Chitosanase-producing and fungus-restraining Burkholderia sp. and application thereof
A technology for producing chitosan enzymes and fungi, applied in the field of microorganisms, to achieve significant growth-promoting effects, wide application prospects, and increased plant height
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The screening of embodiment 1 bacterial strain of the present invention
[0031] Water samples and soil collected near Changqing Garden Park in Wuhan were added to sterilized water and shaken vigorously. Sample: sterile water=1:9 (the water sample is the volume ratio, and the soil sample is the mass-to-volume ratio), and the resulting suspension concentration is 10 -1 , and then the above concentration is 10 -1 The suspension was diluted to 10 -2 ~10 -6series concentration. Take 200 μL of the above-mentioned dilutions of different concentrations and evenly spread them on a chitosan screening plate, incubate at a constant temperature for 3 to 5 days by inverting at 28°C. Pick colonies that grow well and can produce transparent circles for streak purification, and use glycerol preservation method to preserve bacteria.
[0032] Through the above screening, a strain that can use chitosan as the sole carbon source to produce obvious hydrolysis transparent circles on the...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Morphological observation and molecular biological identification of the strain of embodiment 2
[0034] (1) Morphological and physiological and biochemical characteristics
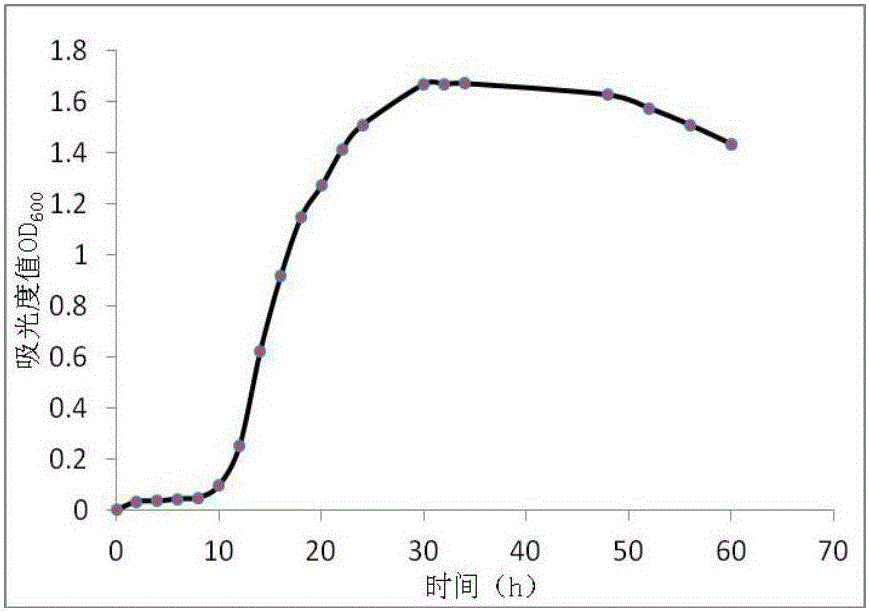
[0035] Morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain MEL01: cultured on a beef extract peptone plate at 28°C for 48 hours, the colony is round, with neat edges, light yellow opaque, moist and viscous surface, initially flat, and grows with the growth of culture time The colonies become thicker, see the specific morphology figure 2 . According to "Bergey's Handbook of Bacteria", MEL01 also has the following physiological and biochemical properties: negative Gram staining, short rod-shaped bacteria, no spores, negative denitrification, positive citrate utilization, positive leucine utilization, catalase Positive, gelatin liquefaction positive.
[0036] (2) 16S rDNA molecular identification
[0037] Preparation of PCR amplification template: Pick a single colony of ME...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3 bacterial strain degrades chitosan performance measurement
[0042] (1) Qualitative experiment of degrading chitosan transparent circle method
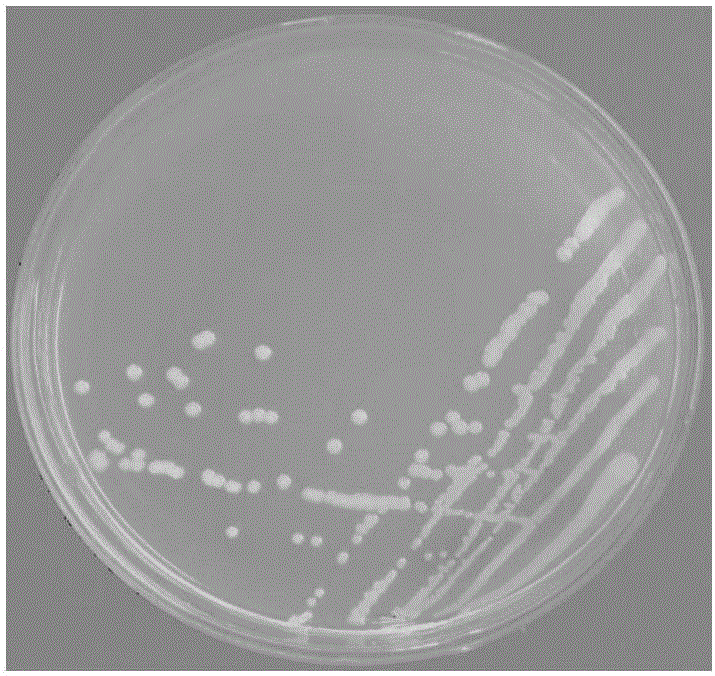
[0043] Take 10 μL of the MEL01 bacterial suspension activated by beef extract peptone liquid medium for 10 hours and plant it on a chitosan plate, plant 4 strains symmetrically at the four corners of the plate, and culture it upside down in a 37°C incubator for 3 days, MEL01 can form a very obvious hydrolysis circle, see the result Figure 4 . Use a vernier caliper with an accuracy of 0.02mm to measure the ratio of the diameter (D) of the hydrolysis zone of each colony to the diameter (d) of the colony, and the D / d is more than 3.5 (the larger the D / d value, the stronger the degradation ability), it can be considered that MEL01 has a significant The degradation effect, the specific measurement results are shown in Table 1.
[0044] (D / d) ratio of chitosan degraded by strain MEL01 in table 1
[0045]
[0046]...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com