Preparation method for electro-oxidation synthesis of one-dimensional nano-oxide structure
A nano-oxide and electro-oxidation technology, applied in the field of photoelectrolysis, can solve problems such as poor stability, easy to fall off, and difficult to control one-dimensional nanostructures, and achieve the effect of enhancing the binding force and enhancing the binding force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
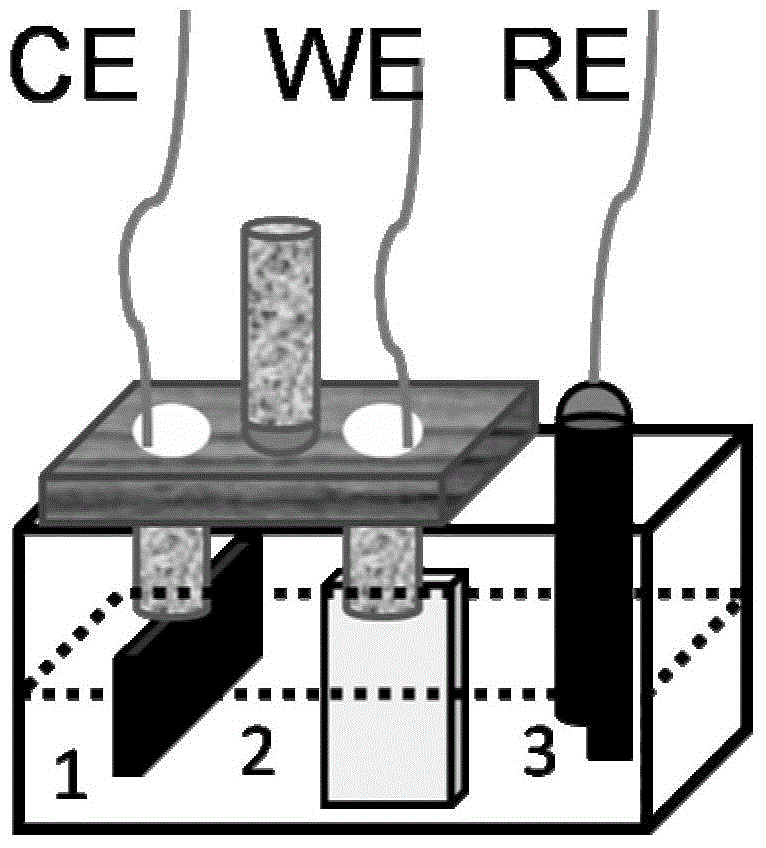
[0034] Using 0.01M FeCl 2 ·5H 2 O was used as the electrolyte solution, and 1M HCl was used to adjust the pH of the solution to 4.1, and α-Fe was prepared using a three-electrode system at 75 °C 2 o 3photoelectrode. Among them, the stainless steel conductive substrate is used as the working electrode, the Pt sheet electrode is used as the counter electrode, the Ag / AgCl electrode (4MKCl solution) is used as the reference electrode, and the electrolyte is deionized water: ethylene glycol = 20:1. The optimized deposition electrode was tested under the condition of 1.4V. The deposition time is 2 min. After the deposition process was completed, the color of the deposited film sample changed from colorless to a layer of transparent yellow substance on the surface. Take out the working electrode and rinse it with deionized water, stir the sample in a solution containing tetraethyl orthosilicate for 1-4 hours, and then place it in a tube furnace for calcination. In the tube furna...
Embodiment 2
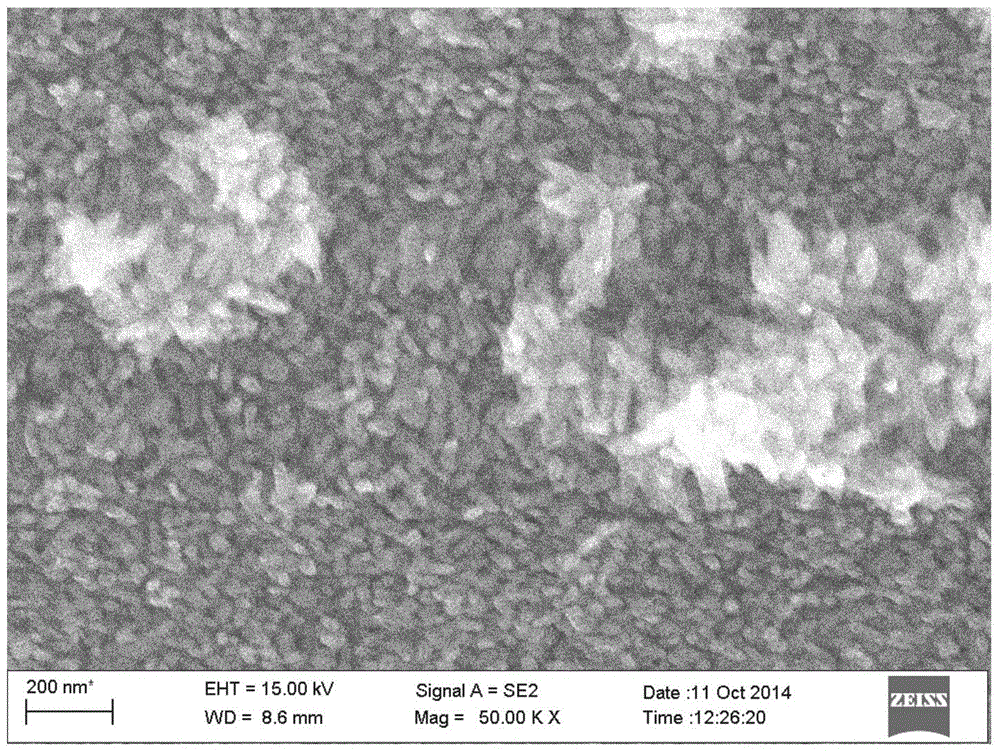
[0036] The difference from Example 1 is that in 0.05M FeSO 4 and 3M NH 4 Cl is used as the electrolyte, the pH value is 7.5, and the electrolyte solvent is deionized water:polyethylene glycol=1:1 under the condition of a voltage of 0.3V. Among them, FTO (conductive glass) is used as the working electrode, the Pt sheet electrode is used as the counter electrode, and the Ag / AgCl electrode (4MKCl solution) is used as the reference electrode. After the deposition process is completed, calcining is carried out in the same manner as in the previous example. One-dimensional α-Fe prepared by this method 2 o 3 The FESEM picture of the photoelectrode is as Figure 4 shown. It can be seen that the prepared iron oxide has a one-dimensional nanorod structure and grows vertically to the substrate.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The difference from Example 1 is that the working electrode is a Ti conductive substrate, the counter electrode is a graphite plate, Ag / AgCl (saturated KCl) is a reference electrode, and the electrolyte solvent is deionized water in different proportions: glycerol. Under the condition of applied voltage 1.0V, 70℃, with 0.1M FeCl 2 4H 2 O, pH=5.1 is the electrolyte solution, and the deposition time is 30min. After the deposition, the sample was sent into a tube furnace for high-temperature calcination at 800°C for 6 hours. α-Fe prepared in different ratios 2 o 3 The UV-visible absorption spectrum of the photoelectrode is as follows: Figure 5 As shown, it shows that the material has the ability to absorb solar energy and can be applied to the photoelectrolysis process.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com