Method for directly observing salt contents of different tissues of halogeton glomeratus
A technology of saline grass and content, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, analysis materials, and material analysis using wave/particle radiation, etc., can solve the problem of inability to directly observe the difference of salt content in different tissues and organs of halo grass, and achieve high reliability , the result is accurate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
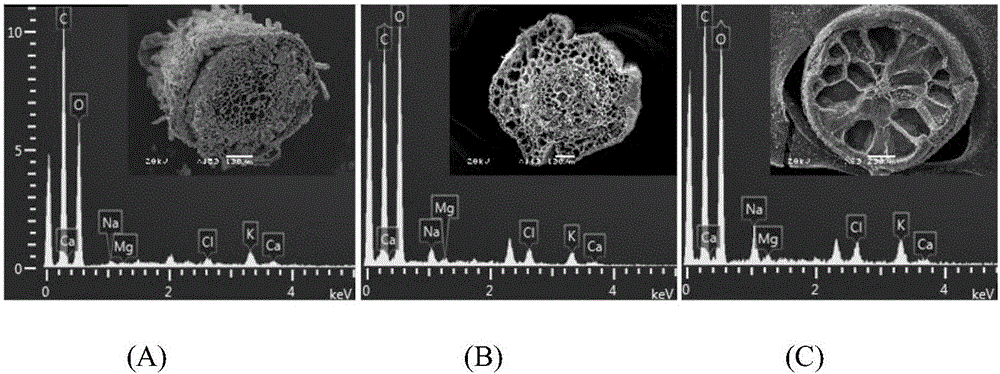
[0023] Embodiment 1: a method for directly observing the salinity content of different tissues of Halophysis saline, its main feature is that the steps are as follows:
[0024] (1) Sample collection: Take the potted halophyte seedlings cultivated under NaCl stress for 1-2 months as the object, first take out a single halophyte plant from the pot, rinse the plant with ultrapure water, and separate the roots, stems, and leaves in turn tissue, and cut with a double-sided blade;
[0025] (2) Agar embedding and cutting: use agar with a mass fraction of 3-5% to embed the roots, stems and leaves obtained in step (1) within 3 minutes and cut them off, leave them at room temperature for 3-5 minutes, and after the agar has solidified, use The double-sided blade cuts the embedded material into slices within 2 minutes;
[0026] (3) Liquid nitrogen freezing: put the material slices obtained in step (2) into liquid nitrogen within 1 min and freeze until the freezing is complete;
[0027] ...
Embodiment 2
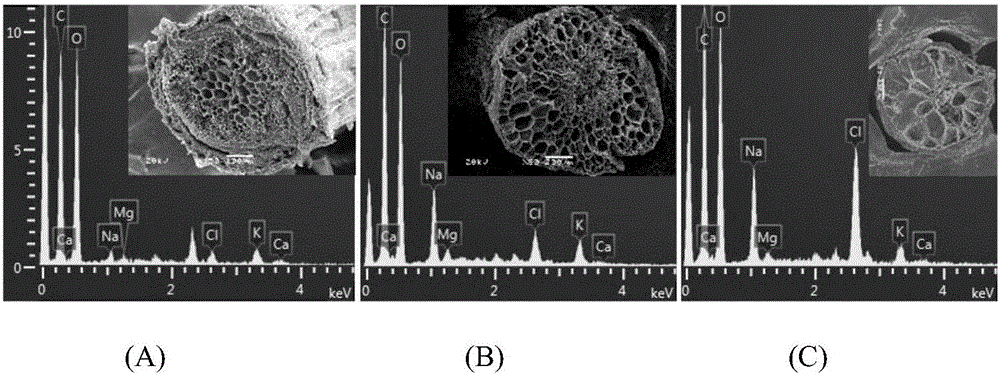
[0033] Embodiment 2: A method for directly observing the salinity content of different tissues of Halophysis saline, the steps are as follows:
[0034] a. Sample collection: take potted grass seedlings cultivated for 1-2 months without NaCl stress (control) as objects, first take out a single plant of halophytes from the flower pot, wash 3 times with ultrapure water, separate roots, Stem and leaf tissue were cut into 1.0 cm cuts with a double-sided blade.
[0035] b. Agar embedding and cutting: use 3% agar to embed the roots, stems, and leaves obtained in step a within 3 minutes, cut off the agar, let it stand at room temperature for 5 minutes to solidify the agar, and quickly cut the embedded material with a double-sided blade Cut into slices with a thickness of 1-2mm.
[0036] c. Liquid nitrogen freezing: put the material slices obtained in step b into liquid nitrogen within 30 seconds and freeze for 3 minutes.
[0037] d. Freeze-drying: Place the completely frozen sample ...
Embodiment 3
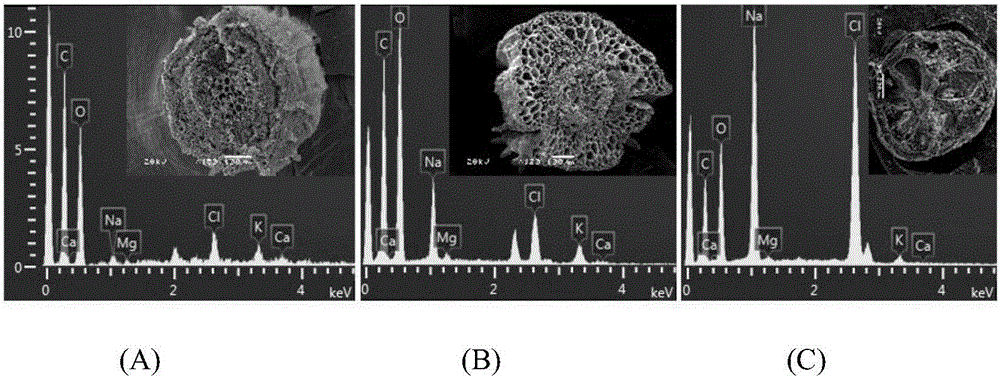
[0039] Embodiment 3: a method for directly observing the salinity content of different tissues of Halophysis saline, the steps are as follows:
[0040] a. Sample collection: take 200mM NaCl stress cultured potted grass seedlings for 1-2 months as the object, first take out a single plant of halophytes from the flowerpot, wash it with ultrapure water for 3 times, and separate the roots, stems, and leaf tissues in turn , and cut into 0.5cm cuts with a double-sided blade.
[0041] b. Agar embedding and cutting: use 5% agar to embed the roots, stems, and leaves obtained in step a within 2 minutes, cut off the agar, let it stand at room temperature for 4 minutes to solidify the agar, and quickly cut the embedded material with a double-sided blade Cut into slices with a thickness of 1-2mm.
[0042] c. Liquid nitrogen freezing: put the material slices obtained in step b into liquid nitrogen within 1 min and freeze for 2 min.
[0043] d. Freeze drying. Place the completely frozen s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com