A method for catalytic conversion of hydrocarbons with high yield of butene and light aromatics
A catalytic conversion method and technology for light aromatics, which is applied in the field of catalytic conversion of hydrocarbons that produce more butenes and light aromatics, can solve the problem of low yields of butenes and/or light aromatics, achieve suppression of hydrogen transfer reactions, and process flexibility High-strength, high-yield effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] The cracking catalyst used in the present embodiment is: based on the total weight of the cracking catalyst, the cracking catalyst used contains 10% by weight of zeolite beta, 20% by weight of ZSM-5 zeolite (the ratio of silicon to aluminum is 40), 45% by weight of Kaolin and 25% by weight of alumina binder, wherein the beta zeolite contains 1% by weight of iron and 1.5% by weight of phosphorus in terms of elements. The cracking catalyst was aged for 10 hours at 800° C. under a 100% steam atmosphere, and the catalyst loading in the device (system catalyst inventory) was 60 kg.
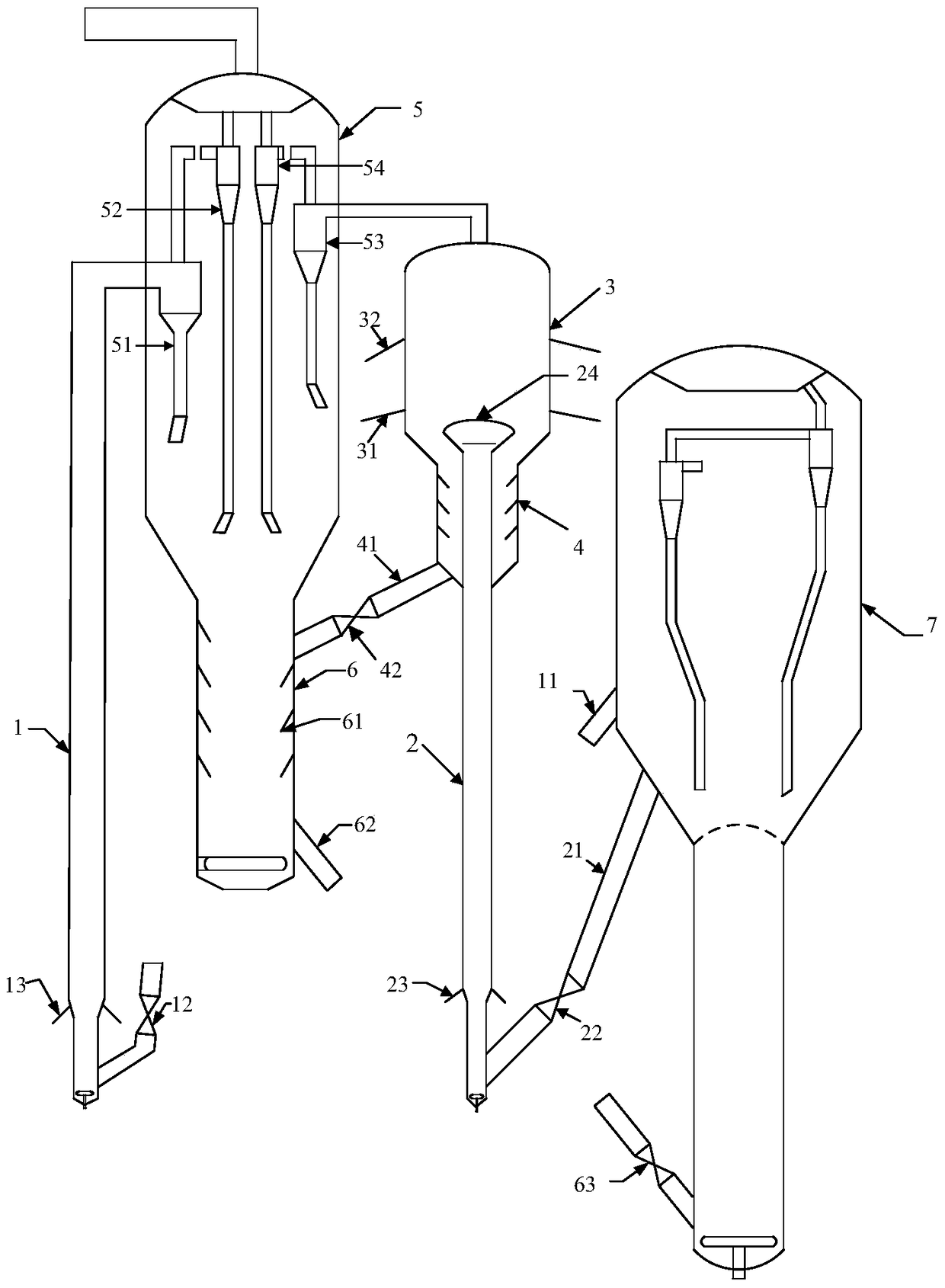
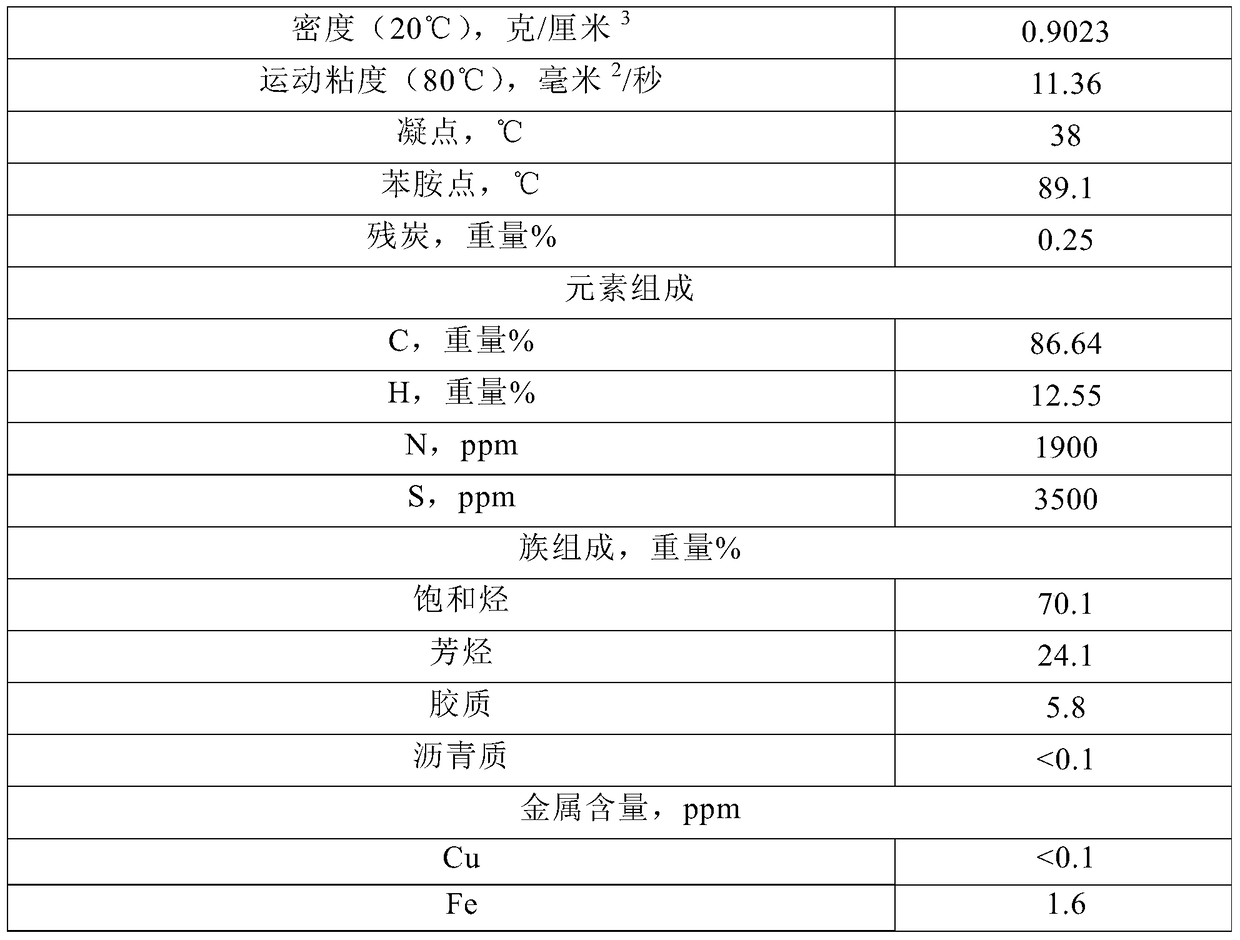
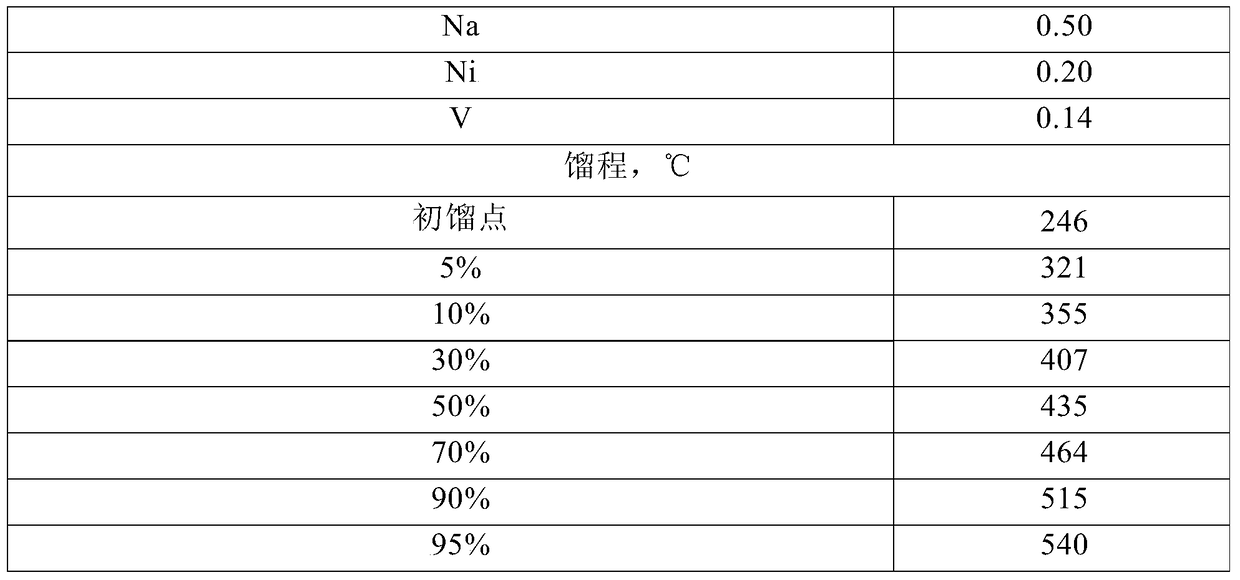
[0094] The heavy hydrocarbon feedstock (its properties are shown in Table 1) is introduced into the riser reactor 1, and after contacting and reacting with the hot catalyst from the regenerator 7, the reaction oil gas is separated from the catalyst, and the reaction oil gas leaves the reactor and is introduced into the fractionation device, separated The obtained coke catalyst is introduced into t...
Embodiment 2
[0096] The process flow and the cracking catalyst used in this example are the same as those in Example 1, except that the light cracked gasoline (see Table 2 for properties) is used at a reaction temperature of 40°C, a reaction pressure of 0.5MPa, and a molar ratio of hydrogen to olefins of 4:1. , on the hydrogenation catalyst (purchased from Sinopec Changling Catalyst Branch, the brand is RDD-1), through selective hydrogenation reaction, the diolefins and alkynes are converted into monoolefins and introduced into the riser reactor 2, and the remaining reaction conditions And the reaction results are shown in Table 4.
Embodiment 3
[0100] The flow process of this embodiment is the same as Example 1, and the difference is that the cracking catalyst used is: based on the total weight of the cracking catalyst, the cracking catalyst used contains 15% by weight of zeolite beta, 15% by weight of ZSM-5 zeolite (silicon Aluminum ratio is 40), 45% by weight of kaolin and 25% by weight of alumina binder, wherein, zeolite beta contains 1% by weight of iron and 1.5% by weight of phosphorus in terms of elements; and reaction conditions and reaction results See Table 6.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com