Milbemycins producing recombinant streptomyces as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of mirbemycin and streptomyces, which is applied in the field of molecular biology and can solve problems such as being difficult to remove
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Example 1: Extraction of total DNA from Streptomyces
[0088] Take 50μL of Streptomyces HS023 cryopreservation tube spore suspension and inoculate it in 30mL TSB medium (purchased from Bacto TrypticSoy Broth. BD). After incubating at 28°C and 220rpm for 48h, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 10min in a 50mL centrifuge tube and remove the supernatant. The precipitate was washed twice with 30 mL of sucrose-Tris buffer (the mass percentage of sucrose was 10.3%, the molar-volume concentration of Tris-HCl was 10 mM, and the pH was 8.0), and then suspended in 5 mL of sucrose-Tris buffer. Add 20μL of lysozyme solution with a mass-volume solubility of 100mg / mL and water bath at 37°C for 2h. Add 500 μL of 10% SDS solution and gently invert until it is almost clear. Add 5 mL of phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (the volume ratio of phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol is 25:24:1 (pH value is 8.0)). After gently inverting several times, centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 10 minutes. Take 4 mL of the u...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2: Construction of Milbemycin-producing Strain Genomic Library
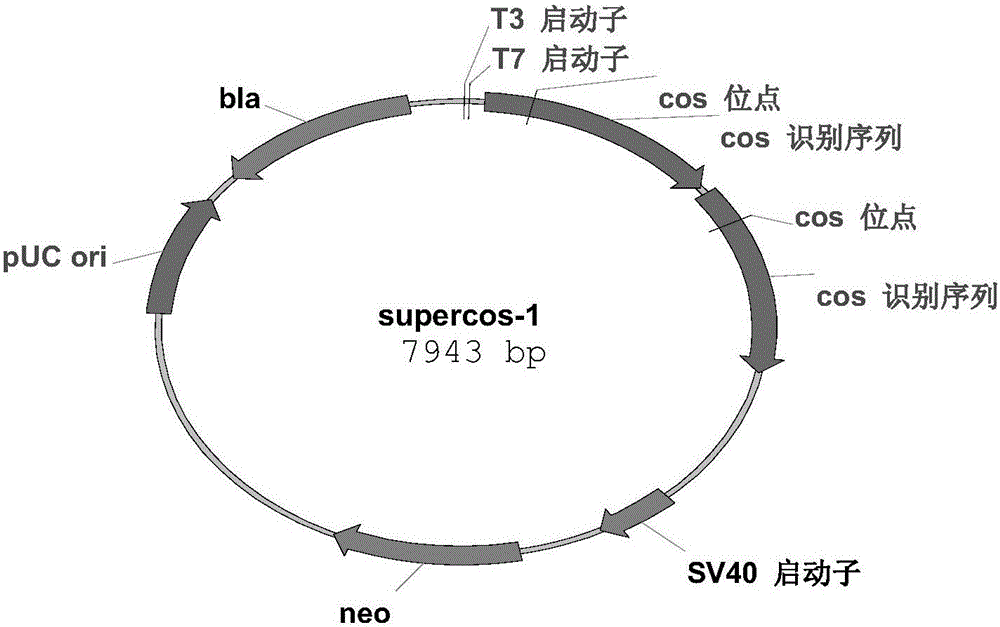
[0090] Apply the cosmid carrier SuperCos 1 (see figure 2 ) Construction of HS023 genome library. First, establish a suitable partial digestion system. Use Sau3A1 to partially digest 50-100μg of high molecular weight chromosomal DNA, and then use Tris saturated phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) to extract twice. Chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (24:1) was extracted once. Transfer the upper aqueous phase to a new tube, add 0.1 volume of 3mol / L sodium acetate and twice the volume of ethanol, mix well, and place at -20°C for 30 minutes. The DNA was precipitated by centrifugation (12000r / min, 10min), the DNA pellet was washed with 70% ethanol, the DNA pellet was dried, and the DNA pellet was suspended in an appropriate volume of TE buffer and stored at 4°C for later use. The double-cos site vector SuperCos 1 first fully digested the plasmid DNA with NheI, then fully treated with CIAP, phenol-chlo...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Example 3: Gene library screening
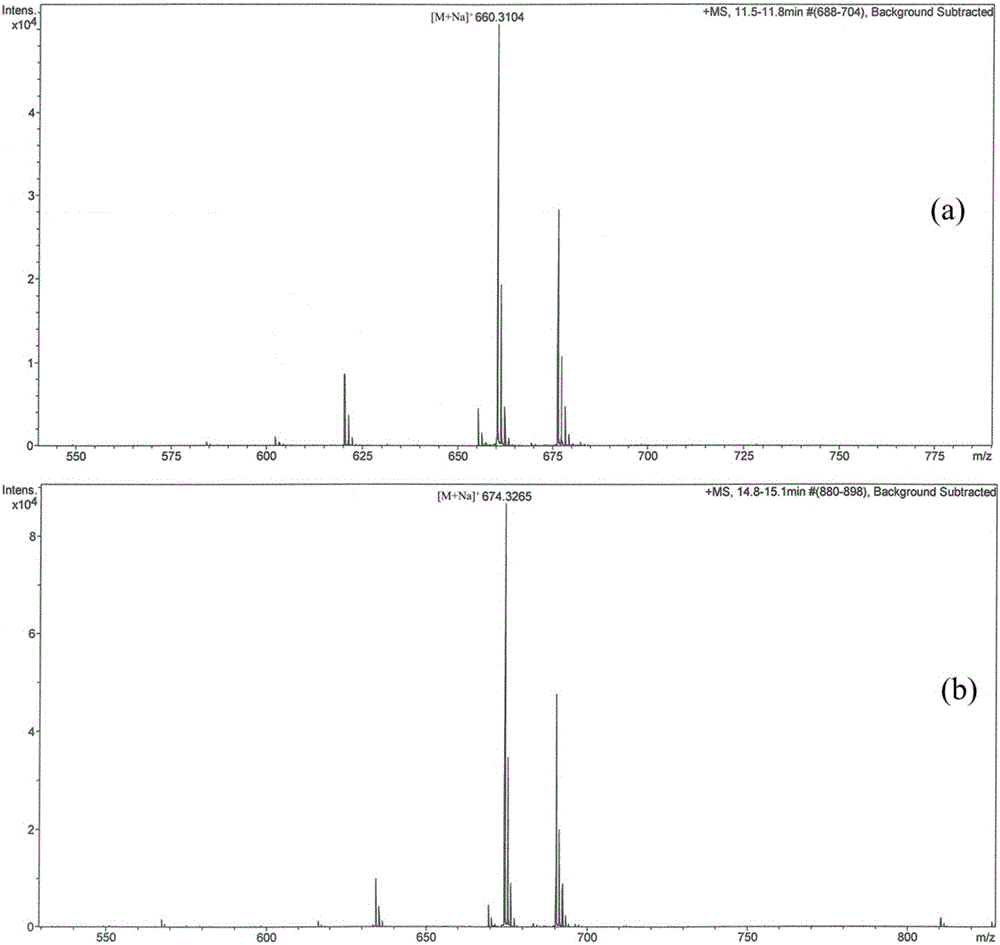
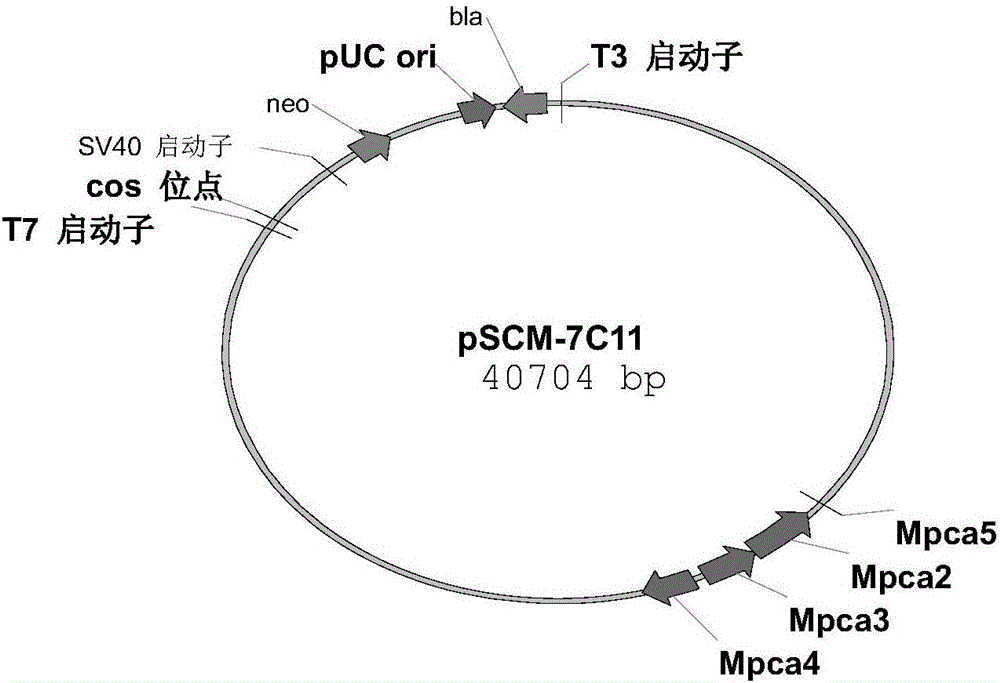
[0092] Design the universal primer PcaF / PcaR (SEQ ID NO:1 / SEQ ID NO:2), screen the genomic library constructed in Example 2 by colony PCR, screen a total of 1000 single colonies, and obtain two Cosmids that may contain the desired sequence, respectively Numbering pSCM-7C11 and pSCM-4C12, using universal primers T7 and T3 both ends of sequencing, the results showed that the four genes in the pSCM-7C11 vector are located in the center of the sequence (see image 3 ), suitable for subsequent gene manipulation, and pSCM-7C11 was sequenced at the same time to obtain the full sequence of the four genes (see SEQ ID NO: 7).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com