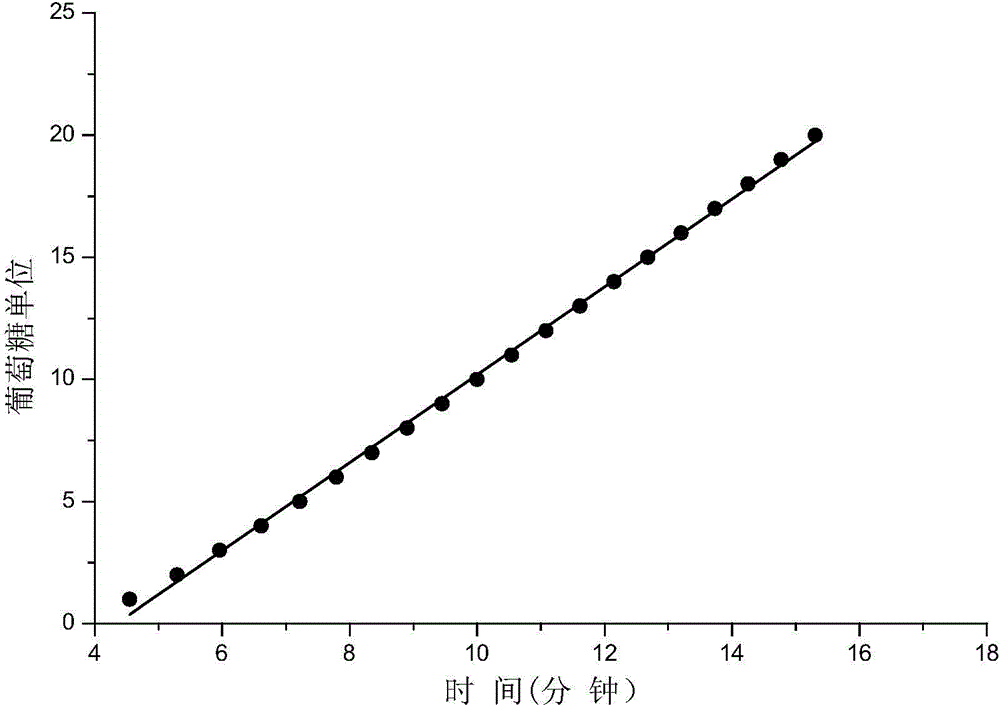
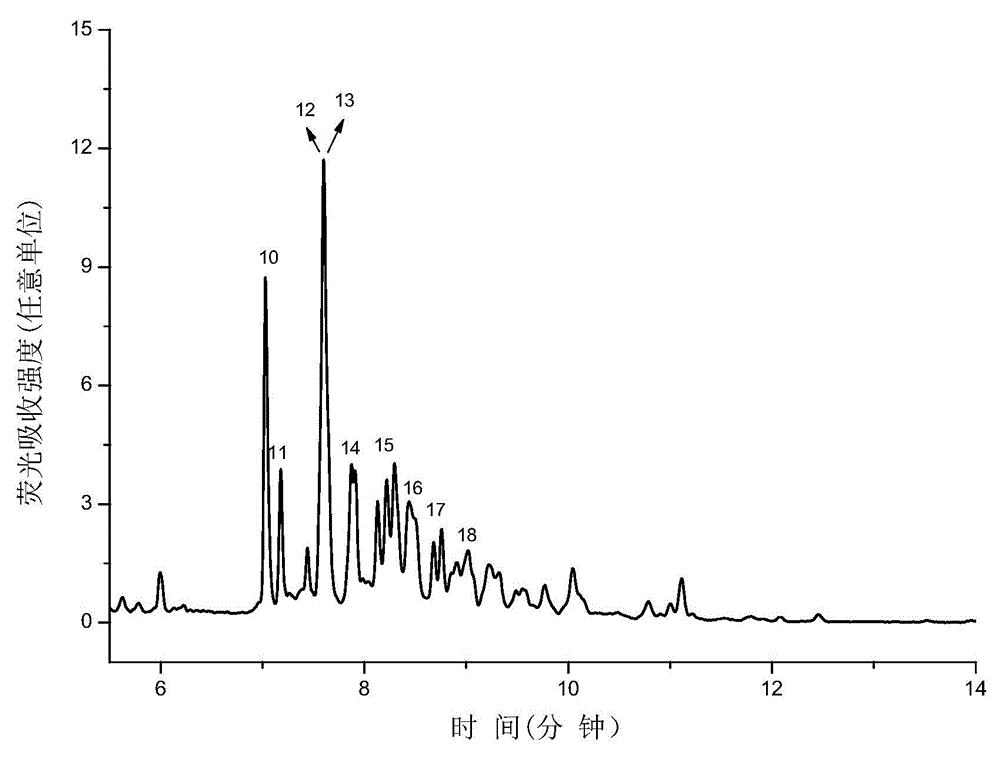
Method for identifying N-linked oligosaccharide structure of novel erythropoiesis stimulating protein
An erythrocyte and oligosaccharide technology, which is applied in the field of identifying N-linked oligosaccharide structures of new erythropoiesis-stimulating proteins, and can solve the problems of difficulty in identifying structures, complex N-linked oligosaccharide structures, and high sialylation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 7
[0050] Embodiment 7 is carried out on Agilent (Agilent) 1260 high performance liquid chromatography instrument.
Embodiment 9
[0051] Example 9 is in Beckman Coulter (Beckman_Coulter) P / ACE TM MDQ was performed on a high-efficiency capillary instrument.
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1 Pretreatment of new erythropoiesis-stimulating protein samples
[0053] Ultrafiltration to remove salt and surfactant: prepare a 1.5mL ultrafiltration tube washed with water in advance, load 100μL of a new erythropoiesis-stimulating protein aqueous solution with a sample protein content of 100μg, and centrifuge at a centrifugal force of 14,000g for 15min to reduce the sample volume to 1 / 10. Add water to dilute to the original volume and centrifuge again at 14000g for 15min. Then dilute and centrifuge again, the conditions are the same as the previous two times. Afterwards, the ultrafiltration tube was inverted, and the protein was recovered by centrifugation at a centrifugal force of 2000 g for 5 minutes. The recovery rate was 95%. The volume of the recovered protein sample containing water was 10 μL, which was lyophilized for use.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com