Separation and application of pseudomonas with significant antagonism to plant pathogenic bacteria
A technology for Pseudomonas and pathogenic bacteria, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of polluted environment, pesticide residues, long degradation cycle and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
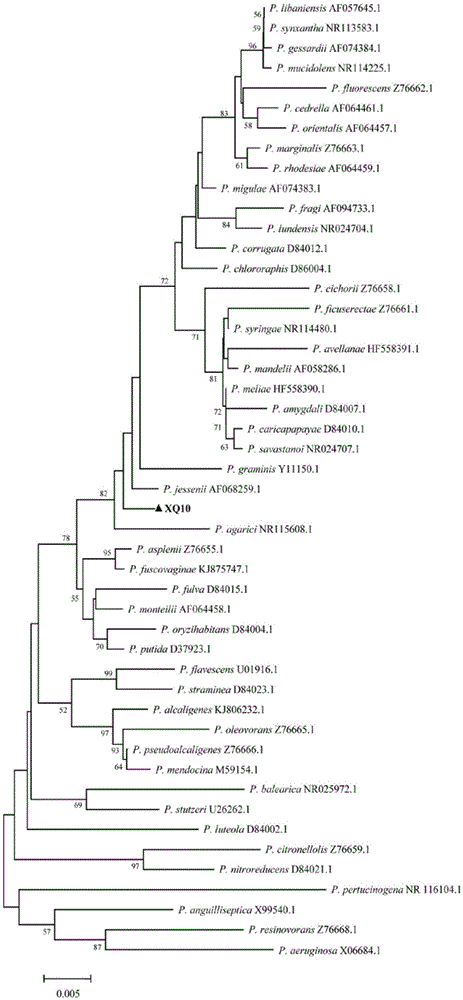
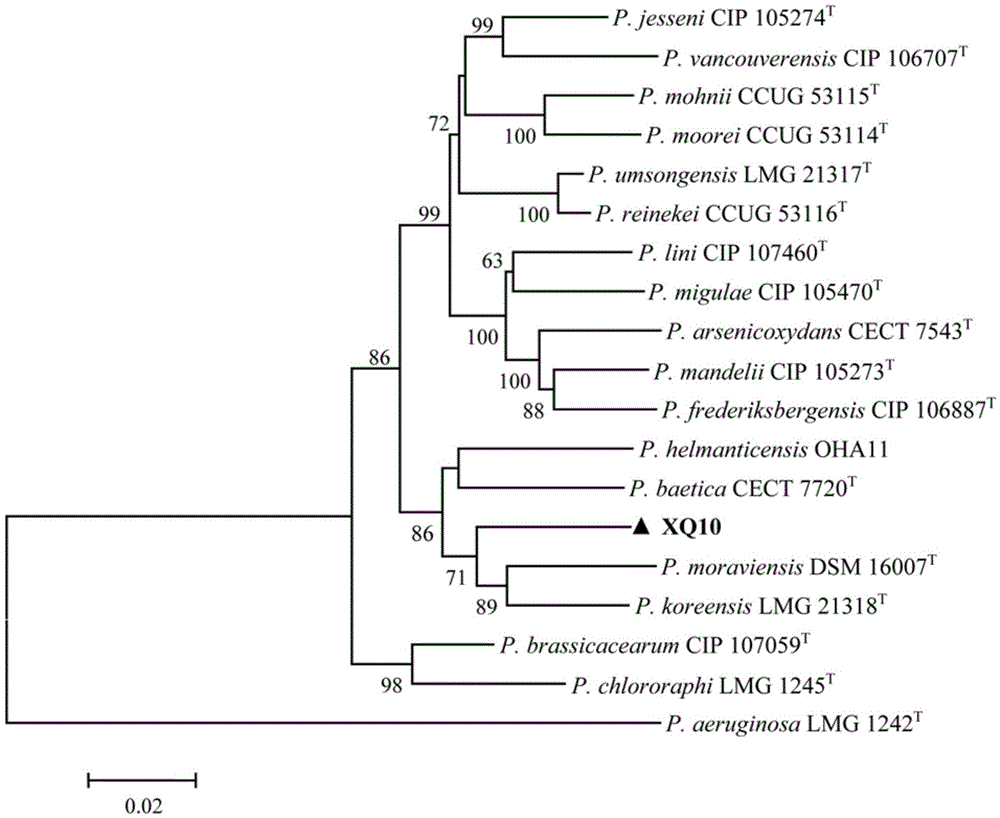
[0017] Example 1: Isolation and preliminary screening of antagonistic bacteria
[0018] The method of Fang Zhongda (1979) was used to isolate the growth-promoting bacteria in the rhizosphere. Take 10 g of the collected tobacco rhizosphere soil, add it into a conical flask filled with 90 mL of sterile water, place the conical flask on a shaker, and vibrate at 180 rpm for 20 min to prepare a soil suspension. Let the prepared soil suspension stand for 5 minutes, take the supernatant, and use the 10-fold serial dilution method to successively dilute to 10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 and 10 -5 , pipette 100 μL of each concentration on the NBY plate, spread evenly, and repeat each concentration three times. Then the coated NBY plates were incubated in a constant temperature incubator at 28°C for 24h. When bacterial colonies appeared on the NBY plate, the bacterial suspension of Ralstonia solanacearum (2.0×10 8 wxya -1 ) evenly sprayed on the NBY plates that have grown colonies, and cult...
Embodiment 2
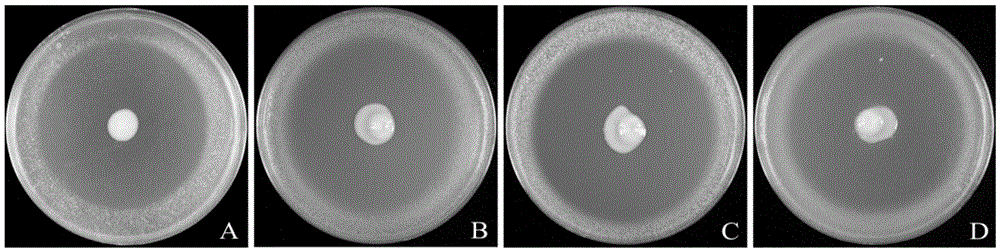
[0020] Embodiment 2: Determination of antagonistic bacteria inhibition spectrum
[0021] Pick a single colony of antagonistic bacteria XQ10 and culture it in 5ml NBY liquid medium at 28°C with shaking at 200rpm for 16-24h. Collect the bacteria by centrifugation, adjust the bacterial concentration to OD with sterile water 420 =0.3 (about 2.0×10 8 wxya -1 ). Pipette 10 μL of the above bacterial suspension to the center of an NBY plate with a diameter of 90 mm. After the surface of the medium is fully absorbed, transfer the plate to a 28°C biochemical incubator for 72 hours. Spray OD 420 =0.3 for the indicator bacteria suspension, count the bacteriostasis after 24 hours. The results of the bacterial antagonism experiment showed that the antagonist XQ10 was effective against the common bacterial pathogens R. The bacteria (P.carotovora) all had significant antagonistic activity, and the size of the inhibition zone against R. solanacearum was 25.67±0.27mm.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Embodiment 3: Physiological and biochemical identification of antagonistic bacteria
[0023] Prepare a culture box, add 5mL sterile water to the box to establish a humid environment, and put the reagent strips into the box. Pick a single colony, resuspend it with sterile saline to prepare a bacterial suspension, and adjust the concentration of the bacterial suspension to OD 420= 0.3. Use a sterile syringe to draw the physiological saline bacterial solution into the test tube from NO3 to PNPG (the cup part does not need to be added). Add mineral oil to the GLU, ADH and URE test tubes until a convex crescent is formed. Open the ampoule of AUX medium, add 200μL (4-8 drops) of the remaining normal saline bacterial solution, mix well and avoid the formation of air bubbles. The test tube from GLU to PAC should be filled with AUX bacterial solution, and the surface of the tube should be flat or slightly convex, but not concave or protruding crescent. Cover and incubate at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com