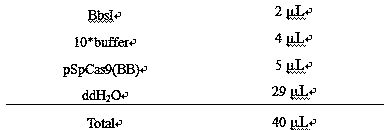CRISPR/Cas9 targeted knockout of human hepatitis B virus p gene and its specific gRNA
A hepatitis B virus, specific technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of difficult to achieve therapeutic effect, easy mutation of HBV, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Example 1 Synthesis of gRNA targeting human hepatitis B virus P gene and construction of CRISPR / Cas9 system vector
[0015] 1. Selection and design of gRNA targeting human hepatitis B virus P gene
[0016] Find the sequence of human hepatitis B virus P gene in Genebank, and design potential target sites in human hepatitis B virus P gene.
[0017] Through the online design tool (http: / / crispr.mit.edu / ) and the design principles of gRNA, the target sites with higher scores on the human hepatitis B virus P gene sequence were evaluated to design gRNA.
[0018] 2. Synthesis of gRNA oligonucleotide sequence targeting human hepatitis B virus P gene and construction of eukaryotic expression vector
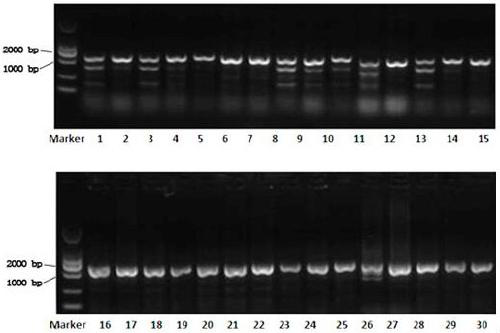
[0019] Digest the pSpCas9(BB)-2A-GFP (PX458) plasmid (Addgene plasmid ID: 48138, hereinafter referred to as pSpCas9(BB)) with BbSI, and after 1 hour in a water bath at 37°C, electrophoresis on 1% agarose to recover the digested product (TAKARA gel recovery kit).
[0020] The enzy...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 Transfection of HEPG2.2.15 cells
[0034] Resuscitate human liver cancer cells (HEPG2.2.15 cells, Shanghai Cell Bank, Chinese Academy of Sciences), put the cells into a culture flask with 10% FBS+DMEM, and store them at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cells were cultured in an incubator, and the day before transfection, the cells were subcultured.
[0035] Aspirate the culture medium in the HEPG2.2.15 T75 bottle, add 2 mL of 0.25% trypsin taken out of the refrigerator at 4°C, make it evenly cover the bottom of the bottle, place it in the incubator at 37°C for 3-5 min, take it out, and shake it. When the cells are found to be detached from the bottom, shake them all down, add 3 mL of 10% DMEM preheated in a 37°C water bath, and blow and beat with a 10 mL pipette for 6 to 8 times without leaving any dead ends. The pipette can be aligned with the mouth of the bottle by blowing, and the medium can be pushed out with a small force to cover the cells close to the mouth of the bottle...
Embodiment 3
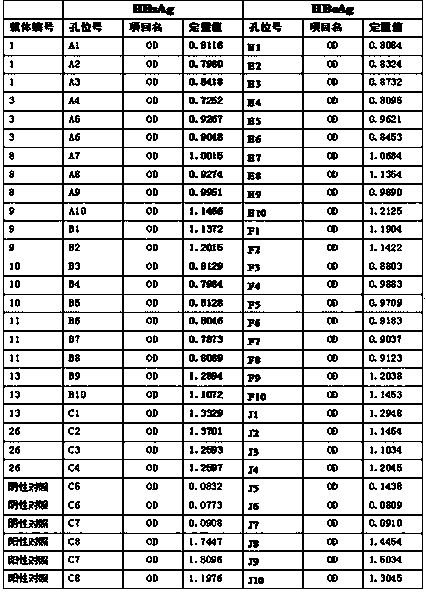
[0047] Example 3 ELISA detection of HBsAg and HBeAg levels in the supernatant of HepG2.2.15 cells
[0048] Cultivate HEPG2.2.15 cells and lay the cells on a 6-well plate, and transfect the 8 high-efficiency targeted knockout hepatitis B virus vectors obtained in Example 2, respectively, into the cells on the 6-well plate, and make 3 for each vector Repeat the well, use the same amount of PBS to replace the carrier (positive control), and refer to Example 2 for the specific transfection method.
[0049] Change the medium 24 hours after transfection, take the cell supernatant, centrifuge to remove the cell bodies or debris in the supernatant, take the cell supernatant 72 hours after transfection, and centrifuge at 5000 rpm to remove the cell bodies or debris in the supernatant, according to Hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) and e antigen diagnostic kit (HBsAg) (enzyme-linked immunoassay, Aikang Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) operating instructions, the supernatant stock soluti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com