Fiber laser integrated collimation optical device
A technology of collimating optics and fiber lasers, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of fiber laser interference, increase laser transmission loss, and many optical interfaces, achieve strong environmental adaptability, and highlight substantive features , the effect of less scattered stray light
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
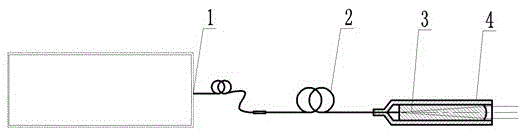
[0027] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the optical path structure of the fiber laser integrated collimating optical device of the present invention. In the figure, the collimator pigtail fiber 2 is welded together with the plane end of the plano-convex optical lens 3, and after the two are welded, they are assembled into the collimator protective sleeve 4 made of metal material, and the collimator protective sleeve 4 is bonded by viscose. fixed. The function of the collimator protective cover 4 is to protect the welding point between the pigtail 2 of the collimator and the plano-convex optical lens 3 from being damaged by external force. In use, the collimator pigtail fiber 2 is fused with the output end of the fiber laser 1 .
[0028] figure 1 Among them, fiber laser 1 uses a fiber with numerical aperture NA=0.06, a core diameter of 20 μm, a material of fused silica, a cladding diameter of 400 μm, an output laser wavelength of 1064 nm, and a beam quality of M 2 ≈1.5...
Embodiment 2
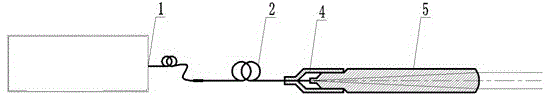
[0030] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the optical path structure of another fiber laser integrated collimating optical device in this embodiment. The basic structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is: in Embodiment 1, the collimating device is a plano-convex optical thick lens; in this embodiment, the collimating device is still a plano-convex lens, but the appearance shape has Big change. The outer diameter of the special-shaped plano-convex optical lens 5 is divided into three parts, the diameter of the part close to the convex surface is 7.5 mm, and the diameter of the middle part is 5 mm. It is 1.5mm, and its diameter is selected to facilitate the automatic centering of the optical fiber fusion splicer, so as to ensure that the collimator pigtail optical fiber 2 and the special-shaped plano-convex optical lens 5 are fused together. During the processing of the special-shaped plano-convex optical lens, the three parts with d...
Embodiment 3
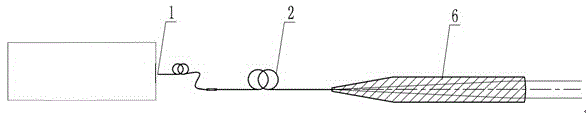
[0033] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the optical path structure of another fiber laser integrated collimating optical device in this embodiment. The basic structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is: in Embodiment 1, the collimating device is a plano-convex optical thick lens; in this embodiment, the collimating device is still a plano-convex lens, but the appearance shape has Big change. The outer diameter of the conical collimating lens 6 is 7.5mm, the diameter of the plane connecting the tapered tail end and the pigtail fiber 2 is 1mm, and the full angle of the conical shape is 20°. The shape selection of the conical collimating lens and the fiber connection part is mainly for convenience. The automatic centering of the optical fiber fusion splicer, and the yield rate of the fusion splicing of pigtail optical fiber 2 and conical collimating lens 6. During the processing of the conical collimating lens, the incident plane and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com