Laser connection method based on laser material additive manufacturing technology
A technology of laser additive manufacturing technology, applied in the field of material processing, which can solve the problems of metallurgical incompatibility, singular stress behavior, structural integrity and reliability effects, etc., to achieve improved tunability, high heating and cooling speed, the effect of improving connection quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
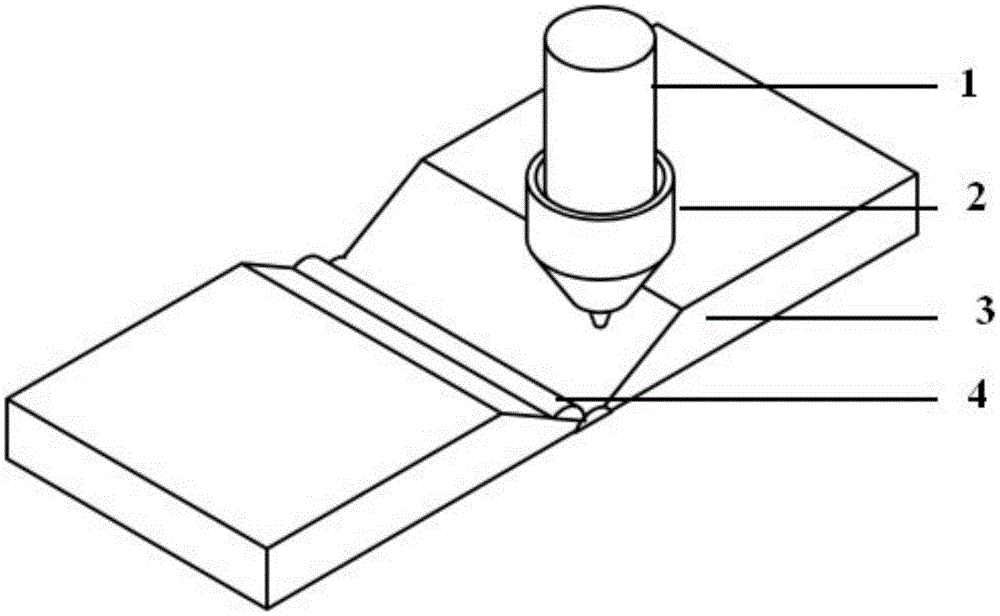
[0027] Specific Embodiment One: A laser connection method based on laser additive manufacturing technology in this embodiment is carried out in accordance with the following steps:
[0028] 1. Before welding, process the groove of the workpiece to be welded, and at the same time, grind and clean the processed groove and the surface of the workpiece, and fix the polished and cleaned workpiece to be welded on the welding fixture;
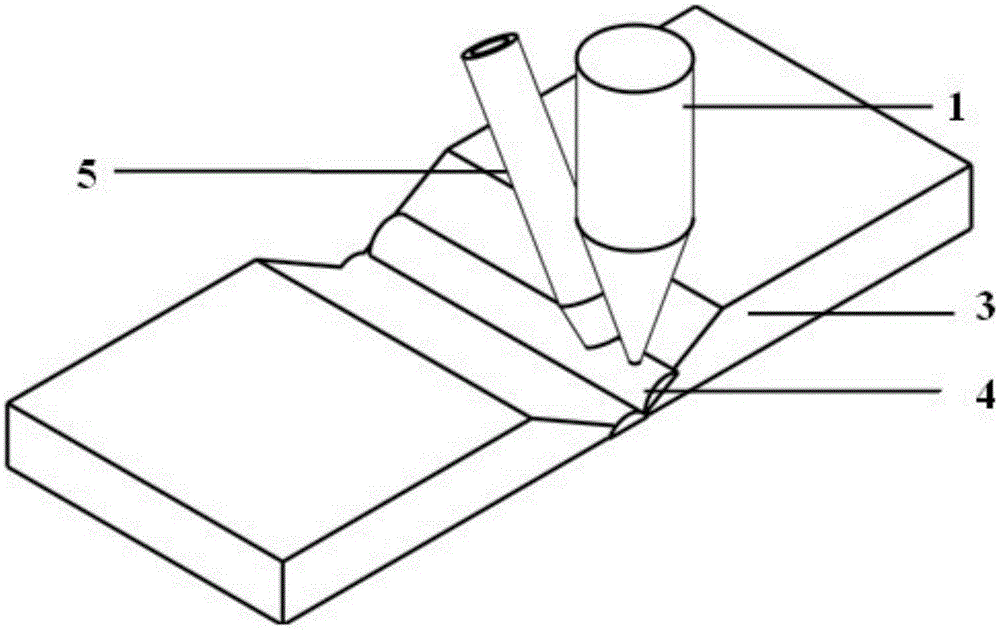
[0029] 2. During the connection process based on laser additive manufacturing using side-axis powder feeding, the laser head and side-axis powder feeding working head are fixed on the joint area to be connected by using a fixture, and the angle between the powder feeding head and the vertical direction is adjusted to 10°~80°;
[0030] If the material to be connected is non-reflective to the laser, keep the laser head vertical to the workpiece to be welded, adjust the angle between the side axis powder feeding head and the laser head to 10°-80°, and ke...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0034]Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the laser emitting laser is a fiber laser, a YAG solid-state laser, a semiconductor laser or a CO 2 laser. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0035] Embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that the cleaning described in step 1 is carried out with acetone, or other cleaning methods for removing oil stains and oxide film impurities on the material surface. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0036] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: if the material to be connected is a material that does not reflect the laser, then keep the laser head and the workpiece to be welded vertically, and adjust the side axis powder feeding working head and the laser head The included angle is 20°~70°, and the distance between the powder feeding nozzle and the laser focal plane is 3~19mm. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com