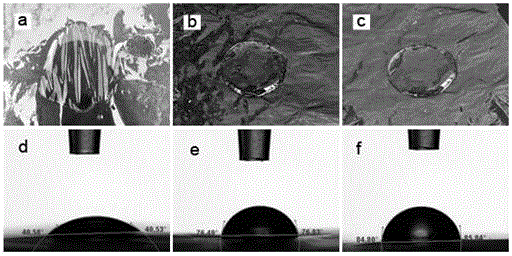
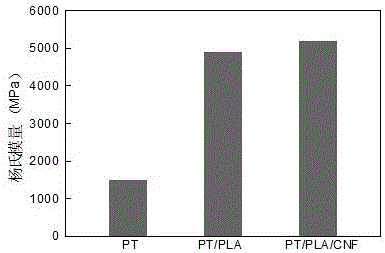
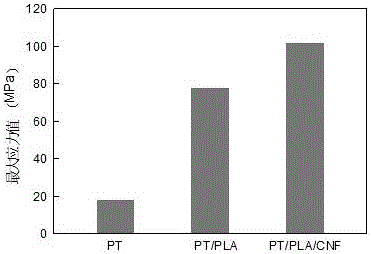
Preparation method of glass paper/polylactic acid/nanocellulose composite membrane
A technology of nano-cellulose and cellophane, applied in cellulose coatings, polyester coatings, coatings, etc., can solve problems such as poor mechanical strength, achieve simple and controllable operation, improve mechanical strength and surface waterproof performance, and compact structure Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Cut the dried cellophane into 8cm*8cm samples and soak them in 0.1% ethanol solution of silane coupling agent. After soaking for 30 minutes, take out the samples and air dry them naturally to obtain the modified cellophane for later use.
[0030] Dissolve 0.3g and 0.6g of polylactic acid (PLA) in 100g of dichloromethane to prepare 0.3% and 0.6% PLA dichloromethane solutions for later use; take 0.2g of PEG-4000 and dissolve in 100g of 0.4% PLA Cellulose nanofiber (CNF) dispersion, after freeze-drying to obtain a CNF-PEG composite with a PEG coating of 50%, take 0.12g of the CNF-PEG composite and disperse it in 100g of dichloromethane solution, and then with the concentration Mix equal volumes of 0.6% PLA solution to obtain PLA / CNF mixed dispersion for later use.
[0031] The modified cellophane samples were respectively immersed in the PLA solution with a concentration of 0.3% and the PLA / CNF dispersion with a ratio of CNF to PLA of 0.2, and the soaking time was 30 min. ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Cut the dried cellophane into 8cm*8cm samples and soak them in 0.2% ethanol solution of silane coupling agent. After soaking for 30 minutes, take out the samples and air dry them naturally to obtain the modified cellophane for later use.
[0034] Dissolve 0.3g and 0.6g of polylactic acid (PLA) in 100g of dichloromethane to prepare 0.3% and 0.6% PLA dichloromethane solutions for later use; take 0.2g of PEG-4000 and dissolve in 100g of 0.4% PLA CNF dispersion liquid, after freeze-drying, obtain the CNF-PEG complex with 50% PEG coating amount, take 0.12g of CNF-PEG complex and disperse it in 100g of dichloromethane solution, and then make it equal volume with 0.6% PLA solution Mix to get the PLA / CNF mixed dispersion for later use.
[0035] The modified cellophane samples were respectively immersed in the PLA solution with a concentration of 0.3% and the PLA / CNF dispersion with a ratio of CNF to PLA of 0.2, and the soaking time was 30 min. After taking it out, it was air-d...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Cut the dried cellophane into 8cm*8cm samples and soak them in 0.2% ethanol solution of silane coupling agent. After soaking for 30 minutes, take out the samples and air dry them naturally to obtain the modified cellophane for later use.
[0038]Dissolve 0.1g and 0.2g of polylactic acid (PLA) in 100g of dichloromethane to prepare 0.1% and 0.2% PLA dichloromethane solutions for use; take 0.2g of PEG-4000 and dissolve in 100g of 0.4% PLA CNF dispersion, after freeze-drying to obtain a CNF-PEG complex with a PEG coating amount of 50%, take 0.04g of the CNF-PEG complex and dissolve it in 100g of dichloromethane solution, and then make it equal to the volume of 0.2% PLA solution Mix to get the PLA / CNF mixed dispersion for later use.
[0039] The modified cellophane samples were respectively immersed in the PLA solution with a concentration of 0.1% and the PLA / CNF dispersion with a ratio of CNF to PLA of 0.2, and the soaking time was 30 min. After taking it out, it was air-d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com