Absorbable iron-base alloy implantable medical device and preparation method thereof
A technology for implanting medical devices and iron-based alloys, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of incomplete skinning, uneven corrosion of iron-based alloy substrates, difficulty in meeting early structural integrity and mechanical properties, etc. The effect of meeting the requirements of the degradation cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] In this embodiment, the absorbable iron-based stent is taken as an example for illustration. Ideally, the absorbable iron-based stent needs to maintain effective radial support (supporting force greater than 55Pa) during the 3-month vascular repair period, and Corrosion occurs as soon as possible after the blood vessel recovers its function, and the degradation period is usually required to be 6-24 months.
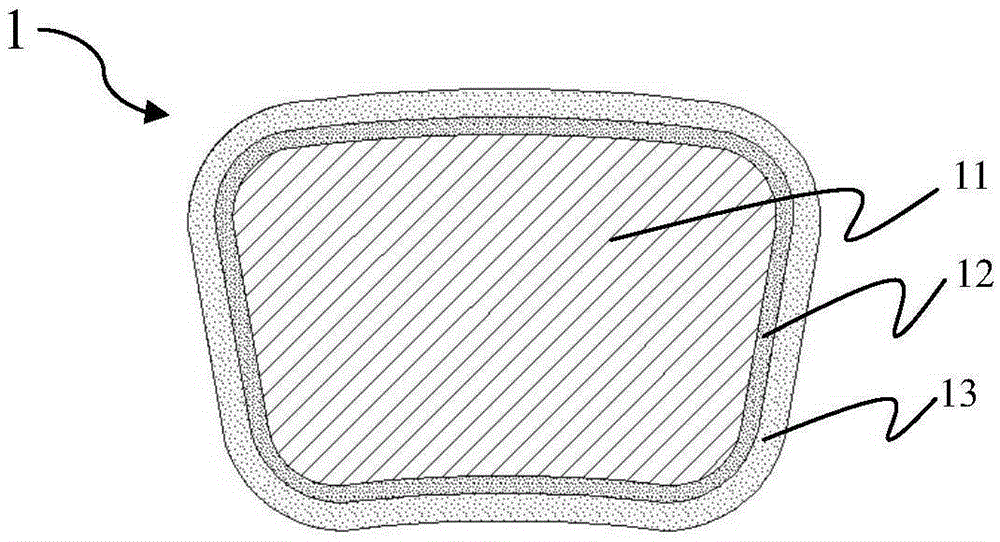
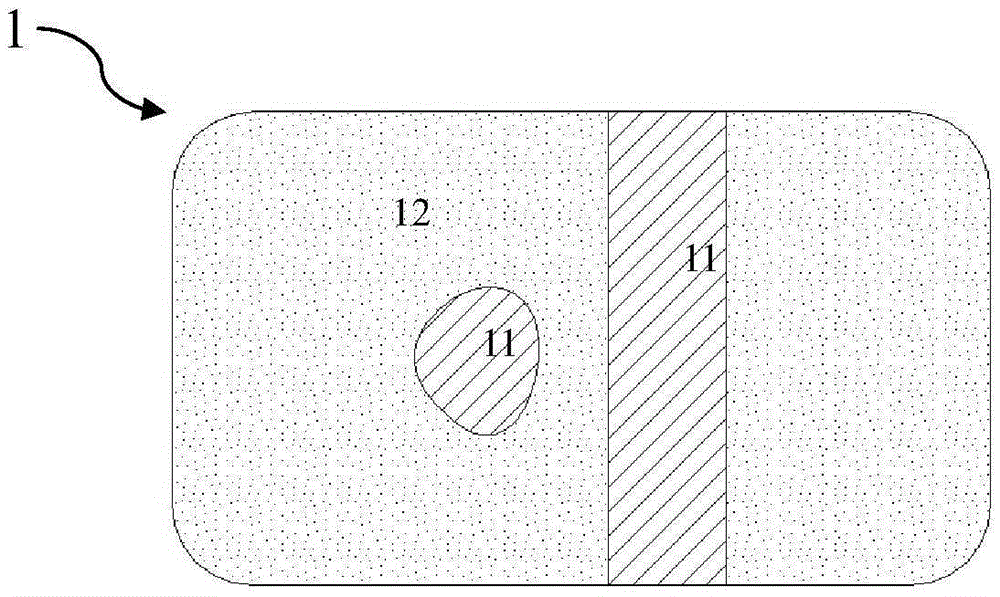
[0050] First, an iron-based alloy matrix is prepared. The matrix is made of pure iron through nitriding, with an initial radial strength of 145kPa and a mass of 4.5-5mg. Fully dissolving sodium hydroxide in ethanol solution to obtain a saturated ethanol solution of sodium hydroxide is used as an alkaline solution for preparing an alkaline protector. The ethanol saturated solution of sodium hydroxide is sprayed on the surfaces of multiple iron-based alloy substrates, so that the sodium hydroxide coating covers all the surfaces of the iron-based alloy substrates. ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The difference from Example 1 is that the thickness of the sodium hydroxide coating of the prepared multiple absorbable iron-based alloy stents is about 20 μm, and the thickness of the polylactic acid coating is about 12 μm. It was taken out 3 months after implantation, and its radial support force was measured to be 100kPa. Complete degradation of the remaining absorbable iron-based scaffold was observed 9 months after implantation. Compared with Example 1, it can be seen that under the same conditions of the iron-based alloy matrix, the thickness of the basic protective body and the thickness of the degradable polymer layer are increased at the same time, and the radial support force of the stent after 3 months of implantation is higher than that of Example 1. One is slightly larger. The stent according to this embodiment simultaneously meets the requirements of radial support force and corrosion cycle in the early stage of implantation.
Embodiment 3
[0055] The difference from Example 2 is that the polylactic acid coating of the obtained absorbable iron-based alloy stent has a thickness of about 8 μm. It was taken out 3 months after implantation, and its radial support force was measured to be 120kPa. Complete degradation of the remaining resorbable iron-based alloy stent was observed 24 months after implantation. Compared with Example 2, it can be seen that under the same conditions of the matrix and the same alkaline protective body, reducing the thickness of the degradable polymer layer can slightly increase the radial support force after implantation for 3 months, but correspondingly prolongs the corrosion resistance. cycle. The stent according to this embodiment simultaneously meets the requirements of radial support force and corrosion cycle in the early stage of implantation.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com