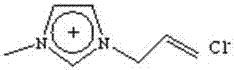
A kind of method for improving 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride dissolving cellulose performance
A methylimidazolium chloride salt and cellulose-dissolving technology, which is applied in the field of improving the cellulose-dissolving performance of 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt, can solve the problems of high-efficiency conversion and deep processing, long dissolution time, and solubility Low-level problems, to achieve the effect of increasing the concentration and ability of dissolution, reducing the dissolution time, and reducing the dissolution temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for improving the cellulose-dissolving performance of 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt, vacuum-drying microcrystalline cellulose with an average degree of polymerization of 265 at 50°C until the water content is less than 0.8%, adding to 1 -Allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt, and then add solid acid-sulfonic acid ion exchange resin; stir at a temperature of 80°C and a mechanical stirring speed of 500rpm for 30min to completely dissolve. Wherein, the concentration of microcrystalline cellulose is 3wt%, the concentration of solid acid is 2.0wt%, the particle size of solid acid is 300 microns, and the resin exchange capacity is 4.2 eq / kg.
[0026] In the prior art, 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt dissolves microcrystalline cellulose (the average degree of polymerization is 265), the concentration of microcrystalline cellulose is 3 wt%, the temperature is 80°C, and the stirring speed is 500 rpm , the time required for microcrystalline cellul...
Embodiment 2
[0029] A method for improving the cellulose-dissolving performance of 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt, vacuum-drying cotton fibers with an average degree of polymerization of 2180 at 40°C until the water content is less than 0.8%, adding to 1-ene Propyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, and then add solid acid-sulfonic acid ion exchange resin; dissolve at a temperature of 115°C and a mechanical stirring speed of 200rpm for 120min. Wherein, the quality of cotton fiber is 18wt% of 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt quality, the concentration of solid acid is 4.0wt%, the particle diameter of solid acid is 200 microns, and resin exchange capacity is 4.3 eq / kg.
[0030] In this example, the solubility of cotton fiber is 60.2%.
[0031] However, in the prior art, 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt dissolves cotton fibers (the average degree of polymerization is 2180), and the quality of cotton fiber is 100% of that of 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt. ...
Embodiment 3
[0034] A method for improving the performance of 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt dissolving cellulose, vacuum-drying eucalyptus wood dissolving pulp fibers with an average degree of polymerization of 520 at 30°C until the water content is less than 1%, adding to 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt, and then add solid acid-sulfonic acid ion exchange resin; at a temperature of 110°C, stir at a mechanical stirring speed of 800rpm for 90min to completely dissolve. Among them, the concentration of eucalyptus wood dissolving pulp fiber is 10wt%, the concentration of solid acid is 1.0wt%, the particle size of solid acid is 300 microns, and the resin exchange capacity is 4.5 eq / kg. The dissolved 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt is recovered by the solvent system and continues to be reused in the dissolution system. After 5 cycles of use, the recovery rate of 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt is was 97%, and the loss rate was 3.0%.
[0035] In the prio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com