Method for improving cottonseed nutritional quality and application thereof
A cottonseed and nutrition technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of carotenoid content and improvement in cottonseed that have not yet been seen, and achieve the effects of simple and easy method, enhanced cottonseed nutrition, and increased carotenoid content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1 Acquisition of cotton phytoene synthase gene GhPSY2
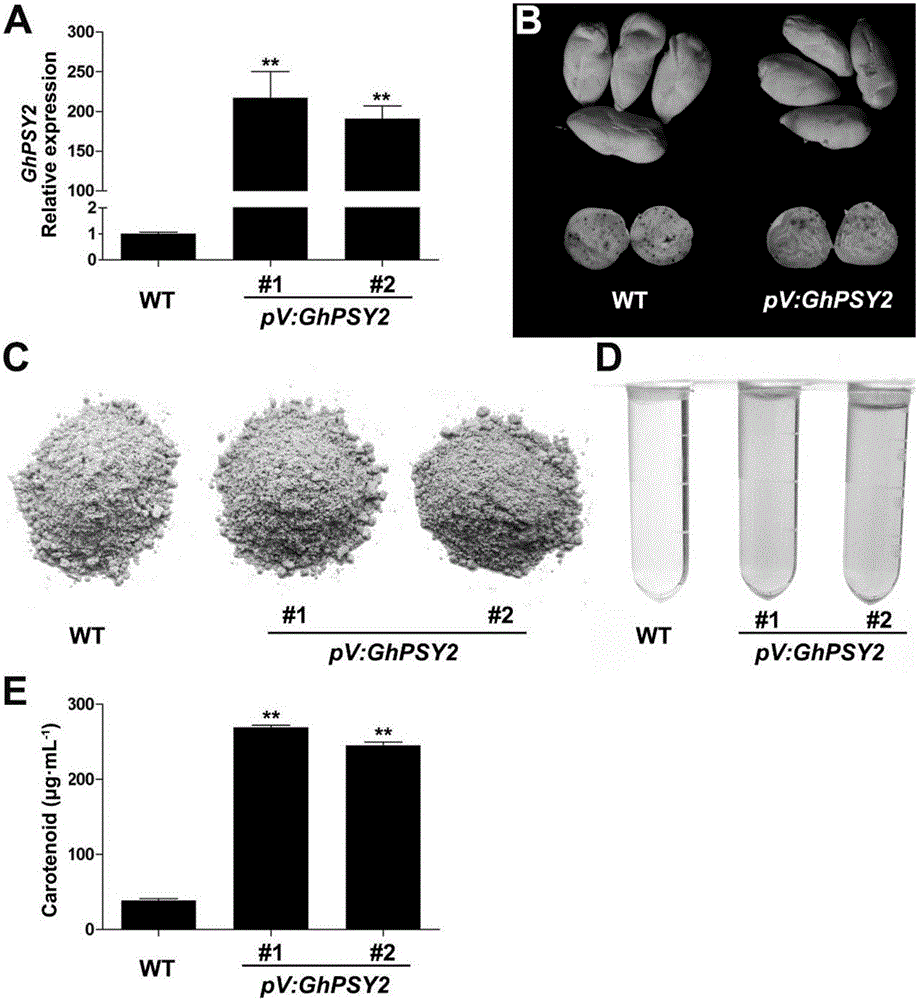
[0049] On the Phytozome public database (https: / / phytozome.jgi.doe.gov), using the base sequence of Arabidopsis phytoene synthase gene AtPSY (At5g17230) as bait, BlastN search homologous genes. The results showed that the gene numbered Gorai.006G009400 in Raymond cotton was highly homologous to At5g17230. Using the CDS sequence of Gorai.006G009400 as a reference, design primers (Table 1, GhPSY2-U&GhPSY2-D), use upland cotton cDNA as a template, amplify the obtained fragment, and add BamHI and EcoRI sites at both ends of the fragment. The sequencing results are as follows: SEQ ID NO.1. Cluster analysis showed that this sequence had high homology with known phytoene synthase genes from other species (such as Arabidopsis, tomato, soybean, etc.), so this sequence was considered to be a cotton phytoene synthase gene. Gene encoding erythromycin synthase (GhPSY2).
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2 Construction of the GhPSY2 expression vector specific to the seed development stage
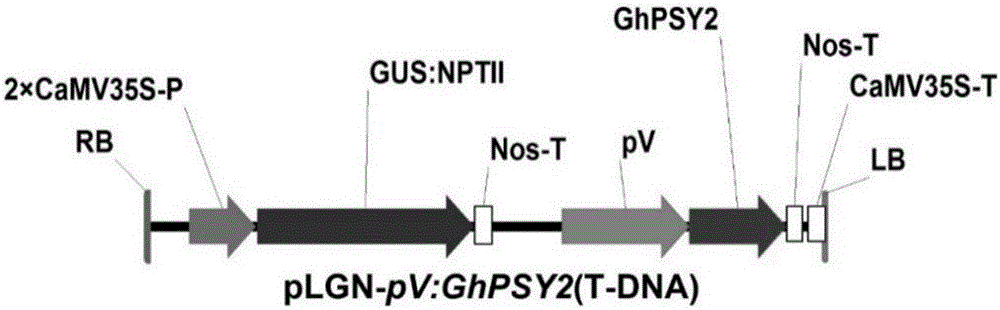
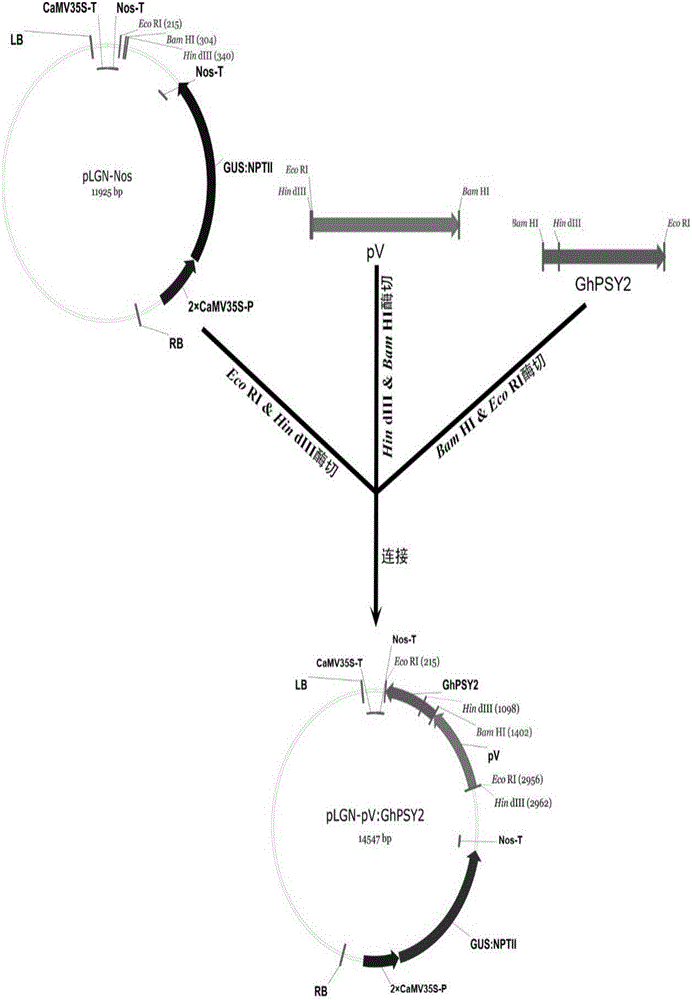
[0051] The procedure for constructing GhPSY2 into the plant expression vector pLGN-Nos is shown in figure 2 . The pLGN-Nos vector is a binary plant expression vector transformed from the traditional plant expression vector pBI121. Its T-DNA segment (region between RB and LB, figure 2 ) was replaced by a fusion gene expression cassette controlled by the constitutive CaMV35S promoter (CaMV35S-P) reporting gene GUS and marker gene NPTII, and another expression cassette controlled by CaMV35S-P.
[0052] Use primers (Table 1, pV-F and pV-R) to amplify and clone the promoter pV from the bean genome, and add HindⅢ and BamHI sites at both ends of the promoter. GhPSY2 was excised from the cloning vector with BamHI and EcoRI, and the promoter pV was excised from the cloning vector with HindIII and BamHI. The above two fragments were simultaneously added to the ligation reaction s...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The genetic transformation of embodiment 3 cotton
[0054] The cotton genetic transformation of the above expression vector was carried out by the method mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and the medium formula used is shown in Table 2. The specific method is as follows: select wild-type Jimian No. 14 cotton seeds (hulled) with full grains, place them in a sterile Erlenmeyer flask, rinse with 75% alcohol for 1 minute, and then rinse with 0.1% HgCl 2 Sterilize for about 10 minutes (shake the Erlenmeyer flask), fully rinse with sterile water 6-8 times, place on a shaker at 30°C (100-110rpm), and wait for the radicle to grow about 1cm (about 24-36h, every 8 hours Change the water once), take it out, and insert the radicle into the seed germination medium. Culture in a dark room at 30°C until the hypocotyls elongate to 2-3cm (about 48h). A single colony of Agrobacterium carrying the expression cassette vector was inoculated in liquid YEB medium containing 50 mg / LKm a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com