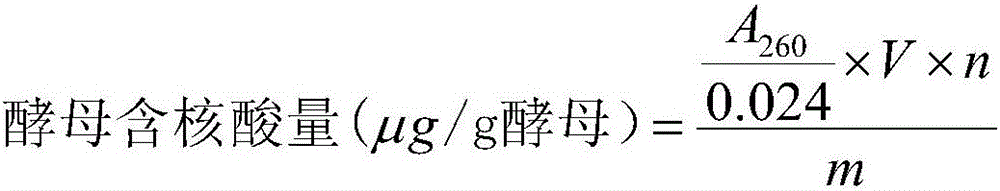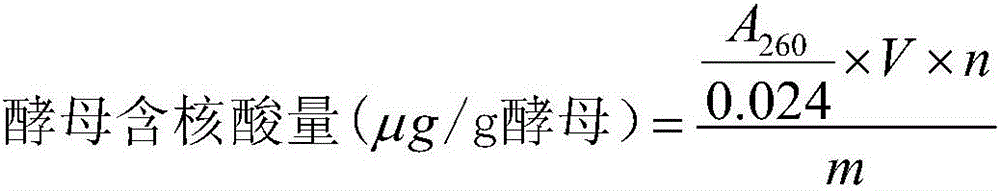Method for brewer's yeast cell disruption based on collaborative driving of pulsed electric field and carbon nano tubes
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells and carbon nanotubes, which is applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, dissolution of microorganisms, and electric/wave energy treatment of enzymes, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of simple operation process, improved extraction rate and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The method for breaking the cell wall of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells based on a pulsed electric field and carbon nanotubes in this embodiment is as follows: 1 g of multi-walled carbon nanotubes is dispersed uniformly in 1000 mL of deionized water by ultrasonic, and the ultrasonic time is 0.5 h. The gradient is 1g / L carbon nanotube-deionized dispersion. Put 1g of beer dry yeast in the ratio of 1:10 in warm water at 35°C for 15 minutes to make a yeast suspension, add 30mL of 1g / L carbon nanotube-deionized dispersion, and stir mechanically for 0.5h to obtain carbon nanotubes Tube - yeast suspension. The prepared carbon nanotube-yeast suspension was placed in a treatment chamber between two plate-shaped iron electrodes, and the distance between the electrodes was kept at 40 cm. The pulse discharge voltage is 10kV, the frequency is 50Hz, the pulse width is 40μs, the number of pulses is 500, and the pulse electric field treatment time is 1s, and the broken yeast cells are...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: A method for synergistically driving Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall breaking by a pulsed electric field and carbon nanotubes, the steps are as follows: 1 g of multi-walled carbon nanotubes is dispersed uniformly in 500 mL of deionized water by ultrasonic, and the ultrasonic time is 0.5 h, configured as The concentration gradient is 2g / L carbon nanotube-deionized dispersion. Put 1.5g of beer dry yeast in the ratio of 1:15 in warm water at 36°C and rehydrate for 18 minutes to make a yeast suspension, add 30mL 2g / L carbon nanotube-deionized dispersion, and stir mechanically for 0.5h to obtain carbon nanotubes Tube - yeast suspension. The prepared carbon nanotube-yeast suspension was placed in a treatment chamber between two plate-shaped iron electrodes, and the distance between the plate electrodes was kept at 20 cm. The pulse discharge voltage is 20kV, the frequency is 100Hz, the pulse width is 60μs, the pulse number is 800 times, and the pulse electric fi...
Embodiment 3
[0035]Example 3: A method for synergistically driving Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall breaking by a pulsed electric field and carbon nanotubes. The steps are as follows: 1 g of multi-walled carbon nanotubes is dispersed evenly in 200 mL of deionized water by ultrasonic, and the ultrasonic time is 0.5 h. The concentration gradient is 5g / L carbon nanotube-deionized dispersion. Put 2g of beer dry yeast in the ratio of 1:20 in warm water at 38°C and rehydrate for 20 minutes to make a yeast suspension, add 30mL of 1g / L carbon nanotube-deionized dispersion, and stir mechanically for 0.5h to obtain carbon nanotubes - Yeast suspension. The prepared carbon nanotube-yeast suspension was placed in a treatment chamber between two plate-shaped iron electrodes, and the distance between the plate electrodes was kept at 10 cm. The pulse discharge voltage is 40kV, the frequency is 200Hz, the pulse width is 100μs, the pulse number is 1000 times, and the pulse electric field treatment time i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com