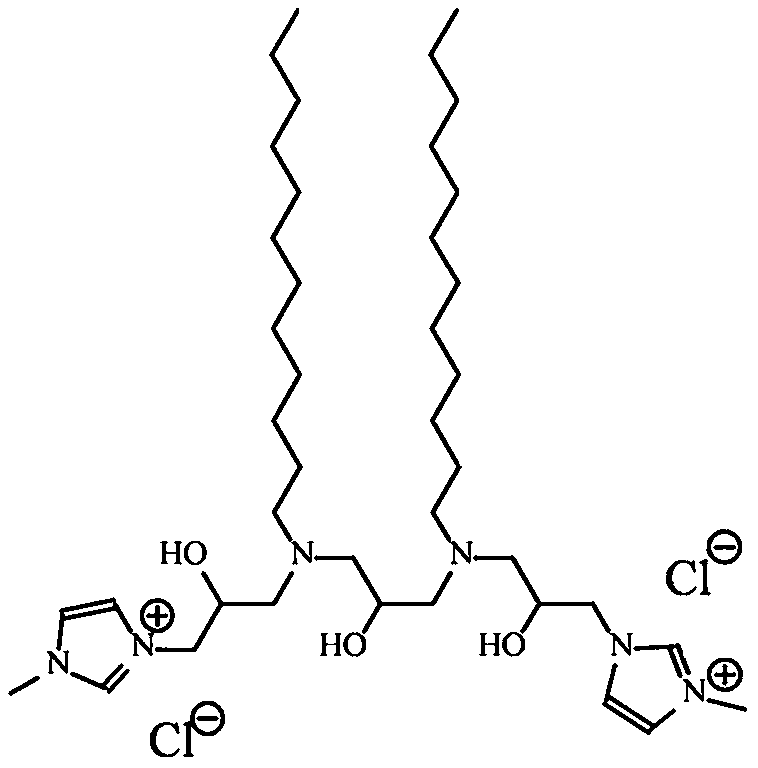
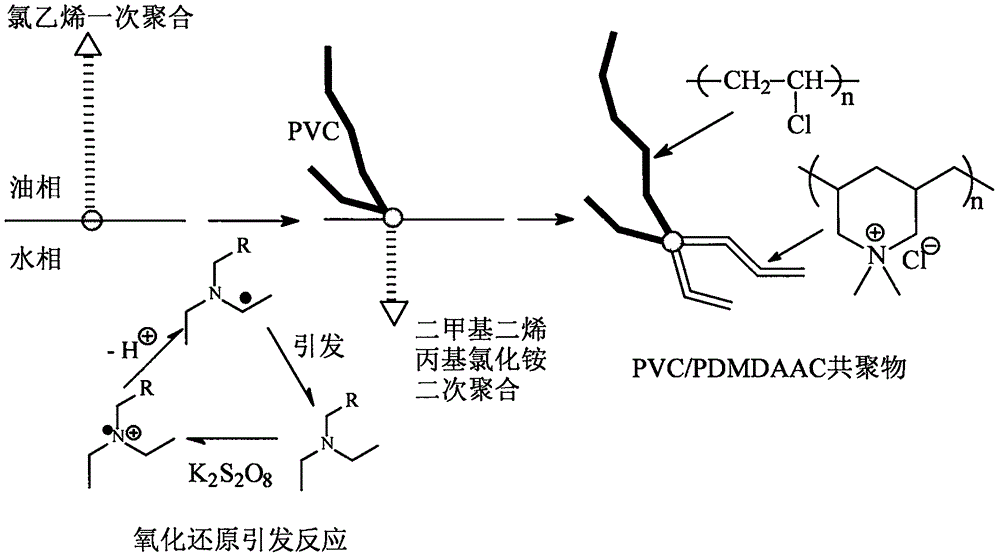
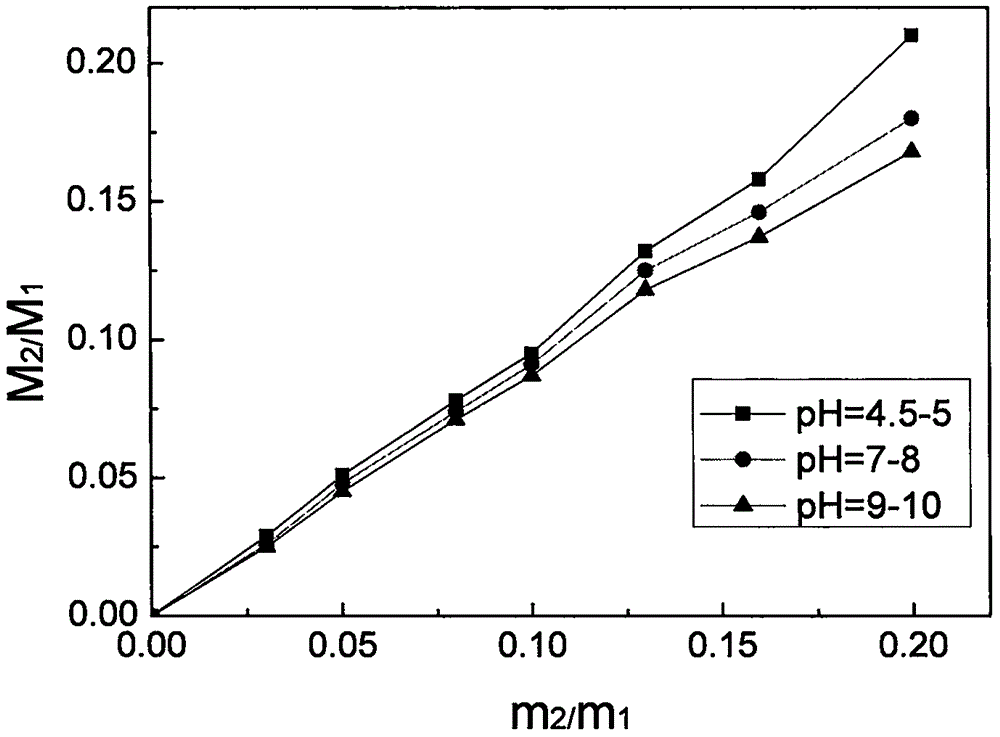
Green preparation method of cationic type polyvinyl chloride membrane material
A technology of vinyl chloride and a new method, which is applied in the field of green preparation of cationic polyvinyl chloride membrane materials, can solve the problems of low polymerization activity and limited space for chemical modification, and achieve mild and controllable conditions, broaden the development space, and low energy consumption effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] Below in conjunction with embodiment the present invention is described in further detail.
[0022] The preparation of vinyl chloride / dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride copolymer is carried out in the following steps:
[0023] a. Dissolve 1.5g cationic surfactant initiator in 500mL water, the concentration is generally in the range of 2.5-3.0‰, the amount of initiator is generally 2.5-3.0% of the weight of vinyl chloride, by adding different amounts of acetic acid and sodium phosphate mixture Adjust the pH value of the aqueous solution (pH=9 to 10; pH=7 to 8; pH=4.5 to 5.0), place the aqueous solution in a closed high-pressure reactor, and pass nitrogen into the reactor to remove the internal air;
[0024] b. Inject 55g of oil-soluble monomer vinyl chloride (boiling point is -13.4°C) into the reactor, stir well at room temperature and then add a saturated solution of potassium persulfate (the amount of potassium persulfate is generally 1.0-1.5% of the weight of the inpu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com