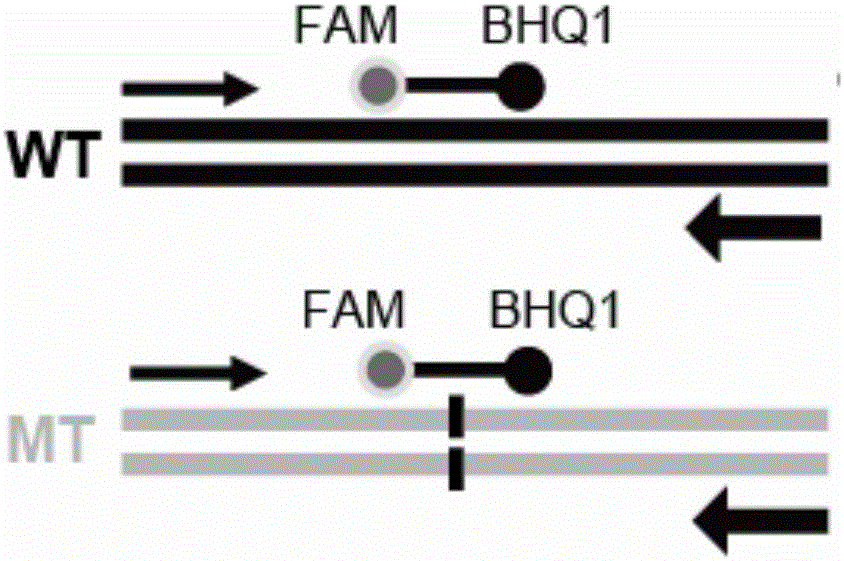
Detection method of hepatitis B virus drug-resistant mutation
A technology for hepatitis B virus and drug-resistant mutations, which is applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., to achieve the effects of improving utilization, high detection specificity, and increased detection throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
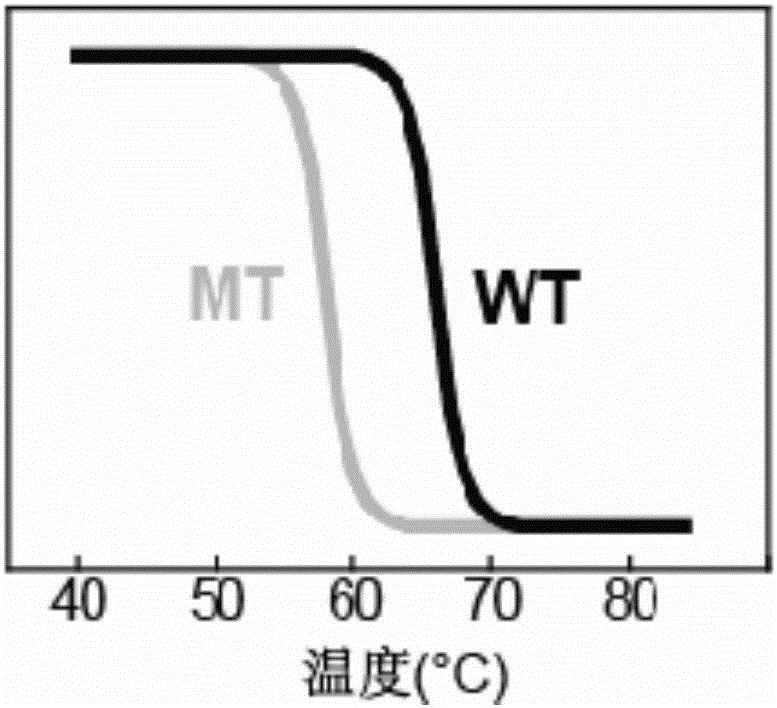
[0043] The detection results of wild-type HBV (WT) and three drug-resistant mutant HBV (204V, 204I and 204S) in the ROX channel are as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0044] The detection process of this embodiment is as follows:
[0045] (1) Prepare the following PCR amplification systems respectively: 75mmol / L Tris-HCl pH 8.5, 20mmol / L (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ,0.1% Tween20, 2.5mmol / L MgCl 2 , 200 μmol / L dNTPs, 1U Taq polymerase, 0.04 μmol / L upstream PCR amplification primer, 0.4 μmol / L downstream PCR amplification primer, 0.2 μmol / L fluorescent probe, wild-type HBV (WT) and three drug-resistant mutations Type HBV (204V, 204I and 204S) DNA template each 5μl. The base sequence of the upstream PCR amplification primer is 5'-AGACTCGTGGTGGACTTCTCTCA-3'; the base sequence of the downstream PCR amplification primer is 5'-TTGACATACTTTTCCAATCAAT-3'. The base sequence of the fluorescent probe is 5'-TGGCTTTCAGTTATGTGGATGATTGGT-3', the 5' end is marked with ROX fluorescent group, and the 3' en...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The detection results of wild-type HBV (WT) and two kinds of drug-resistant mutant HBV (173L and 173G) in the FAM channel are as follows: Figure 5 shown.
[0050] The detection process of this embodiment is as follows:
[0051] (1) Prepare the following PCR amplification systems respectively: 75mmol / L Tris-HCl pH 8.5, 20mmol / L (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 0.1% Tween20, 2.5mmol / L MgCl2, 200μmol / L dNTPs, 1U Taq polymerase, 0.04μmol / L upstream PCR amplification primer, 0.4μmol / L downstream PCR amplification primer, fluorescent probe 0.2μmol / L, wild type 5 μl each of HBV (WT) and two drug-resistant mutant HBV (173L and 173G) DNA templates. The base sequence of the upstream PCR amplification primer is 5'-AGACTCGTGGTGGACTTCTCTCA-3'; the base sequence of the downstream PCR amplification primer is 5'-TTGACATACTTTTCCAATCAAT-3'. The base sequence of the fluorescent probe is 5'-CTATGGGAGTGGGCCTCAGT-3', the 5' end is marked with a FAM fluorescent group, and the 3' end is marked with a BH...
Embodiment 3
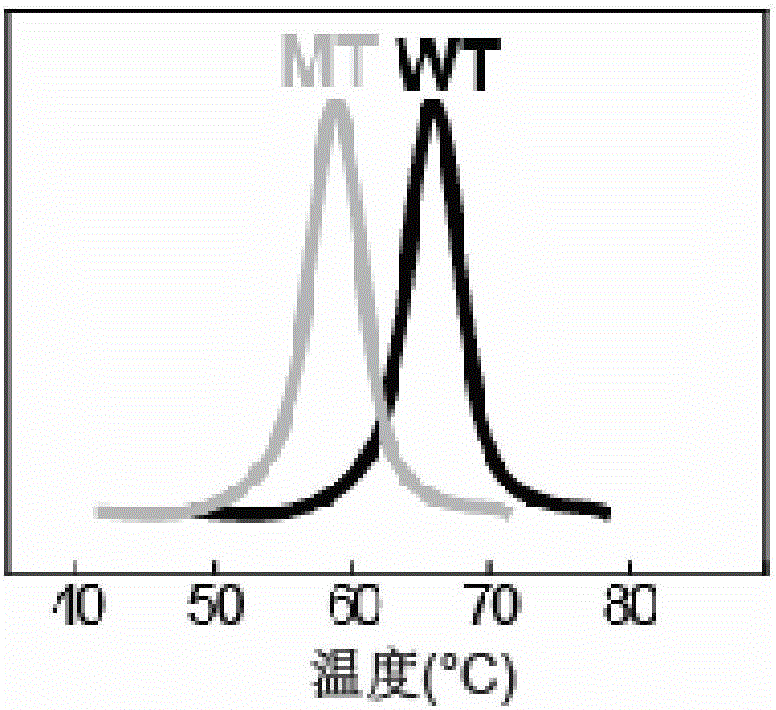
[0055] The present invention is to wild-type HBV (WT) detection sensitivity investigation result such as Figure 6 Shown; Drug-resistant mutant HBV (204V) detection sensitivity investigation result is as follows Figure 7 shown.
[0056] The detection process of this embodiment is as follows:
[0057] (1) Prepare the following PCR amplification systems respectively: 75mmol / L Tris-HCl pH 8.5, 20mmol / L (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ,0.1% Tween20, 2.5mmol / L MgCl 2 , 200 μmol / L dNTPs, 1U Taq polymerase, 0.04 μmol / L upstream PCR amplification primer, 0.4 μmol / L downstream PCR amplification primer, 0.2 μmol / L fluorescent probe, the concentration is 1×10 6 ,1×10 5 ,1×10 4 ,1×10 3 ,1×10 2 ,1×10 1 5 μl each of wild-type HBV (WT) and drug-resistant mutant HBV (204V) DNA templates / μL.
[0058] The base sequence of the upstream PCR amplification primer is 5'-AGACTCGTGGTGGACTTCTCTCA-3';
[0059] The base sequence of the downstream PCR amplification primer is 5'-TTGACATACTTTTCCAATCAAT-3'.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com