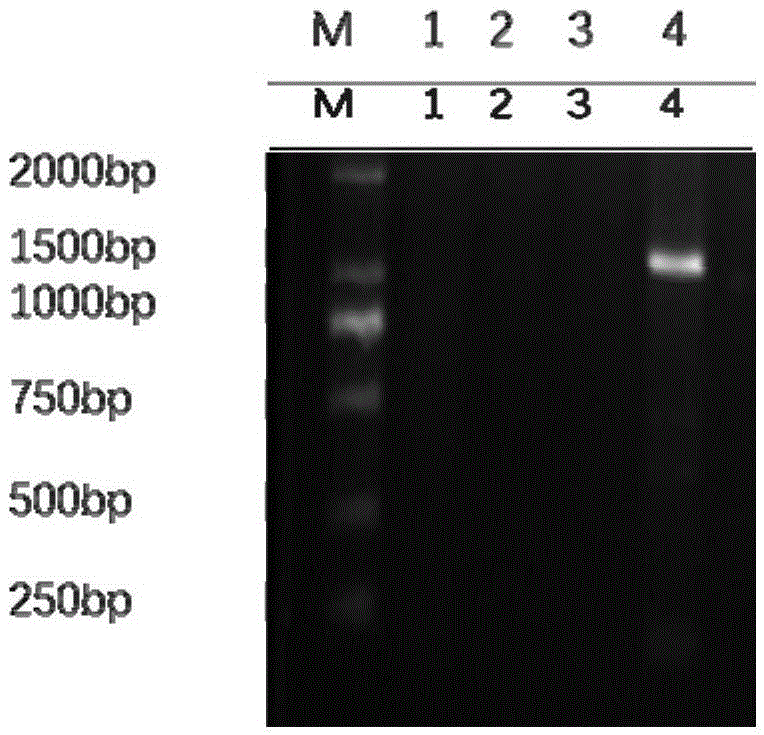
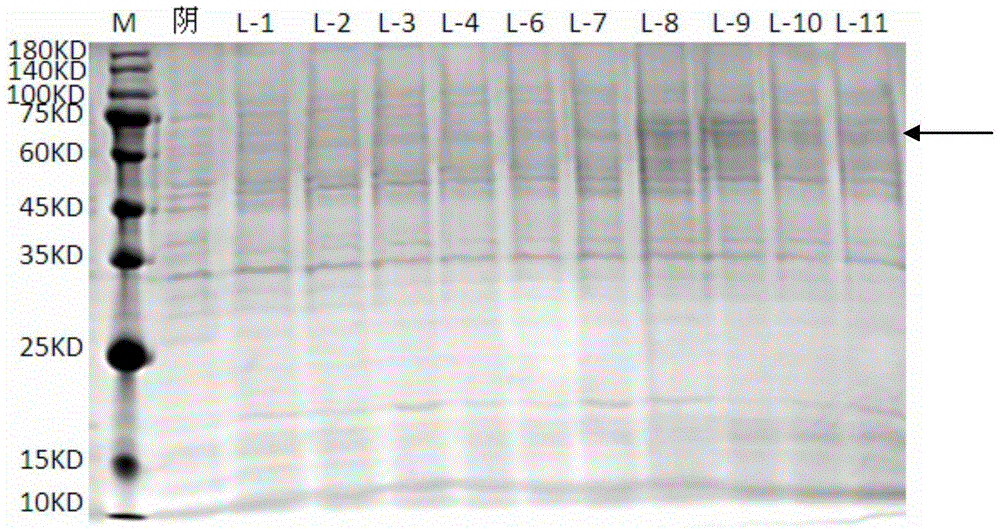
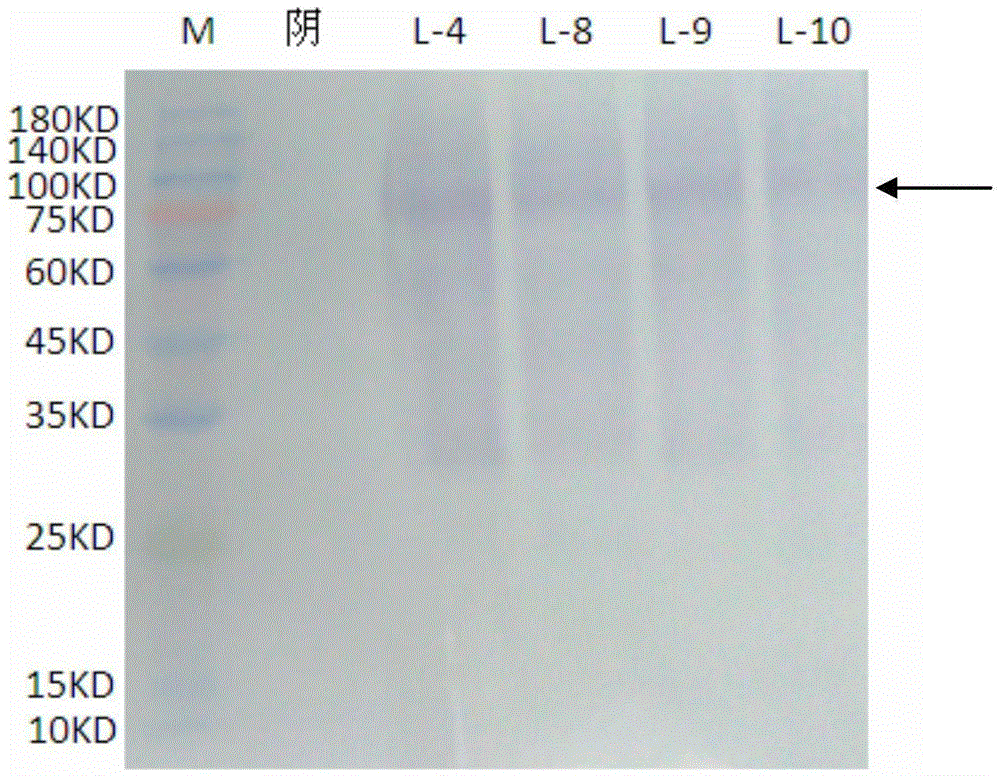
Armillariella tabescens laccase gene, recombined pichia pastoris engineering bacteria thereof and application
A Pichia pastoris, engineering bacteria technology, applied in genetic engineering, application, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problems of high cost of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes and lignin-degrading enzymes, inability to meet industrial needs, and low yields.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] For a better understanding of the present invention, the following are specifically described by examples. Wherein, unless otherwise specified, the methods used are conventional methods; the materials used are all purchased from conventional biochemical reagent stores; the % in the examples, unless otherwise specified, are mass percentages, and the quantitative tests are all set to repeat the experiment three times , and the results are averaged.
[0028] 1. Material preparation
[0029] 1. The species of bright bacteria used
[0030] Bright bacteria (A. tabescens) strains were preserved by the Institute of Biopharmaceuticals of Zhejiang Medical College. The bright bacteria in the experiment of the present invention was donated by Professor Ling Qingzhi of Zhejiang Medical College.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com