Method for rapidly identifying resistance of peanut varieties to aspergillus flavus
A technology of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus flavus spores, which is applied in the field of rapid identification of peanut varieties against Aspergillus flavus, and achieves the effects of improving efficiency, high equipment requirements and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1: the cultivation of Aspergillus flavus and the collection of spores
[0056] (1) Streak and activate the Aspergillus flavus strains on the PDA solid medium, and cultivate them in a dark incubator at 30°C for 6 days;
[0057] The components per liter of PDA solid medium are as follows:
[0058] Potato 300g, glucose 20g, agar 20g, pH value natural.
[0059] (2) After Aspergillus flavus hyphae cover the surface of the culture medium, wash it down with sterilized distilled water, resuspend in sterile water, calculate its concentration with a hemocytometer, and adjust the spore concentration to 10 6 per ml, as a suspension of Aspergillus flavus spores for later use.
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2: the processing of peanut seed
[0061] (1) Take 15 seeds each of peanut varieties Yueyou 20, Tifrunner, Luhua No. 14, Jihua No. 11, Zhonghua No. 5, Yuhua No. 6, and Zhonghua No. 6 healthy peanut plants, peel off the peel, and take Seeds with intact seed coats are used as samples and divided into Erlenmeyer flasks (if the seeds are dried, the seeds need to be soaked in sterile water and fully absorbed);
[0062] (2) add mercuric chloride of mass concentration 0.1% to disinfect for 10 minutes, shake at 100 r / min during this period, then rinse three times with distilled water, and rinse at 100 r / min for 5 minutes during the third rinse, and then make 6mm×5mm wounds on the seeds, Remove the seed coat from the wounded part.
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3: Inoculation of Aspergillus flavus
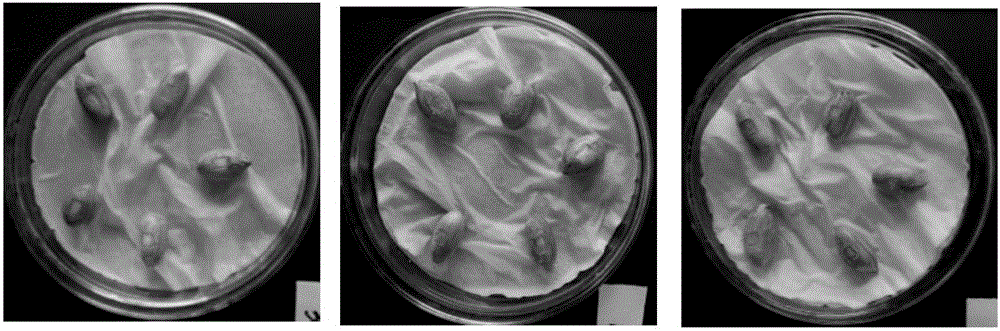
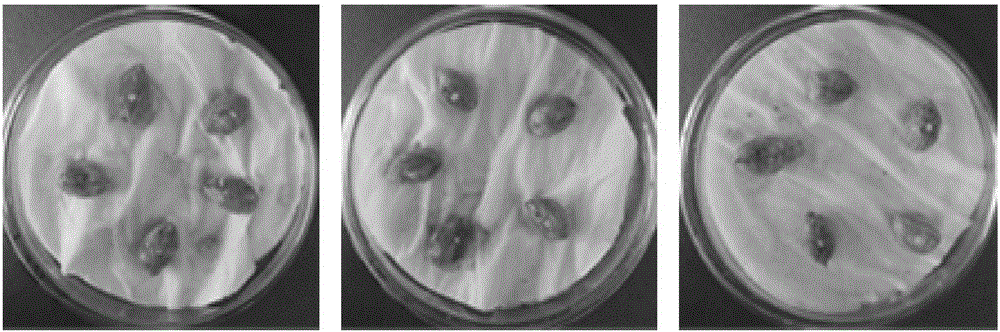
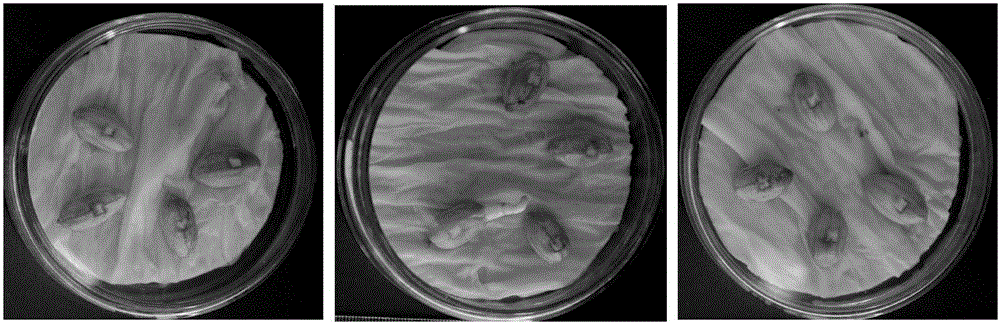
[0064] (1) Cover the wound of the seed in Example 2 with a sterile tampon of the same size, drop 20 microliters of the Aspergillus flavus spore suspension prepared in Example 1 on the tampon, and distribute it in numbered sterile Bacteria culture dish for cultivation;
[0065] (2) Fold two layers of absorbent paper and cut it into a circle and lay it in a petri dish. Add 5ml of sterilized distilled water to each petri dish to moisten the toilet paper so that the water content in the petri dish reaches 80%. Five seeds, 3 replicates for each sample;
[0066] (3) Place the petri dish in an incubator, culture in dark at 30° C. for 24 hours, remove the cotton sliver, and culture in dark for 144 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com