Method for improving efficiency of degrading organic pollutants in water by homogeneous-phase UV-Fenton system
A technology for uv-fenton, organic pollutants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
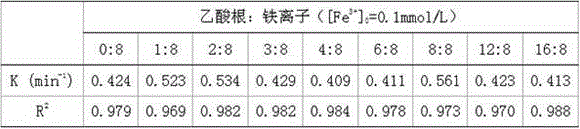
[0013] The specific application measures are as follows. A quartz sleeve is set in the center of the photochemical reactor (or the center of the reaction pool), with a built-in ultraviolet lamp. The middle area between the quartz sleeve and the photochemical reactor (the center of the reaction pool) is the reaction degradation area. The lower part of the area is provided with a stirring device. The initial pH value is 3.0, the water temperature is 30°C, and a 6W-30W ultraviolet lamp (254 nm) is placed in the quartz sleeve in the center of the reactor / pool as a light source. Add ferric sulfate and hydrogen peroxide to the reaction zone to build a homogeneous UV-Fenton system, add different concentrations of sodium acetate as a synergist, the concentration range of sodium acetate can be adjusted according to the actual situation (the molar ratio of acetate to iron ion is 1:8 to 16 :8), the specific ratio depends on the actual situation.
Embodiment 2
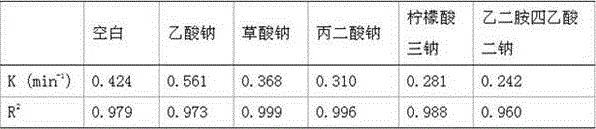
[0023] A quartz sleeve is set in the center of the cylindrical photochemical reactor, with a built-in ultraviolet lamp, magnetic stirring is set below, and the middle layer is the reaction degradation zone. In this experiment, the iron ion concentration was set to 0.1 mmol / L, the concentration of azo dye Golden Orange II was 0.2 mmol / L, and the concentration of hydrogen peroxide was 10 mmol / L. A basic homogeneous UV-Fenton was constructed with a 6W UV lamp as the light source. system. The concentration of synergist sodium acetate, ammonium acetate and potassium acetate is 0.1 mmol / L. In the three synergistic homogeneous UV-Fenton systems, the degradation rate constants of the dye Golden Orange II are 0.561min respectively -1 、0.503min -1 and 0.494min -1 , are higher than the rate constant (0.424min -1 ). It shows that different acetates can enhance the degradation ability of the homogeneous UV-Fenton system, and sodium acetate is the best synergist for the homogeneous UV-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com