Polypeptide sustained-release microsphere preparation and preparation method thereof
A slow-release microsphere preparation and polypeptide slow-release technology, which is applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of short half-life and poor patient compliance, and achieve the effects of good encapsulation rate, long drug release time and small particle size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
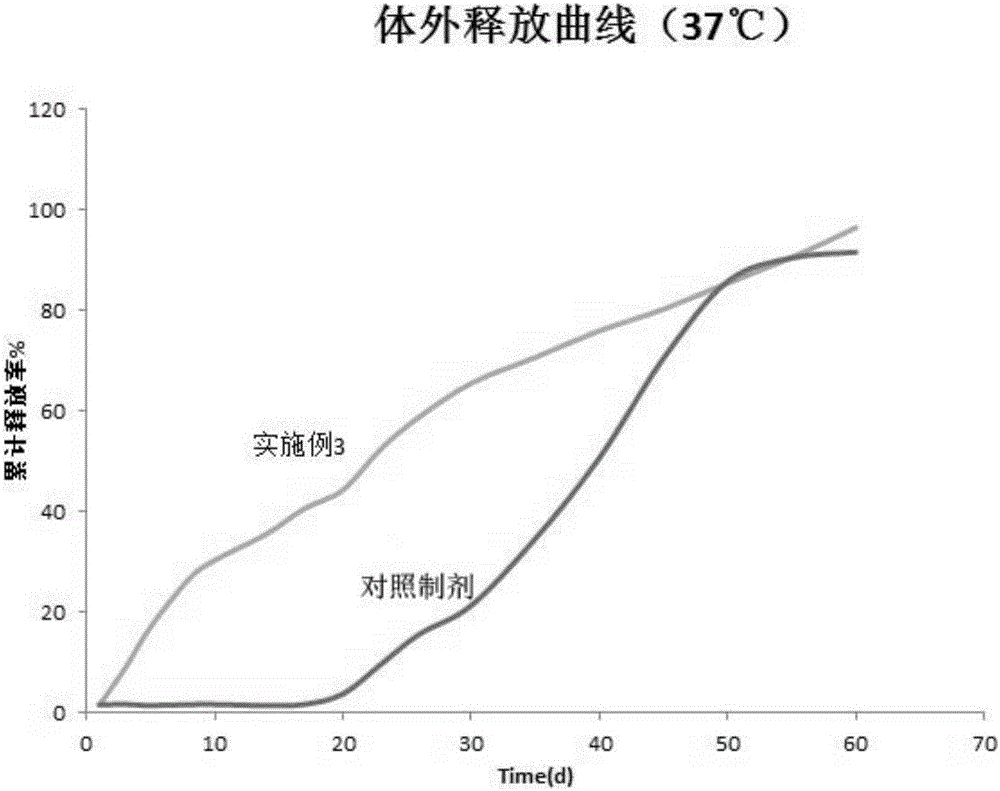
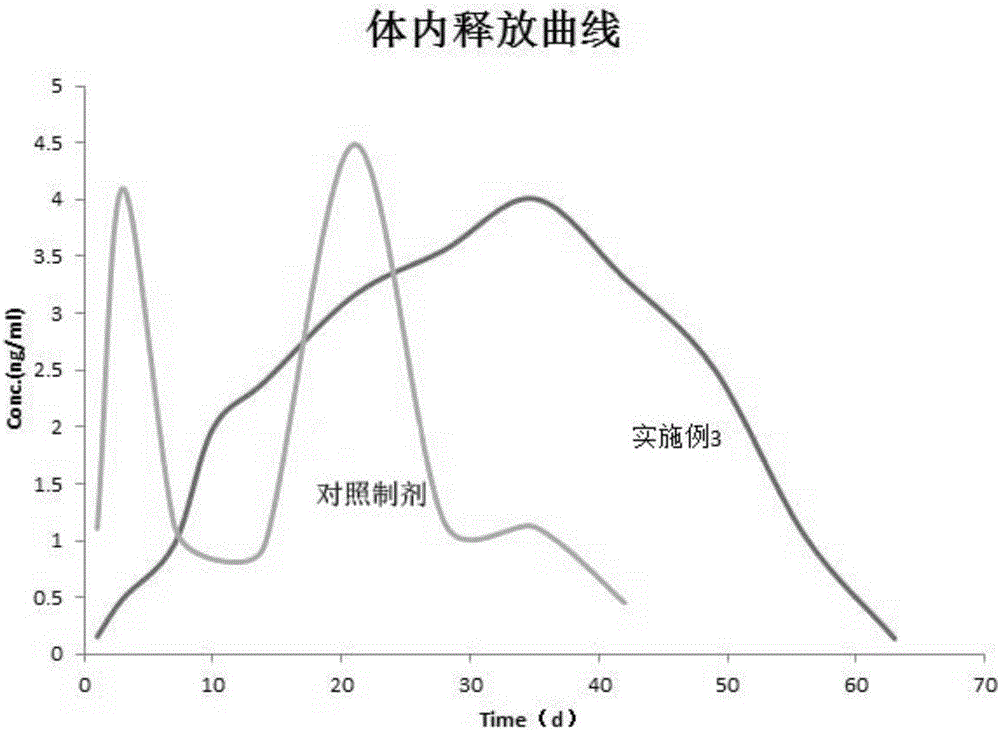
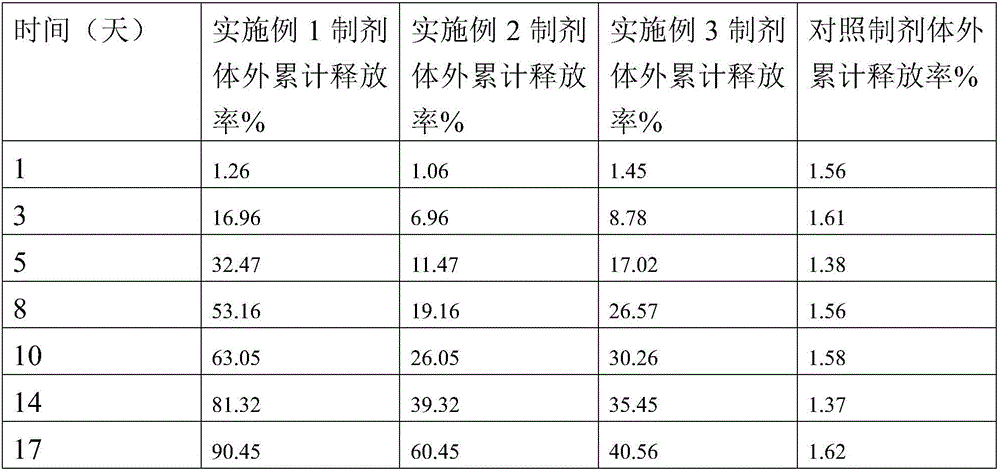
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Embodiment 1 microsphere preparation and preparation method thereof
[0103] (1) Dissolve 5g of purified 50:50 DLG 2A PLGA (polymerization ratio 1:1, PLGA inherent viscosity around 1, PLGA with carboxyl group at the end group), 0.3g of exenatide in 50ml of glacial acetic acid, forming a solution of polymer and drug;
[0104] (2) Mix 200ml of n-heptane and 200ml of silicone oil to prepare coagulant; shear the solution of polymer and medicine prepared in step (1), and add the coagulant prepared at the same time to obtain initial microspheres;
[0105] (3) Transfer the initial microspheres prepared in step (3) to a mixed solution of 1800ml n-heptane and 1800ml ethanol, and stir at 20°C for 1-2h;
[0106] (4) with 200ml 50% n-heptane-ethanol solution flushing the residual solvent on the microsphere surface that step (3) obtains;
[0107] (5) Using a multilayer sieve to collect the microspheres obtained in step (4), rinse with 50% n-heptane-ethanol solution. Dry at 4°C fo...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Embodiment 2 microsphere preparation and preparation method thereof
[0109] (1) Dissolve 5g of purified 50:50 DLG 3A PLGA, 0.3g of exenatide in 50ml of glacial acetic acid to form a solution of polymer and drug;
[0110] (2) Mix 200ml of n-heptane and 200ml of silicone oil to prepare coagulant; shear the solution of polymer and medicine prepared in step (1), and add the coagulant prepared at the same time to obtain initial microspheres;
[0111] (3) the initial microspheres prepared by step (2) are transferred to the mixed solution of 1500ml n-heptane and 1500ml ethanol;
[0112] (4) with 200ml 50% n-heptane-ethanol solution flushing the residual solvent on the microsphere surface that step (3) obtains;
[0113] (5) Using a multilayer sieve to collect the microspheres obtained in step (4), rinse with 50% n-heptane-ethanol solution. Dry at 4°C for 24h, vacuum dry at 25°C for 24h, and vacuum dry at 35°C for 24h.
Embodiment 3
[0114] Embodiment 3 microsphere preparation and preparation method thereof
[0115] (1) Dissolve 5g of purified 100 2A PLA and 0.3g of exenatide in 50ml of glacial acetic acid to form a solution of polymer and drug;
[0116] (2) Mix 200ml of n-heptane and 200ml of silicone oil to prepare coagulant; shear the solution of polymer and medicine prepared in step (1), and add the coagulant prepared at the same time to obtain initial microspheres;
[0117] (3) Transfer the initial microspheres prepared in step (2) to a mixed solution of 2100ml n-heptane and 2100ml ethanol, and stir at 20°C for 1-2h;
[0118] (4) with 200ml 50% n-heptane-ethanol solution flushing step (3) microsphere surface residual solvent that obtains;
[0119] (5) Using a multilayer sieve to collect the microspheres obtained in step (4), rinse with 50% n-heptane-ethanol solution. Dry at 4°C for 24h, vacuum dry at 25°C for 24h, and vacuum dry at 35°C for 24h.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| percent by volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com