Method for discriminating admixing of starch syrup in honey
A technology for syrup and starch, applied in the field of food safety, can solve the problems such as the inability to effectively separate and measure oligosaccharides, and achieve the effects of standardizing the bee product market, protecting legitimate rights and interests, and avoiding false positive test results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
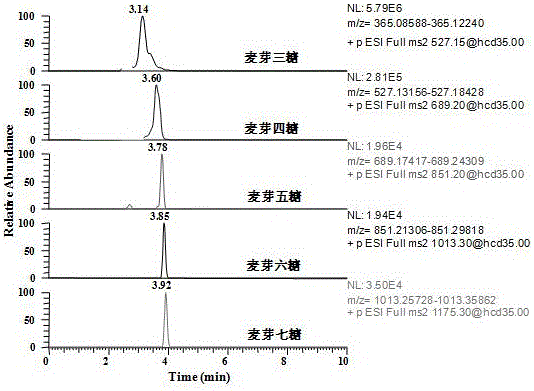
[0050] Example 1 Establishment of liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry methods for oligosaccharides
[0051] Standards and reagents used in this embodiment are: maltotriose, maltotetraose, maltopentaose, maltohexaose and maltoheptaose with a purity greater than 99.9%, purchased from Aldich-Sigma Company; experimental acetonitrile (chromatographically pure) Purchased from Merck Company of Germany; formic acid (chromatographically pure) was purchased from TEDIA Company of the United States.
[0052] Accurately weigh an appropriate amount of oligosaccharide standard substance, make a 1.0 mg / mL standard stock solution with water, and store it in the refrigerator at 4 °C. Dilute with acetonitrile water (1+1 v / v) to a working solution with a concentration of 100 μg / ml.
[0053] 1. Establishment of liquid chromatography conditions
[0054] In the process of liquid phase analysis, adding a small amount of formic acid is beneficial to the ionization of the target compound in t...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Embodiment 2 Determination of oligosaccharide content in syrup and honey
[0067] 1. Content analysis of oligosaccharides in syrup
[0068] The main components of pure natural honey are glucose, fructose and a small amount of sucrose, while the rice syrup and corn syrup used in adulteration will have unhydrolyzed oligosaccharides due to production process problems, so when natural honey is mixed with starch syrup , there will be trace amounts of oligosaccharides present.
[0069] For honey and syrup samples without crystallization, stir them evenly; for samples with crystallization, warm them in a water bath not exceeding 60°C under airtight conditions, shake them, stir well after the samples are completely melted, and cool them rapidly to room temperature. Accurately weigh 1.0 g of the melted sample (accurate to 0.01 g) into an appropriate scale container, dilute to 10.0 mL with water, vortex until dissolved, take an appropriate amount of supernatant and mix with an ...
Embodiment 3
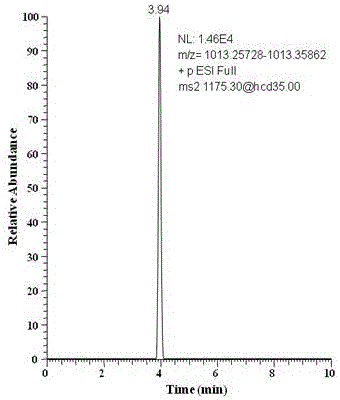
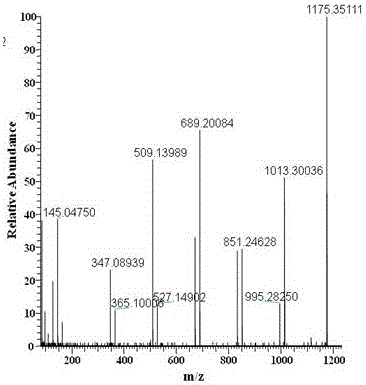
[0078] Example 3 Methodological investigation of maltoheptaose as a characteristic marker of starch syrup
[0079] The standard stock solution of maltoheptaose was diluted with water into a standard working solution, and the standard solutions with contents of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10 and 20 μg / mL were successively obtained, which were determined according to the optimized instrument conditions and quantified by the external standard method. Taking the accurate mass chromatographic peak area of the characteristic ion of maltoheptaose as the ordinate and the content as the abscissa, the standard curve was drawn. The correlation coefficient (r) was greater than 0.99, indicating that the linear relationship was good in the range of 0.5 to 10.0 μg / mL. Three different spiked levels of 20, 50 and 100 mg / kg were added to 3 kinds of honey samples including rapeseed honey, acacia honey and linden honey, and each level was repeated 6 times. The average recoveries ranged between 75-82%, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com