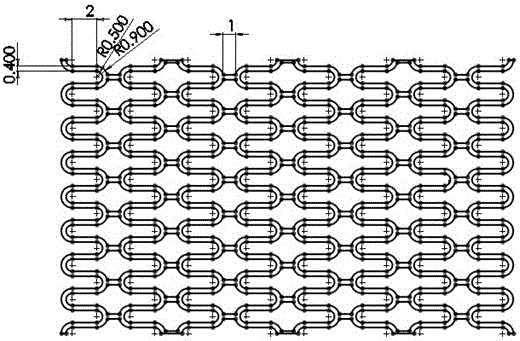
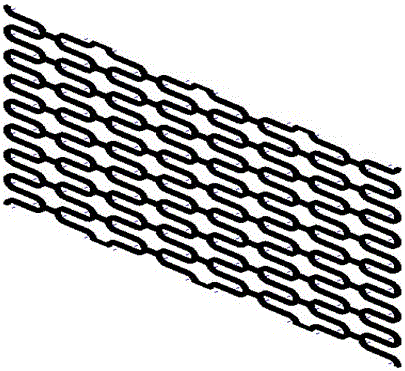
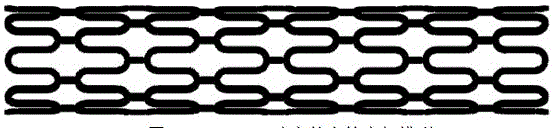
Method for preparing biodegradable polymer self-expansion type intravascular stent based on 3D printing technology
A technology for degrading polymers and vascular stents, applied in the field of biodegradable polymer self-expanding vascular stents based on 3D printing technology. The effect of improving long-term patency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) Synthesis of biodegradable polylactic acid-based shape memory polyurethane
[0032] With a molar ratio of 7:3 D,L - Lactide ( D,L -LA) with e- Caprolactone ( e- CL) as raw material, through ring-opening polymerization
[0033] Preparation of random copolymer PCLA, PCLA and hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) and flexible oligomer polytetrahydrofuran (PTMEG) chain extension to prepare biodegradable polylactic acid-based shape memory polyurethanes (PCLAUs), in which HDI and PCLA The mol ratio is 1.2:1, and the consumption of PTMEG is 10% of system gross mass;
[0034] (2) Biodegradable polylactic acid-based shape memory polyurethanes (PCLAUs) / Fe 3 o 4 Synthesis of Nanocomposites
[0035] The PCLAUs obtained in step (1) and the surface-modified magnetic Fe 3 o 4 Composite nanoparticles to prepare PCLAUs / Fe 3 o 4 nanocomposites; among them, the magnetic Fe 3 o 4 Nanoparticles are surface treated with oleic acid. In the composite system, the magnetic Fe 3 o 4 ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] (1) Synthesis of biodegradable polylactic acid-based shape memory polyurethane
[0048] With a molar ratio of 8:2 D,L - Lactide ( D,L -LA) with e- Caprolactone ( e- CL) as raw material, through ring-opening polymerization
[0049] Preparation of random copolymer PCLA, PCLA and hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) and flexible oligomer polytetrahydrofuran (PTMEG) chain extension to prepare biodegradable polylactic acid-based shape memory polyurethanes (PCLAUs), in which HDI and PCLA The mol ratio is 1.04:1, and the consumption of PTMEG is 10% of system gross mass;
[0050] (2) Biodegradable polylactic acid-based shape memory polyurethanes (PCLAUs) / Fe 3 o 4 Synthesis of Nanocomposites
[0051] The PCLAUs obtained in step (1) and the surface-modified magnetic Fe 3 o 4 Composite nanoparticles to prepare PCLAUs / Fe 3 o 4 nanocomposites; among them, the magnetic Fe 3 o 4 Nanoparticles are surface treated with oleic acid. In the composite system, the magnetic Fe 3 o ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] (1) Synthesis of biodegradable polylactic acid-based shape memory polyurethane
[0066] With a molar ratio of 9:1 D,L - Lactide ( D,L -LA) with e- Caprolactone ( e- CL) as raw material, through ring-opening polymerization
[0067] Preparation of random copolymer PCLA, PCLA and hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) and flexible oligomer polytetrahydrofuran (PTMEG) chain extension to prepare biodegradable polylactic acid-based shape memory polyurethanes (PCLAUs), in which HDI and PCLA The mol ratio is 1.10:1, and the consumption of PTMEG is 10% of system gross mass;
[0068] (2) Biodegradable polylactic acid-based shape memory polyurethanes (PCLAUs) / Fe 3 o 4 Synthesis of Nanocomposites
[0069] The PCLAUs obtained in step (1) and the surface-modified magnetic Fe 3 o 4 Composite nanoparticles to prepare PCLAUs / Fe 3 o 4 nanocomposites; among them, the magnetic Fe 3 o 4 Nanoparticles are surface treated with oleic acid. In the composite system, the magnetic Fe 3 o ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com